MCA and temporal lobe
- MCA arising from ICA
- Branches
- M1, from the carotid bifurcation to the limen insulae;
- Only the M1 segment is related to the mesial temporal lobe.
- Because of differences in topographical anatomy, the M1 segment can be divided into a proximal and a distal half.
- The proximal half of the M1 segment is related superiorly to the anterior perforated substance, posteriorly to the semilunar gyrus and the temporal amygdala, and inferiorly to the entorhinal area of the uncus
- M2, all branches related to the insula, from the limen insulae to the opercula of the temporal, frontal, or parietal lobes;
- M3, all branches related to the opercula of the temporal, frontal or parietal lobes;
- M4, the cortical branches of the middle cerebral artery, after exiting from the sylvian fissure.
- The M1 can be divided into
- Proximal half:
- Is just anterior to the amygdala which itself is anterior to the hippocampal head
- Distal half:
- Is just anterior to the insula pole which itself is anterior to the temporal horn
- The insula pole is ahead of the amygdala
Images of MCA
1, cingulate gyrus;
2, corpus callosum and septum pellucidum;
3, fornix;
4, thalamus;
5, genu of the internal capsule and thalamostriate vein;
6, anterior commissure and column of the fornix;
7, M2 segment of the middle cerebral artery;
8, limen insulae;
9, anterior cerebral artery;
10, lenticulostriate arteries;
11, M1 segment of the middle cerebral artery;
12, internal carotid artery;
13, optic nerve;
14, anterior clinoid process.
2, corpus callosum and septum pellucidum;
3, fornix;
4, thalamus;
5, genu of the internal capsule and thalamostriate vein;
6, anterior commissure and column of the fornix;
7, M2 segment of the middle cerebral artery;
8, limen insulae;
9, anterior cerebral artery;
10, lenticulostriate arteries;
11, M1 segment of the middle cerebral artery;
12, internal carotid artery;
13, optic nerve;
14, anterior clinoid process.
1, middle cerebral artery;
2, internal carotid artery;
3, anterior cerebral artery;
4, anterior choroidal artery;
5, posterior communicating artery;
6, tuber cinereum and P1 segment of the posterior cerebral artery;
7, anterior segment, apex, and posterior segment of the uncus;
8, oculomotor nerve and P2A segment of the posterior cerebral artery;
9, P2P segment of the posterior cerebral artery;
10, parahippocampal gyrus;
11, P3 segment of the posterior cerebral artery;
*, inferior temporal arteries.
2, internal carotid artery;
3, anterior cerebral artery;
4, anterior choroidal artery;
5, posterior communicating artery;
6, tuber cinereum and P1 segment of the posterior cerebral artery;
7, anterior segment, apex, and posterior segment of the uncus;
8, oculomotor nerve and P2A segment of the posterior cerebral artery;
9, P2P segment of the posterior cerebral artery;
10, parahippocampal gyrus;
11, P3 segment of the posterior cerebral artery;
*, inferior temporal arteries.
1, ICA
2, PCOM
3, A Cho A
4, P1 PCA
5, P2A
6, uncus
7, P3 seg
8, Vein of galen
9, P4 seg
2, PCOM
3, A Cho A
4, P1 PCA
5, P2A
6, uncus
7, P3 seg
8, Vein of galen
9, P4 seg
1, internal carotid artery;
2, posterior communicating artery;
3, P1 segment of the posterior cerebral artery;
4, middle cerebral artery;
5, P2 segment;
6, beginning of the P3 segment;
7, beginning of the P4 segment;
8, inferior temporal arteries from the posterior cerebral artery and parahippocampal gyrus;
9, isthmus of the cingulate gyrus;
10, parieto-occipital sulcus;
11, cuneus;
12, calcarine sulcus and lingual gyrus.
2, posterior communicating artery;
3, P1 segment of the posterior cerebral artery;
4, middle cerebral artery;
5, P2 segment;
6, beginning of the P3 segment;
7, beginning of the P4 segment;
8, inferior temporal arteries from the posterior cerebral artery and parahippocampal gyrus;
9, isthmus of the cingulate gyrus;
10, parieto-occipital sulcus;
11, cuneus;
12, calcarine sulcus and lingual gyrus.
