Supratentorial choroidal arteries
Anterior choroidal artery (ACh)
- Origin
- (1–3 mm distant to the PComA origin) usually arises from the posterior aspect of the ICA
- Course:
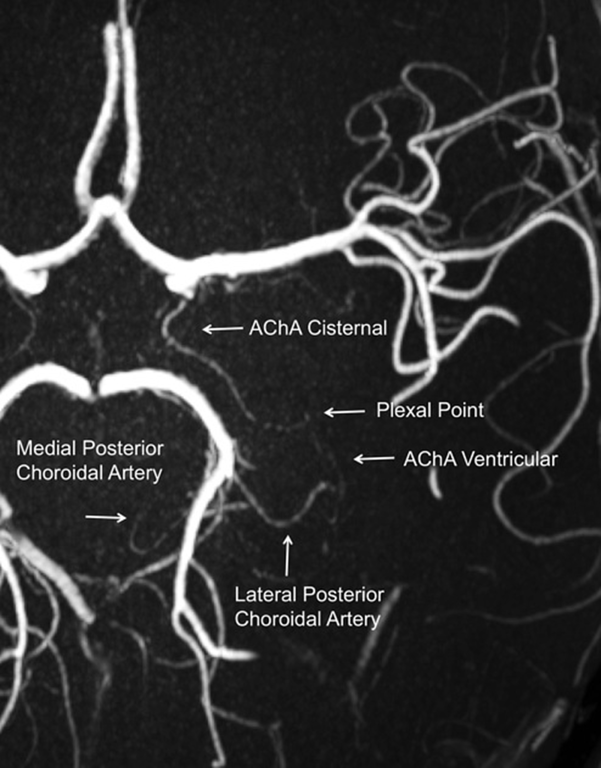
- Lateral to optic tract, curves medially to be inferomedial to optic tract --> curve laterally to run along the lateral aspect of the optic tract --> circumvents the cerebral peduncles to reach the lateral geniculate body --> traverses in the posterolateral direction above the uncus to enter the choroidal fissure, at the plexal point.
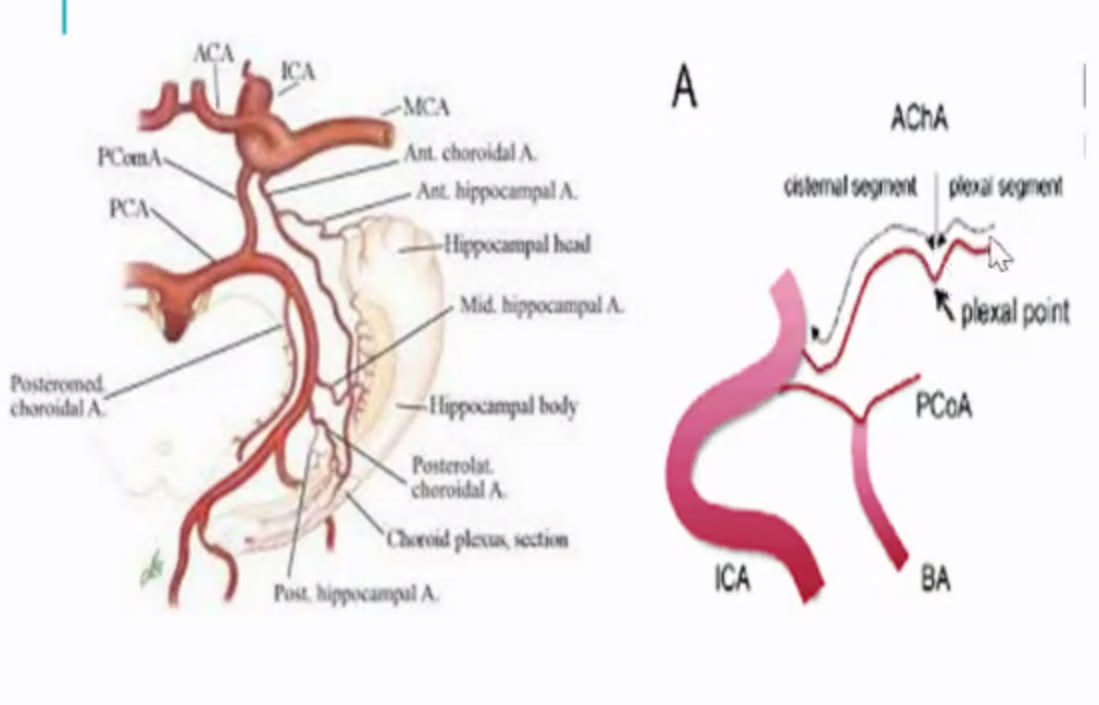
- Plexal point is always constant
- Two segments
- Cisternal segment:
- Extends from its origin until the choroidal fissure; measures ~2.5 cm
- Plexal/Intraventricular segment (3-10 perforators)
- Plexal point: where anterior choroidal artery enter temporal horn
