Axial sclerotome
- Formation of the human craniovertebral junction. Sclerotomal primordia and their vertebral phenotypes are colour-matched.
- Dens fusion from 3 sclerotome
- Proatlas sclerotome (PA).
- Form during resegmentation
- Formed from
- Caudal half of the fourth somite (fourth occipital somite)
- Rostral half of the fifth somite combine to form the
- Derived from the proatlas are:
- The axial zones (Ad and Al) which become the basion (B) of the basioccipital or clivus (CL) and the apical segment of the dens (AD);
- The lateral dense zone (Ld) becomes the exoccipital comprising the
- Occipital condyle (OC)
- Lateral rim and opisthion (OT) of the foramen magnum;
- The proatlas’ hypochordal bow (HBp) forms the ventral clival tubercle (CT).
- C1 resegmented sclerotome (C1)
- Formed from adjacent halves of the fifth and sixth somites.
- Derived from the C1 sclerotome are:
- axial zones form the basal segment of the dens (BD);
- lateral zone forms the posterior atlantal arch (C1P);
- hypochordal bow (HBc) forms the anterior atlantal arch (C1A).
- C2 resegmented sclerotome (C2)
- Formed from the sixth and seventh somites.
- From the C2 sclerotome:
- the axial zone forms the C2 vertebral body (AB);
- the lateral zone forms the neural arch of C2 vertebra.
- The intervertebral boundary zone (IBZ) between the proatlas and C1 sclerotome forms the upper dental synchondrosis (US)
- The IBZ between the C1 and C2 sclerotomes forms the lower dental synchondrosis (LS)
Lateral sclerotomes
- Lateral dense zone
- 1st cervical sclerotome → posterior arch C1
- 2nd cervical sclerotome → arch of the C2.
- Loose zones
- 1st cervical sclerotome → 2nd cervical nerves and segmental arteries
- 2nd cervical sclerotome → 3rd cervical nerves and segmental arteries
Formation of the anterior arch of C1
- Hypochordal bow of the first cervical sclerotome ventral to the notochord subsequently forms the anterior arch of the atlas
- No definite hypochordal bows are seen caudal to this level and equivalent cells in the lower segments appear to play no role in the formation of the vertebral column.
Ossification of the C2 over time
- The three developmental phases of the axis (C2) and the three waves of ossification.
- The primordia for the dens components are assembled during the membranous phase. Upper and lower dental synchondroses are shown as dense lines.