1, Ant Cho A
2, uncus
3, P2A
4, basal vein of rosenthal
5, dentate gyrus & fimbrae
6, Ant and post longitudinal hippocampal vein
7, Pulvinar of thalamus
8, P2P
* Hippocampal arteryEnters hippocampal sulcus betweenthe dental gyrus above and the parahippocampal gyrus below
** lateral posterior choroidal arteryEnters the choroidal fissure
When doing a amygdalohippocampectomy you have to disconnect the hippocampal artery and not the lateral posterior chorodial artery
2, uncus
3, P2A
4, basal vein of rosenthal
5, dentate gyrus & fimbrae
6, Ant and post longitudinal hippocampal vein
7, Pulvinar of thalamus
8, P2P
* Hippocampal arteryEnters hippocampal sulcus betweenthe dental gyrus above and the parahippocampal gyrus below
** lateral posterior choroidal arteryEnters the choroidal fissure
When doing a amygdalohippocampectomy you have to disconnect the hippocampal artery and not the lateral posterior chorodial artery
1, Calcar avis (medial wall of atrium)
2, herschl's gyrus and branches of MCA
3, globus thalamus
4, Lateral geniculate body
5, optic tract
6, Floor of 3rd and mamillary bodies
7, anterior choroidal artery
8, head of hippocampus and inferior choriodal point
9, Super Sag Sinus
10, ICA
11, A1
12, Optic nerve
13, M1
2, herschl's gyrus and branches of MCA
3, globus thalamus
4, Lateral geniculate body
5, optic tract
6, Floor of 3rd and mamillary bodies
7, anterior choroidal artery
8, head of hippocampus and inferior choriodal point
9, Super Sag Sinus
10, ICA
11, A1
12, Optic nerve
13, M1
1, Calcar avis (medial wall of atrium)
2, Insula
3, Vein of galen
4, Choroid plexus
5, colliculi
6, posterior lateral choroidal artery
7, parahippocampal gyrus
8, Hippocampal body
9, basal vein of rosenthal
10, PCom
11, anterior choroidal artery and P2
12, anterior choroidal artery
13, hippocampal head
14, amygdala
15, M1
16, M2
17, olfactory tract
*, entry site of the anterior choroidal artery in the temporal horn.
2, Insula
3, Vein of galen
4, Choroid plexus
5, colliculi
6, posterior lateral choroidal artery
7, parahippocampal gyrus
8, Hippocampal body
9, basal vein of rosenthal
10, PCom
11, anterior choroidal artery and P2
12, anterior choroidal artery
13, hippocampal head
14, amygdala
15, M1
16, M2
17, olfactory tract
*, entry site of the anterior choroidal artery in the temporal horn.
1, tegmentum of midbrain
2, substantia nigra
3, inferior ventricular vein and basal vein of rosenthal
4, cerebral peduncle/crus
5, inferior choridal point
6, P1 and peduncular vein
7, P2A and cisternal segment of anterior choroidal artery
8, posterior segment of uncus
9, CN3
10, Uncus apex
11, hippocampus head
12, Pcom
13, anterior segment of uncus
14, semilunar gyrus
15, origin of Ant Cho artery from ICA
16, ACA
17, MCA
18, Optic nerve
2, substantia nigra
3, inferior ventricular vein and basal vein of rosenthal
4, cerebral peduncle/crus
5, inferior choridal point
6, P1 and peduncular vein
7, P2A and cisternal segment of anterior choroidal artery
8, posterior segment of uncus
9, CN3
10, Uncus apex
11, hippocampus head
12, Pcom
13, anterior segment of uncus