- Supplies
- Visual system: Inferior optic chiasm, Posterior portion of optic tract, Optic radiation, Lateral geniculate body
- Temporal lobe: Uncus, Parahippocampal gyrus, Amygdala, Choroid plexus, Temporal horn, Atrium
- Basal ganglia: Globus pallidus medial, Tail of caudate, Internal capsule (genu)
- Diencephalon: Subthalamus, Thalamus (Lateral ventrolateral nucleus, Lateral ventroanterior nucleus)
- Midbrain: Middle 1/3 of cerebral peduncle, Upper red nucleus, Substantia nigra
- Very rare to have perforating branches outside of origin of anterior choroidal artery
- Anastomoses with lateral posterior choroidal artery
- Anterior choroidal artery-Clinical
- Use to be ligated to tx Parkinson's in the past
- Aneurysm: located superior/superiorlaterally to origin of anterior choroidal artery
- Stroke → Anterior choroidal artery syndrome: (3H)
- Hemisensory loss
- Hemiplegia
- Homonymous hemianopia
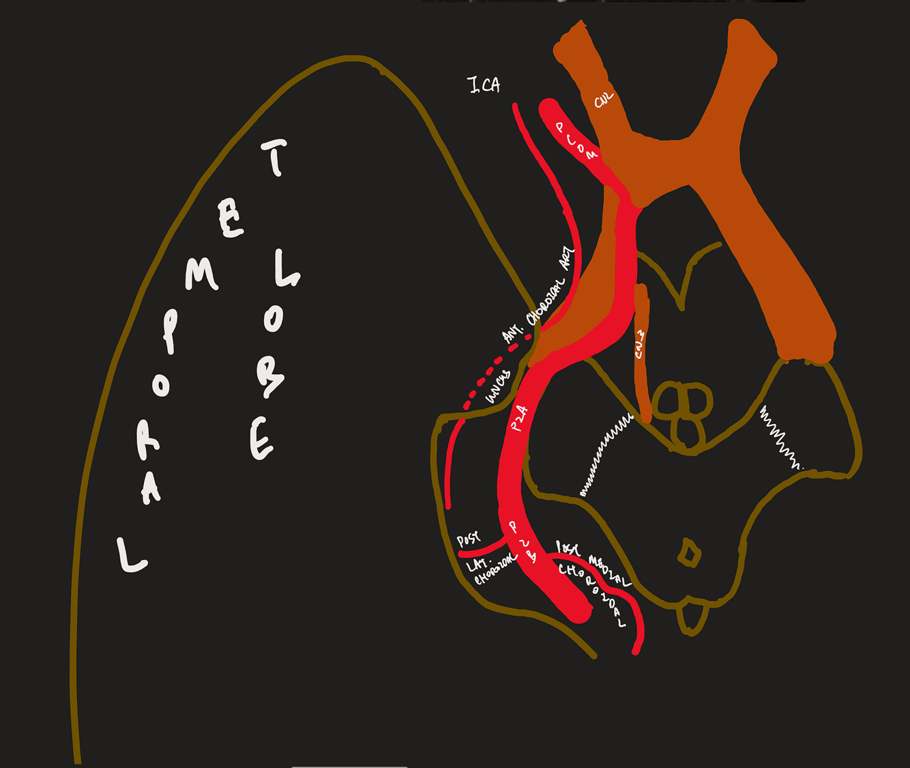
Difference between PCOM vs Anterior choroidal artery
Features | Anterior choroidal | PComA |
Origin | More distal | More proximal |
Size | Smaller | Larger |
Direction of travel | Has a superior hump (plexal point) where it passes through the inferior choroidal point to enter the temporal horn. | Goes up and down the straight back up and usually bifurcates |
Relation between each | More lateral | More medial |
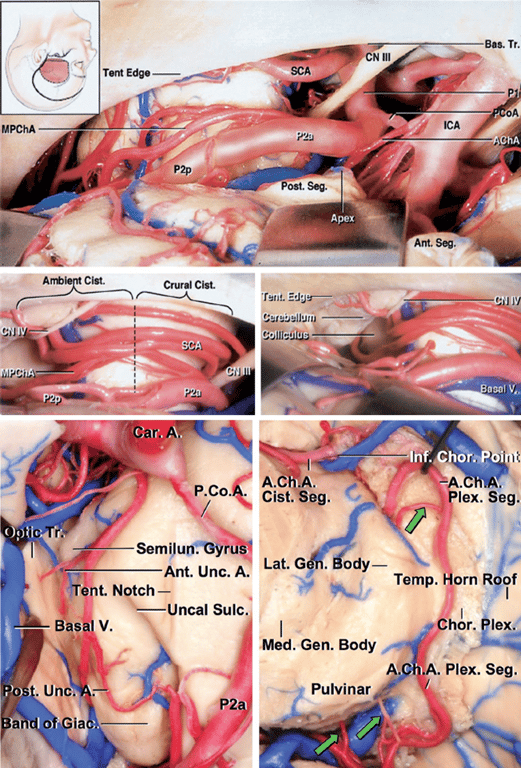
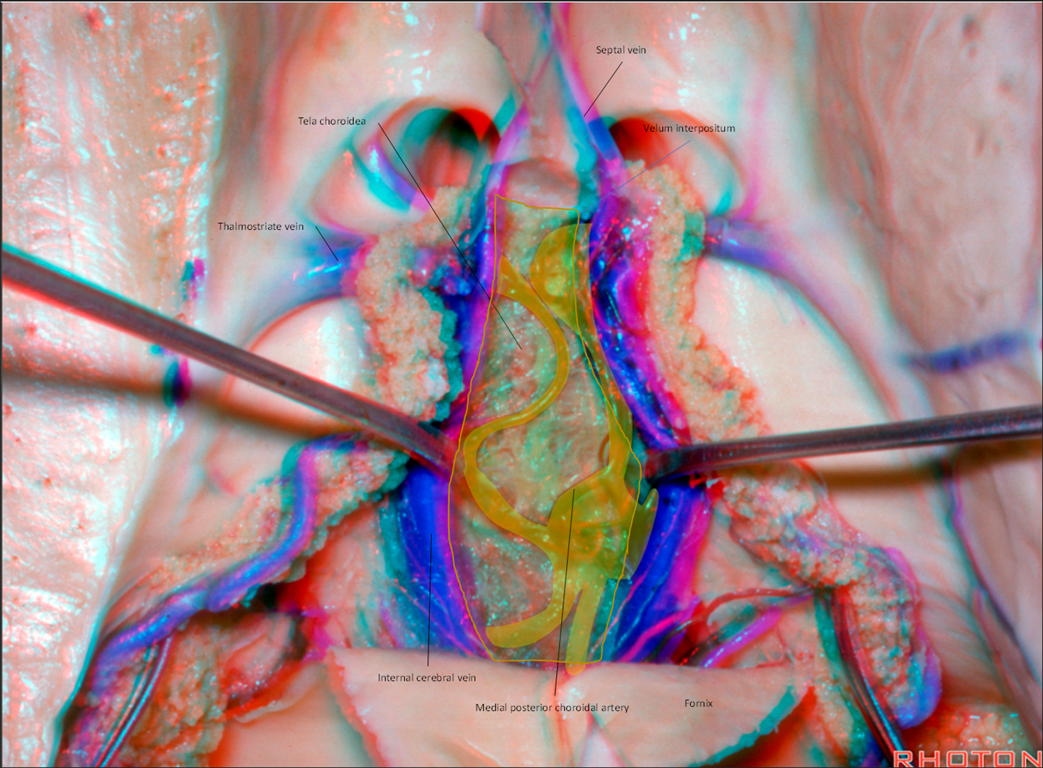
Medial posterior choroidal artery (MPChAs)
- Origin:
- They arise most frequently from the posteromedial aspect of the proximal part of the PCA (P1 or P2) in the interpeduncular and crural cisterns.