- 1st wave of ossification
- 4th foetal month
- consists of bilateral centres for the neural arches and a single centre for the centrum.
- 2nd wave
- 6th foetal month
- consists of bilateral ossification centres for the basal dental segment.
- At birth, the basal dental centres should have integrated in the midline and begun to be fused to the centrum.
- 3rd wave
- 3 to 5 years post-natal life
- at the apical dental segment, which does not become fused to the basal dens till the 6–9th year, and fully formed during adolescence
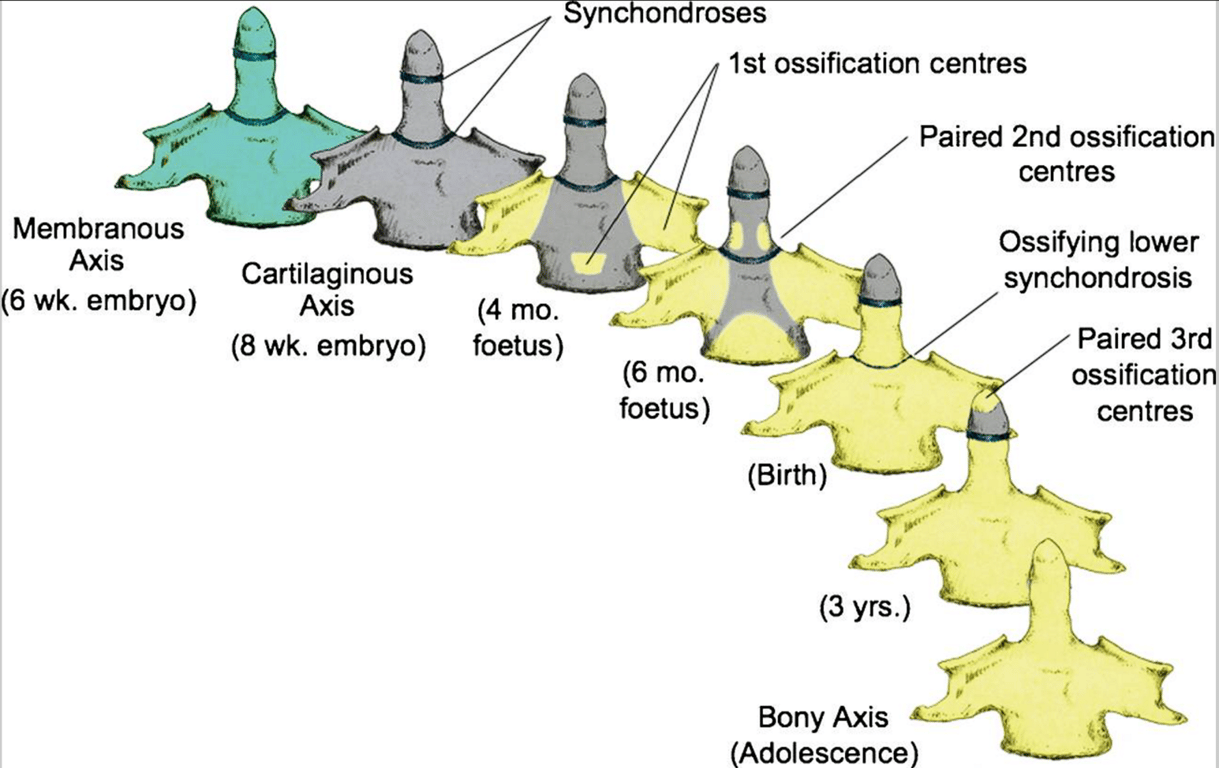
- develops from 5 ossification centres
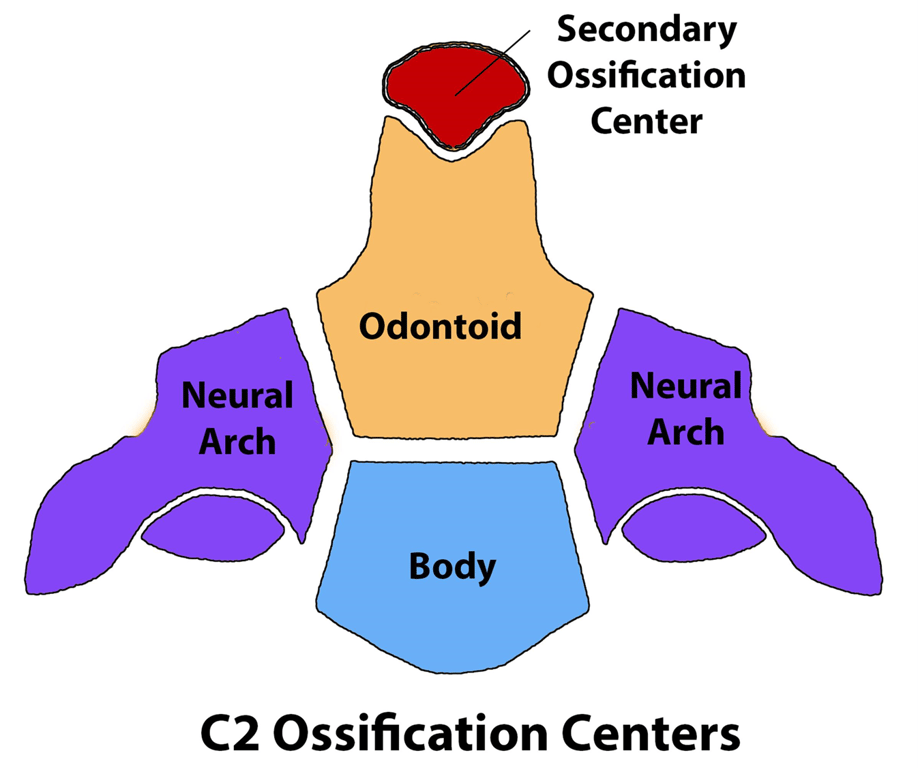
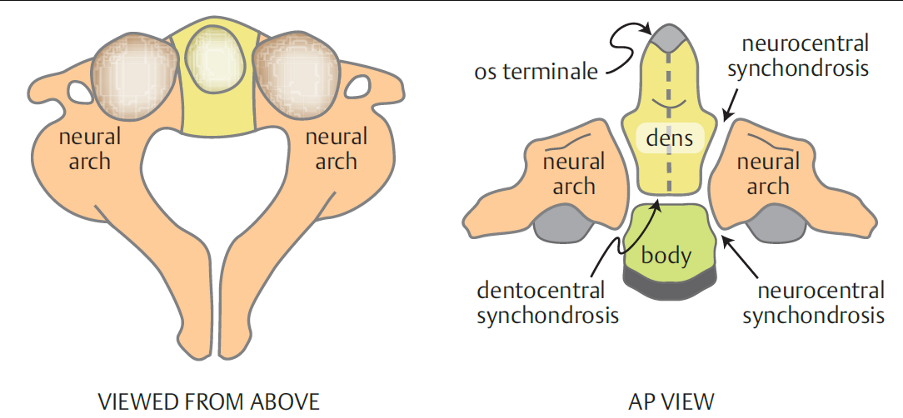
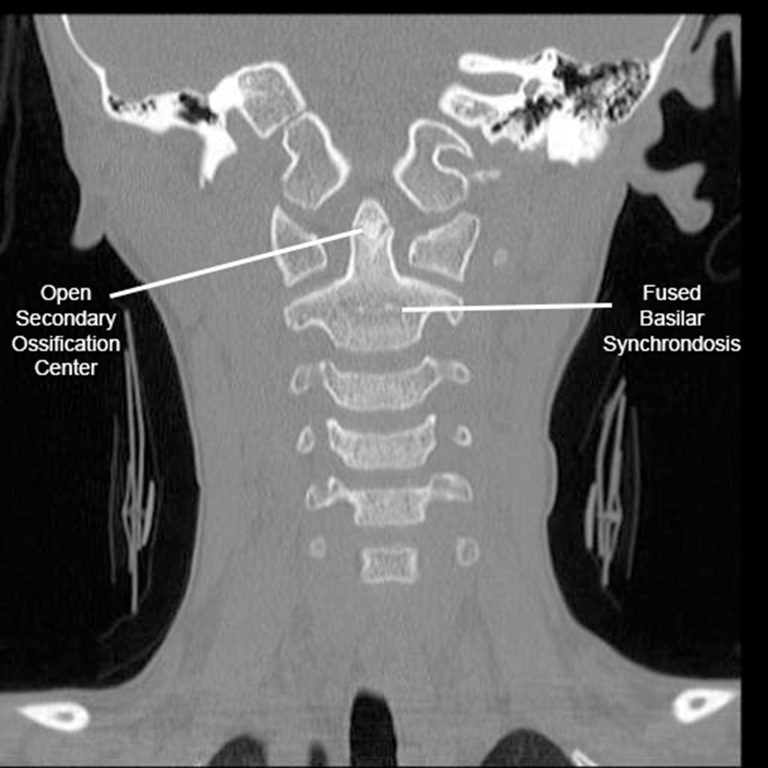
- Subdental (basilar) synchondrosis is an initial cartilaginous junction between the dens and vertebral body that does not fuse until ~6 years of age
Ligament formation
- Apical ligament
- derived from the axial proatlas
- Alar and transverse atlantal ligaments
- Derived from the axial component of the first cervical sclerotome in association with the basal dental segments