14, semilunar gyrus
15, origin of Ant Cho artery from ICA
16, ACA
17, MCA
18, Optic nerve
1, great cerebral vein of galen
2, posterior medial choroidal artery
3, cerebellomesencephalic segment of the SCA and free edge of the tentorium
4, PCA, parahippocampal gyrus
5, fimbrae, lateral posterior choroidal artery, dentate gyrus
6, basal vein of Rosenthal
7, inferior ventricular vein
8, SCA and tentorial edge
9, CN3
10, optic tract
11, amygdala
2, posterior medial choroidal artery
3, cerebellomesencephalic segment of the SCA and free edge of the tentorium
4, PCA, parahippocampal gyrus
5, fimbrae, lateral posterior choroidal artery, dentate gyrus
6, basal vein of Rosenthal
7, inferior ventricular vein
8, SCA and tentorial edge
9, CN3
10, optic tract
11, amygdala
1, Parietal occipital artery
2, lingual gyrus
3, Calcarine artery
4, Calcar avis
5, CN 4
6, parahippocampal gyrus
7, Dentate gyrus
8, Fornix
9, Anastomosis between anterior and posterior lateral choridal artery 10, basal vein of rosenthal
11, Hippocampal head
2, lingual gyrus
3, Calcarine artery
4, Calcar avis
5, CN 4
6, parahippocampal gyrus
7, Dentate gyrus
8, Fornix
9, Anastomosis between anterior and posterior lateral choridal artery 10, basal vein of rosenthal
11, Hippocampal head
1, ICA
2, Optic tract
3, Anterior choroidal artery (cisternal segment)
4, Peduncular vein
5, Peduncular segment of basal vein
6, Inferior choroidal point
7, Inferior ventricular vein
8, Lateral geniculate body
9, anterior choroidal artery (plexal segment)
10, Medial geniculate body and lateral mesencephalic vein
11, Pulvinar of thalamus
12, Posterior mesencephalic segment of basal vein
13, Posterior longitudinal hippocampal and internal occipital veins
14, internal cerebral vein
15, Great cerebral vein of galen
2, Optic tract
3, Anterior choroidal artery (cisternal segment)
4, Peduncular vein
5, Peduncular segment of basal vein
6, Inferior choroidal point
7, Inferior ventricular vein
8, Lateral geniculate body
9, anterior choroidal artery (plexal segment)
10, Medial geniculate body and lateral mesencephalic vein
11, Pulvinar of thalamus
12, Posterior mesencephalic segment of basal vein
13, Posterior longitudinal hippocampal and internal occipital veins
14, internal cerebral vein
15, Great cerebral vein of galen
1, foramen of munro & column of fornix
2, Thalamus
3, Aqudeuct of sylvian
4, mamillary body
5, Crux cerebri and posterior perforating substance
6, ICA
2, Thalamus
3, Aqudeuct of sylvian
4, mamillary body
5, Crux cerebri and posterior perforating substance
6, ICA
1, corpus callosum
2, fornix column and anterior commissure
3, foramen of munro
4, thalamus
5, aqueduct
6, ACA
7, MCA
8, Anterior choroidal artery (cisternal segment)
9, distal portion of the cisternal segment of the anterior choroidal artery (on the upper portion of the posteromedial surface of the uncus) entering the temporal horn
10, ICA
11, PCOM
12, P2A
13, P1
14, Tegmentum/pons
15, 4th ventricle
16, Rhinal sulcus
2, fornix column and anterior commissure
3, foramen of munro
4, thalamus
5, aqueduct