- Course
- Travels inferior and medial to the PCA through the crural → ambient cisterns and turns medially to enter the quadrigeminal cistern.
- Passes beneath the splenium of the corpus callosum
- The artery then turns forward to enter the velum interpositum and supplies the choroid plexus in the roof of the third ventricle
- Destination: Lateral + 3rd ventricle
- Supplies:
- Cerebral peduncle
- Tegmentum
- Geniculate bodies (medial > lateral)
- Colliculi
- Pulvinar
- Pineal gland
- Medial thalamus
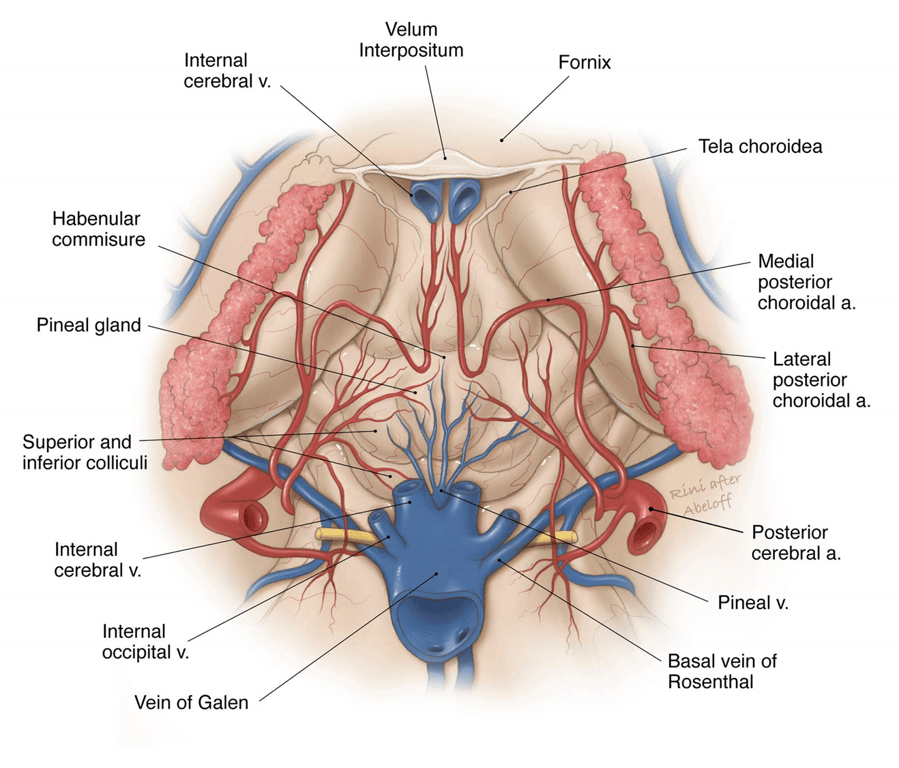
Lateral posterior choroidal artery (LPChAs)
- Origin: They arise from the PCA (most commonly the P2P segment) or its cortical branches in the ambient and quadrigeminal cisterns.
- Course
- They pass laterally around the pulvinar
- Course laterally along the upper edge of the parahippocampal gyrus within the ambient cistern
- Pass through the choroidal fissure to enter the posterior part of the temporal horn and atrium
- enters the ventricle adjacent to the lateral geniculate nucleus through the choroid fissure
- Destination: temporal horn of lateral ventricle
- The number of LPChAs in a hemisphere averages four (ranging from one to nine).
