- Social cognition:
- A set of cognitive, affective and emotional processes involved in the understanding of other peoples’ behaviour.
- Social cognition is built up on
- Mentalizing (or theory of mind)
- Empathy
- Mentalizing
- The ability to make assumptions on mental states (such as intentions, desire, knowledge, etc) in order to both anticipate and predict other’s their behaviour
- Location
- Brain-wide neural network extending to both the lateral and medial aspects on the brain, including
- Ventral precuneus/posterior cingulate cortex and
- Medial prefrontal cortex,
- Temporo-parietal junction along with the posterior superior temporal sulcus,
- Temporal pole
- Inferior frontal gyrus
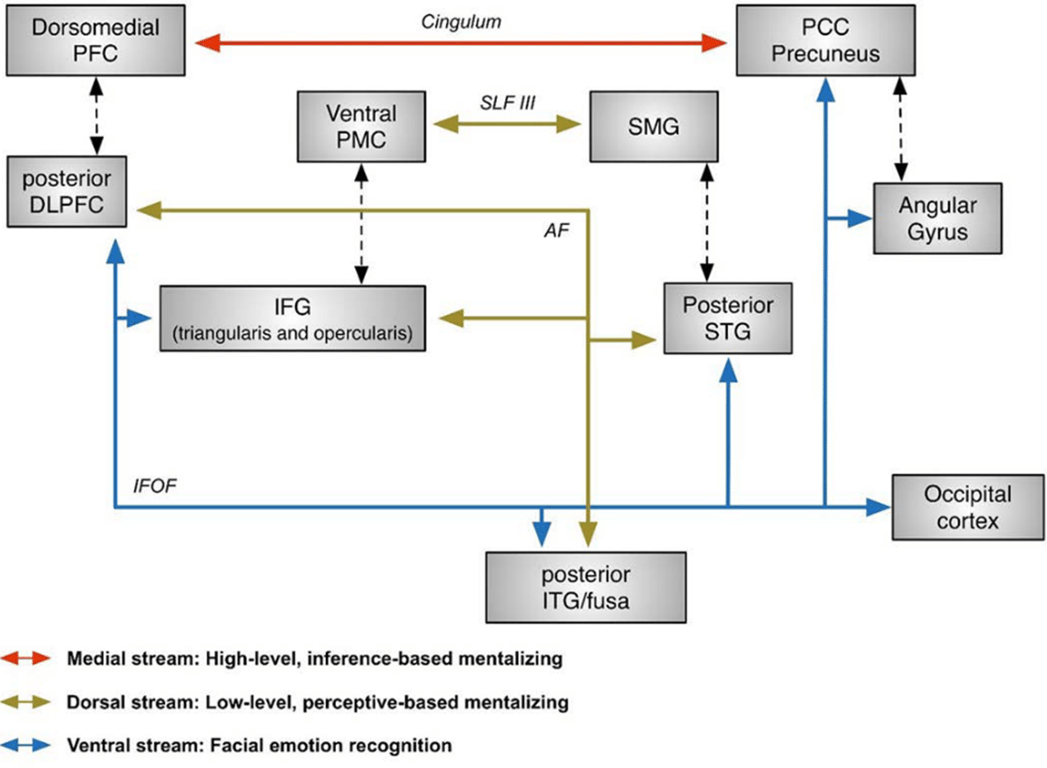
- White matter tracts involved
- Medial stream: Cingulum
- Linking together two well-established medial areas of the mentalizing system, is associated to high-level, inference-based mentalizing or cognitive empathy (a synonym term for cognitive mentalizing) difficulties in the right and the left hemisphere
- Dorsal stream: Perisylvian network, including the AF and the SLF III
- Damaged: Low-level, perceptive-based mentalizing is impaired
- Interconnects cortical regions belonging to the “mirror neuron” network, typically involved in low-level social cognition processing such as emotional empathy and imitation, including the inferior frontal gyrus, the supramarginal gyrus and the superior temporal sulcus
- Ventral stream: Right IFOF
- Basic emotion recognition and face processing, caused mentalizing difficulties on face-based mentalizing tasks, suggesting that this ventral pathway carries important information for mentalizing when visual affective cues has to be processed