6, ACA
7, MCA
8, Anterior choroidal artery (cisternal segment)
9, distal portion of the cisternal segment of the anterior choroidal artery (on the upper portion of the posteromedial surface of the uncus) entering the temporal horn
10, ICA
11, PCOM
12, P2A
13, P1
14, Tegmentum/pons
15, 4th ventricle
16, Rhinal sulcus
1, Acom
2, MCA
3, semilunar gyrus
4, Cisternal segment of anterior choroidal artery
5, inferior choroidal point
6, Posterior medial surface of uncus
7, P2P
8, ambient gyrus
9, P2A
10, ICA
11, PCOM
12, parahippocampal gyrus
13, P1
14, Fusiform gyrus (Collateral gyrus)
15, pons
2, MCA
3, semilunar gyrus
4, Cisternal segment of anterior choroidal artery
5, inferior choroidal point
6, Posterior medial surface of uncus
7, P2P
8, ambient gyrus
9, P2A
10, ICA
11, PCOM
12, parahippocampal gyrus
13, P1
14, Fusiform gyrus (Collateral gyrus)
15, pons
1, Isthmus of cingulate gyrus
2, P3
3, P3
4, Inferior temporal artery
5, Parahippocampal gyrus
6, collateral gyrus (fusiform gyrus)
7, Rhinal sulcus
*, P2P
2, P3
3, P3
4, Inferior temporal artery
5, Parahippocampal gyrus
6, collateral gyrus (fusiform gyrus)
7, Rhinal sulcus
*, P2P
1, anterior choroidal artery (proximal cisternal segment)
2, anterior choroidal artery (distal Cisternal segment)
3, MCA
4, P2A
5, PCOM
6, ICA
7, P1
8, Ophthalmic artery
9, Basilar artery
*, inferior choroidal point
2, anterior choroidal artery (distal Cisternal segment)
3, MCA
4, P2A
5, PCOM
6, ICA
7, P1
8, Ophthalmic artery
9, Basilar artery
*, inferior choroidal point
1, Lingual gyrus
2, parahippocampal gyrus
3, Uncal apex
4, Posterior border uncus
5, anterior border uncus
6, uncal notch
7, tentorial notch
8, fusiform gyrus
2, parahippocampal gyrus
3, Uncal apex
4, Posterior border uncus
5, anterior border uncus
6, uncal notch
7, tentorial notch
8, fusiform gyrus
1, Olfactory tract
2, A2
3, M2
4, Limen insulae
5, optic nerve and ICA
6, entorhinal area of uncus
7, M1
8, Semilunar gyrus of uncus
9, PCOM
10, P1 + peduncular vein
11, head of the hippocampus and choroid plexus of the temporal horn
12, Cisternal segment of anterior choroidal artery + Peduncular vein
13, Plexal point (inferior choroidal point)
14, P2P and parahippocampal gyrus
15, Vein of Galen
16, Sylvian point and heschl's gyrus
17, Calcarine artery
18, parieto-occipital artery
2, A2
3, M2
4, Limen insulae
5, optic nerve and ICA
6, entorhinal area of uncus
7, M1
8, Semilunar gyrus of uncus
9, PCOM
10, P1 + peduncular vein
11, head of the hippocampus and choroid plexus of the temporal horn
12, Cisternal segment of anterior choroidal artery + Peduncular vein
13, Plexal point (inferior choroidal point)
14, P2P and parahippocampal gyrus
15, Vein of Galen
16, Sylvian point and heschl's gyrus
17, Calcarine artery
18, parieto-occipital artery
1, ICA
2, PCOM
3, M1
4, A1 + P1 superimposed
5, Genu of MCA
6, P2A superimposed with Cisternal segment of Ant Cho artery
7, M2
8, Calcarine
2, PCOM
3, M1
4, A1 + P1 superimposed
5, Genu of MCA
6, P2A superimposed with Cisternal segment of Ant Cho artery
7, M2
8, Calcarine
1, ACA and corpus callosum
