General
- The tela choroidea is a critical anatomical structure, primarily defined as a double layer of pia mater located deep within the brain's ventricular system.
- It plays an essential role in forming the roof of the fourth ventricle and the roof of the third ventricle,
- Serves as the origin point for the highly vascular choroid plexus.
Structure and Composition
- The tela choroidea consists of two thin, semiopaque membranes derived from the pia mater.
- These two membranes are interconnected by loosely organized trabeculae.
- It is specifically defined as the double layer of pia mater situated between the cerebellum and the fourth ventricle.
- In the roof of the third ventricle, the tela choroidea also forms two thin membranous layers that, along with a vascular layer, constitute the four layers of the roof, situated below the neural layer formed by the fornix.
Role in Choroid Plexus Development and Location
- The tela choroidea is the structure in which the choroid plexus arises and to whose inner surface it is attached.
- Choroid Plexus Formation:
- Vascular tissue develops within the tela choroidea and sprouts, covered by an ependymal layer, into the inferior half of the roof of the fourth ventricle to become the choroid plexus.
- Choroidal Fissure Connection:
- In the lateral and third ventricles, the choroid plexus is attached along the choroidal fissure.
- The edges of the thalamus and fornix bordering this fissure have small ridges, the teniae, along which the tela choroidea is attached.
- The teniae are specifically named based on the side of attachment: the tenia thalami (or tenia choroidea, on the thalamic side) and the tenia fornicis (on the forniceal side).
Role in the Fourth Ventricle
- The tela choroidea forms the caudal part of the roof of the fourth ventricle.
- Formation of the Roof:
- The inferior half of the fourth ventricle's roof is formed by three structures: the nodulus of the vermis, the inferior medullary velum, and the tela choroidea.
- The velum and nodulus are continuous inferiorly with the tela choroidea.
- Double Layer Separation:
- The two layers of the tela choroidea separate inferiorly into an anterior and a posterior layer.
- The posterior layer is continuous with the pia mater over the inferior vermis.
- The anterior layer is reflected ventrally and caudally, remaining in contact with the ependymal lining of the fourth ventricle's roof. This anterior layer is continuous with the pia mater over the dorsal aspect of the medulla.
- Attachment:
- The tela choroidea is attached to the medulla and pons along the inferolateral borders of the floor of the fourth ventricle. This attachment is marked by a narrow, white ridge known as the taenia. The taeniae from each side meet at the obex, marking the periphery of the ventricular floor.
- Lateral Recesses and Foramina:
- The caudal margin of the lateral recess and the foramen of Luschka are formed by the tela choroidea, which is attached along the taenia to the lower border of the fourth ventricle floor.
- The choroid plexus extends through the foramina of Luschka and Magendie, which are formed by local resorptions of the thin roof plate (which includes the tela choroidea) during embryonic development.
- Embryonic Development
- During early embryonic development, the area destined to become the roof of the fourth ventricle stretches into a thin membrane composed of a pial and ependymal layer.
- The developing cerebellum folds caudally over this thin roof, causing the pia mater over the cerebellar vermis to rest against the pia mater of the roof of the fourth ventricle.
- These two layers of pia mater fuse to become the tela choroidea of the roof of the fourth ventricle.
