Embryology and the circle of Willis
- During initial embryological development, the internal carotid artery (ICA) supplies the anterior, middle, and posterior cerebral arteries.
- Later, the posterior communicating artery (PComA) atrophies, with the basilar artery supplying the posterior cerebral artery (PCA).
- However, if the PComA remains larger than the ipsilateral P1, this is termed a fetal PComA (found in 25% individuals).
- In the majority of individuals, a completely intact circle of Willis is not present, with other common variants including
- PComA hypoplasia or absence
- A1 hypoplasia
- Anterior communicating artery (AComA) absence
Spinal artery embryogenesis
- These ventral and dorsal axes themselves develop in- utero as paired metameric arteries.
- 4-6th week gestation:
- Fusion
- of the anterior metameric pairs ultimately → ASA.
- Failure of fusion accounts for the occasional fenestrations seen in the ASA.
- Desegmentation: occurs with involution of many metameric arteries.
- Simultaneously occurs with fusion
- 62 metameric vessels initially
- dorsal 31 → 10-20 remain
- ventral 31 → 4– 8 remain
- There is great variability in the degree to which anterior metameric arteries regress, but two relatively constant remnants are named.
- The artery of the lumbar enlargement
- Aka
- Larger radiculomedullary artery
- Arteria radicularis magna
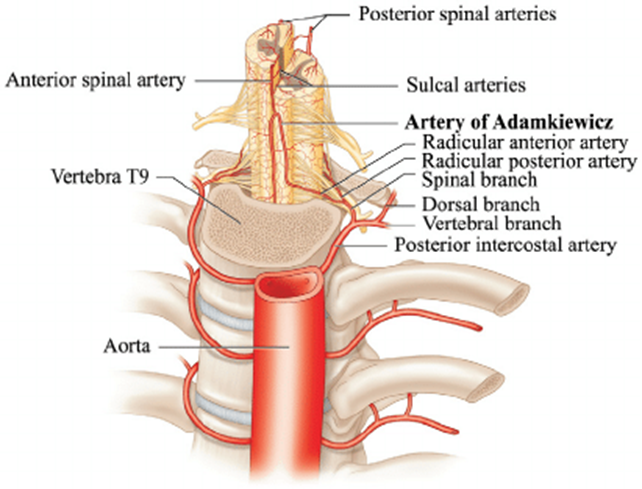
- Artery of Adamkiewicz
- Most often arises from the left side.
- 75% of cases it arises between T9 and T12.
- When it arises outside of that area there is usually a second large, persisting metameric artery to be found cranially or caudally.
- Artery of Adamkiewicz.
- In 75% of patients, the AKA arises between T9 and T12, more commonly on the left.
- When its origin is above T8 or below L2, another major contributor to the ASA can be found either cranially or caudally.
- In 30-50% of cases, it also contributes significantly to the PSA.
- Generally, a pair of arteries arises in the cervical region from the intradural segment of each vertebral artery that fuse to one “Y”-shaped ASA running in the subpial space in the ventral sulcus of the spinal cord (dorsal to the anterior spinal vein) to the terminal film.
- The typical hairpin anastomosis between the radiculomedullary arteries and the ASA is found angiographically at the lower thoracic and lumbar levels.
- The artery of the cervical enlargement
- Entering the C5/ 6 level
- arises from
- Thyrocervical trunks
- Costocervical trunks.
- subclavian artery (rarer)
- Variation is again frequent
- 15– 20 weeks gestation
- Posterior axes fuses