2, Septum pellucidium
3, Fornix
4, Velum interpositium, internal cerebral vein, Medial posterior chroidal artery
5, Interthalamic adhesion (massa intermedia)
6, Lamina terminalis
7, Optic and infundibular recess
8, posterior cerebral artery (above the third nerve)
9, Midbrain (crus cerebri)
10, SCA
11, optic nerve
12, CN3 + uncus
13, ophthalmic artery and supraclinoid segment of the internal carotid artery
14, pons
15, Pituitary gland
16, Intracavernous segment of ICA
17, Basilar artery
18, 4th ventricle
2, Septum pellucidium
3, Fornix
4, Velum interpositium, internal cerebral vein, Medial posterior chroidal artery
5, Interthalamic adhesion (massa intermedia)
6, Lamina terminalis
7, Optic and infundibular recess
8, posterior cerebral artery (above the third nerve)
9, Midbrain (crus cerebri)
10, SCA
11, optic nerve
12, CN3 + uncus
13, ophthalmic artery and supraclinoid segment of the internal carotid artery
14, pons
15, Pituitary gland
16, Intracavernous segment of ICA
17, Basilar artery
18, 4th ventricle
1, ICA branching into MCA
2, PCOM
3, Entorhinal area of the uncus
4, CN3 and apex of uncus
5, Post perforated substance
6, Opthalmic artery and dural ring with a cut optic nerve
7, Basilar artery and free edge of the tentorium;
8, Intercavernous segment of ICA
9, Pituitary gland
2, PCOM
3, Entorhinal area of the uncus
4, CN3 and apex of uncus
5, Post perforated substance
6, Opthalmic artery and dural ring with a cut optic nerve
7, Basilar artery and free edge of the tentorium;
8, Intercavernous segment of ICA
9, Pituitary gland
1, A1
2, semilunar gyrus and anterior choroidal artery
3, PCA
4, Crux cerebri
5, Supra clinoid segment of ICA
6, origin of PCOM
7, Entorhinal area of uncus
8, CN3 and apex of uncus
9, SCA
10, CN2
11, Dural ring, Opthalmic artery
12, Intercavernous segment of ICA
13, Pituitary gland
14, tentorial edge and Dorsum sellae
15, Basilar artery
2, semilunar gyrus and anterior choroidal artery
3, PCA
4, Crux cerebri
5, Supra clinoid segment of ICA
6, origin of PCOM
7, Entorhinal area of uncus
8, CN3 and apex of uncus
9, SCA
10, CN2
11, Dural ring, Opthalmic artery
12, Intercavernous segment of ICA
13, Pituitary gland
14, tentorial edge and Dorsum sellae
15, Basilar artery
1, Corpus callosum
2, head of caudate in Lateral ventricles
3, Fornix
4, internal cerebral vein
5, Great cerebral vein of Galen
6, Straight sinus
7, MCA cut
8, Mamillary body and posterior perforated substance
9, Striate segment of basal vein of Rosenthal
10, CN3 and tenorial edge
11, peduncular segment of basal vein
12, CN4
13, superior petrosal sinus
2, head of caudate in Lateral ventricles
3, Fornix
4, internal cerebral vein
5, Great cerebral vein of Galen
6, Straight sinus
7, MCA cut
8, Mamillary body and posterior perforated substance
9, Striate segment of basal vein of Rosenthal
10, CN3 and tenorial edge
11, peduncular segment of basal vein
12, CN4
13, superior petrosal sinus
1, internal cerebral vein
2, foramen of munro
3, Splenium of corpus callosum
4, Anterior commissure
5, Vein of galen
6, straight sinus