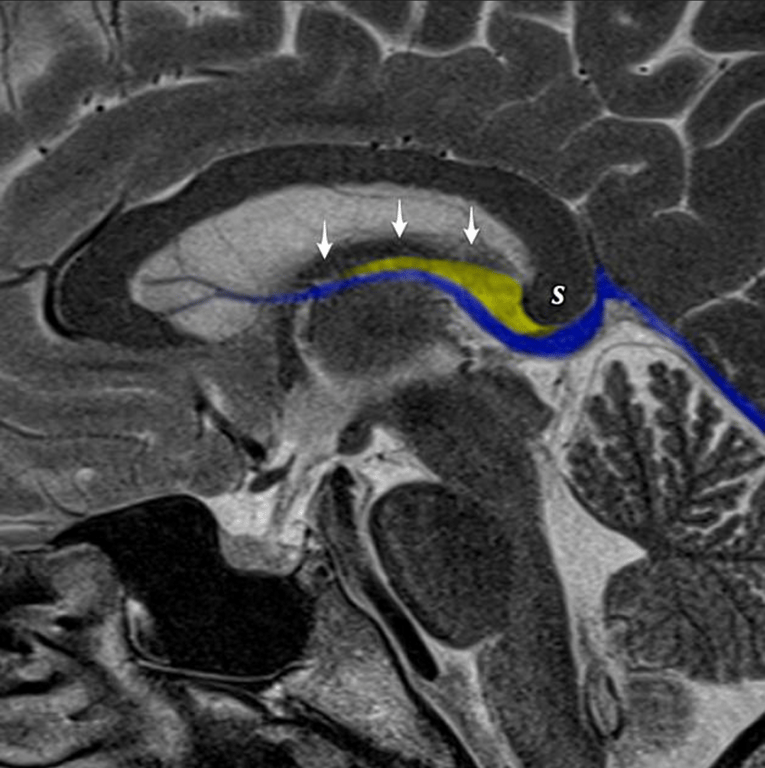
Role in the Third Ventricle (Velum Interpositum)
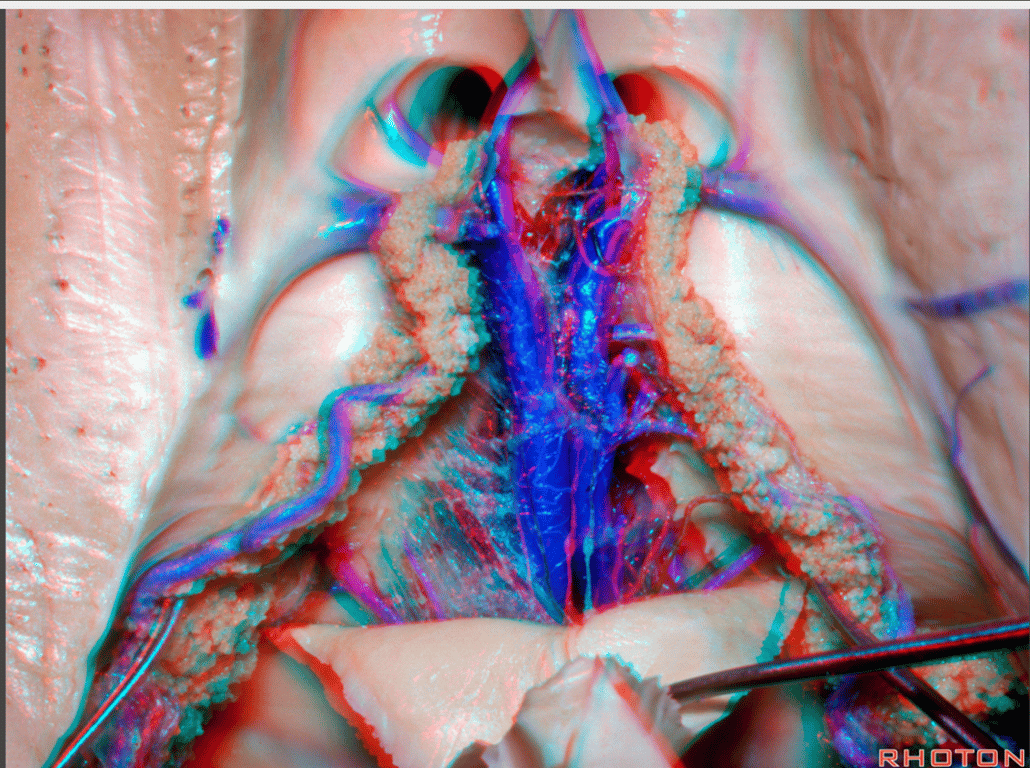
- In the roof of the third ventricle, the space located between the two layers of tela choroidea (4 layers of Pia) is called the velum interpositum.
- The velum interpositum contains the internal cerebral veins and the medial posterior choroidal arteries.
- The upper layer of the tela choroidea is attached to the lower surface of the fornix and hippocampal commissure,
- The lower layer of the tela choroidea is attached to the striae medullaris thalami (ridges on the thalamus) and the superior surface of the pineal body.