7, posterior perforated substance
8, CN2-tract and ICA
9, CN3 and striate segment of the basal vein;
10, Tentorial edge, superior cerebellar artery
11, CN4 and lateral mesencephalic vein;
12, Cerebellum
2, foramen of munro
3, Splenium of corpus callosum
4, Anterior commissure
5, Vein of galen
6, straight sinus
7, posterior perforated substance
8, CN2-tract and ICA
9, CN3 and striate segment of the basal vein;
10, Tentorial edge, superior cerebellar artery
11, CN4 and lateral mesencephalic vein;
12, Cerebellum
Note that the location of the thalamus on the lateral angiographic view is approximately depicted by the foramen of Monro anteriorly, the internal cerebral vein superiorly, and the basal vein inferiorly.
1, venous angle (angle formed by the thalamostriate and internal cerebral veins that usually denotes the location of the foramen of Monro)
2, internal cerebral vein
3, Inferior sagittal sinus
4, great cerebral vein of galen
5, Striate segment of basal vein
6, Peduncular segment of basal vein
7, Mesencephalic segment of basal vein
8, straight sinus
1, venous angle (angle formed by the thalamostriate and internal cerebral veins that usually denotes the location of the foramen of Monro)
2, internal cerebral vein
3, Inferior sagittal sinus
4, great cerebral vein of galen
5, Striate segment of basal vein
6, Peduncular segment of basal vein
7, Mesencephalic segment of basal vein
8, straight sinus
1, Frontal lobe
2, Olfactory tract
3, Right orbit
4, Pars orbitalis (inferior frontal gyrus)
5, Corpus callosum (genu)
6, Head of caudate head
7, Optic nerve and internal carotid artery
8, Rhinal sulcus
9, uncus
10, superior temporal gyrus
11, insula
12, thalamus
13, 3rd ventricle floor
14, Crus cerebri and CN3
15, PCA
16, Hippocampus
17, heschl's gyrus (anterior temporal gyrus)
18, Planum temporale (middle and posterior transverse temporal gyrus)
19, Splenium Corpus callosum
2, Olfactory tract
3, Right orbit
4, Pars orbitalis (inferior frontal gyrus)
5, Corpus callosum (genu)
6, Head of caudate head
7, Optic nerve and internal carotid artery
8, Rhinal sulcus
9, uncus
10, superior temporal gyrus
11, insula
12, thalamus
13, 3rd ventricle floor
14, Crus cerebri and CN3
15, PCA
16, Hippocampus
17, heschl's gyrus (anterior temporal gyrus)
18, Planum temporale (middle and posterior transverse temporal gyrus)
19, Splenium Corpus callosum
1, Cingulate gyrus
2, Occipital horn of lateral ventricle
3, corpus callosum and septum pellucidium
4, collateral trigone
5, Fornix
6, parahippocampal gyrus and tentorium
7, Cerebral aqueduct and posterior commissure
8, dentate gyrus
9, Planum Temporale
10, Anterior transverse temporal gyrus (Heschl's gyrus)
11, Superior temporal gyrus
12, collateral eminence
13, Amygdala
14, Middle temporal gyrus
15, Uncus, inferior temporal gyrus
16, Collateral (fusiform) gyrus
17, Collateral sulcus
18, parahippocampal gyrus
19, Optic nerve
20, ICA
2, Occipital horn of lateral ventricle
3, corpus callosum and septum pellucidium
4, collateral trigone
5, Fornix
6, parahippocampal gyrus and tentorium
7, Cerebral aqueduct and posterior commissure
8, dentate gyrus
9, Planum Temporale
10, Anterior transverse temporal gyrus (Heschl's gyrus)
11, Superior temporal gyrus
12, collateral eminence
13, Amygdala
14, Middle temporal gyrus
15, Uncus, inferior temporal gyrus
16, Collateral (fusiform) gyrus
17, Collateral sulcus
18, parahippocampal gyrus
19, Optic nerve
20, ICA
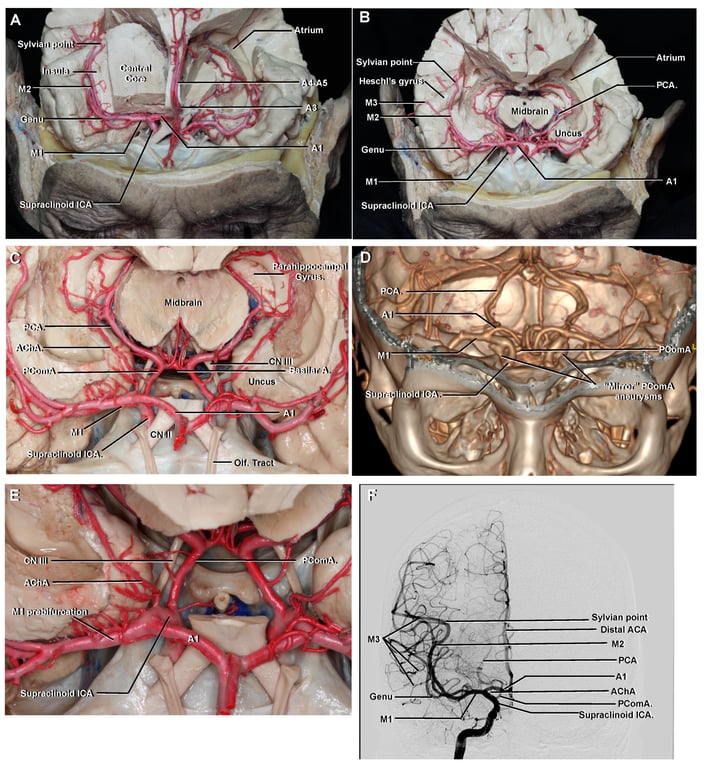
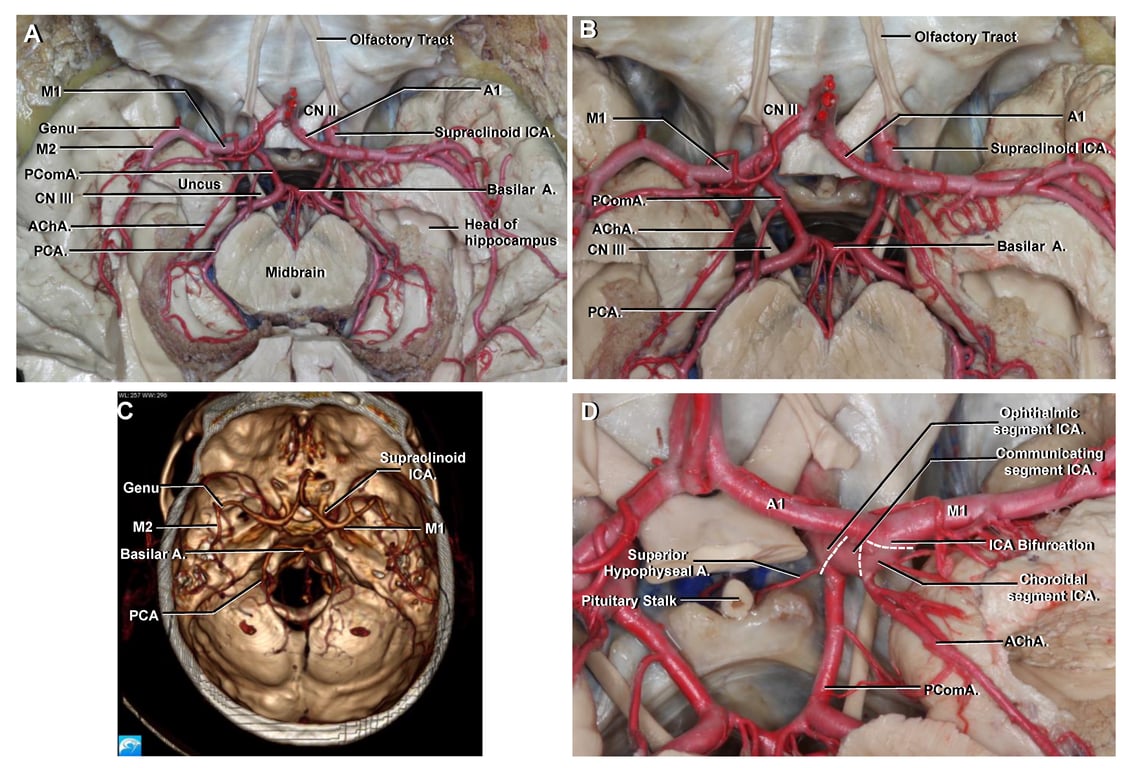
Arterial relationship of the uncus
- ICA-Supraclinoid segment
- Located at the most anterior aspect of the anterior segment of the uncus.
- Posterior communicating artery is not truly in contact with any surface of the uncus;
- but it is closely related to the tentorial notch.
- The anterior choroidal artery
- Arises from ICA in the carotid cistern
- Course
- Initially it is closely related to the Anterior segment of the uncus at a variable height
- (the height of its origin depends on the height of the bifurcation of the internal carotid artery).
- It then runs posteriorly, superiorly, and laterally in the crural cistern on the upper part of the posteromedial surface of the uncus
- It finally enter the choroidal fissure close to the inferior choroidal point.
- The entire uncus is situated ahead of and below the inferior choroidal point.
- PCOM-P2A segment
- Originates in the interpeduncular cistern, runs laterally and then posteriorly around the crus cerebri in the ambient cistern
- Related to the inferior portion of the posteromedial surface of the uncus
- MCA-M1 segment
- Is hardly seen because of its almost parallel course to our pterional approach.
- Relation with uncus varies
- When the M1 segment presents a straight course, most of the uncus is located posteriorly to it
- When the M1 segment is tortuous and closer to the semilunar gyrus, the entorhinal area of the uncus becomes anterior and inferior to the M1
Hippocampal arteries
- By Miranda 2010
Type of Artery | Distribution | Parent Vessel |
Anterior uncal artery | Anterior segment of uncus | AChA, MCA, ICA |
Posterior uncal artery | Posterior segment of uncus | AChA |
Unco-hippocampal artery | Uncus (posterior segment) + hippocampus (head) | AChA |
Unco-parahippocampal artery | Uncus (anterior segment) + parahippocampal gyrus (entorhinal area) | PCoA |
Hippocampal-unco-parahippocampal artery | Uncus (posterior segment) + hippocampus (head) + parahippocampal gyrus (entorhinal area) | AChA, MCA, ICA |
Anterior parahippocampal artery | Anterior parahippocampal gyrus (entorhinal area) | AChA, PCA, PCoA |
Anterior hippocampal-parahippo. Artery | Hippocampus (head) + anterior parahippocampal gyrus (entorhinal area) | MCA, PCA–AITA/P2, ICA |
Posterior parahippocampal artery | Posterior parahippocampal gyrus | PCA–AITA/P2 |
Posterior hippocampal-parahippo. artery | Hippocampus (body) + posterior parahippocampal gyrus | PCA–MITA/PITA/P2 |
- Hippocampal head
- Unco-hippocampal artery
- Anterior hippo-parahippocampal artery
- Hippocampal body
- Posterior hippo-parahippocampal artery
- Hippocampal tail
- Posterior hippocampal artery