- Supplies:
- Cerebral peduncle
- Posterior commissure
- Fornix (Part of crura and body)
- Lateral geniculate body
- Pulvinar
- Dorsomedial thalamic nucleus
- Body of the caudate nucleus
- Anastomosis with
- Ant Choroidal Artery
- Medial Posterior Choroidal Artery

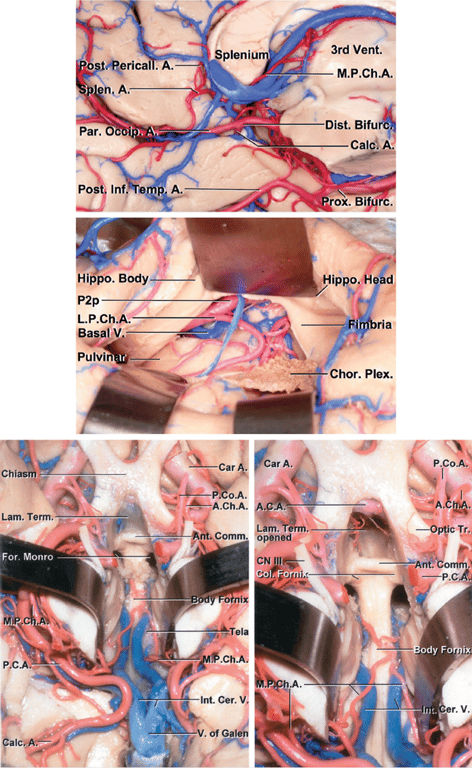
Images
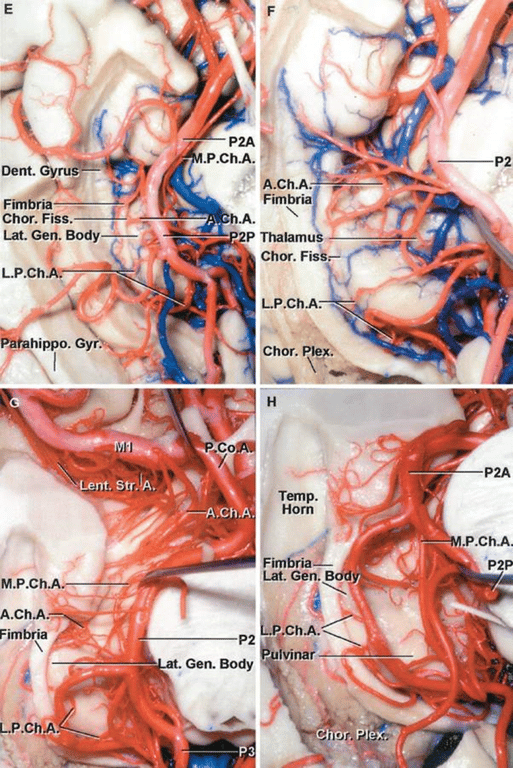
Infratentorial choroidal arteries
- Upper: Posterior or suboccipital view.
- The choroid plexus is composed of
- 2 medial segments.
- Each medial segment is divided into a
- Rostral or nodular part
- Caudal or tonsillar part
- 2 lateral segments.
- Each lateral segment is divided into a
- Medial or peduncula part
- Lateral or floccular part
- The medulla, fourth ventricle, vertebral arteries, and origin of the PICAs are below.
- The choroidal arteries arise from the
- PICA
- SCA
- AICA.
- The choroid plexus is attached to the tela choroidea, which is attached to the taenia along the border of the floor of the fourth ventricle.
- Lower: Anterolateral view.
- The choroid plexus is seen through the brainstem.
- The AICA arises from the basilar artery and sends branches that enter the choroid plexus near the flocculus.
- The SCA may also send choroidal branches to the floccular part of the choroid plexus.
- Right Center: Diagram showing subdivision of the choroid plexus into medial and lateral segments.
- The medial segments have nodular and tonsillar parts and the lateral segments have peduncular and floccular parts.
- The floccular parts protrude through the foramina of Luschka, and the tonsillar parts extend through the foramen of Magendie.

Abbreviation
Abbreviation | Full Form | Abbreviation | Full Form | Abbreviation | Full Form |
A. | Artery | Gen. | Geniculate | Plex. | Plexus |
Ac. | Acoustic | He. | Hemispheric | Pon. | Pontine |
A.I.C.A. | Anteroinferior cerebellar artery | Hem. | Hemispheric | Post. | Posterior |
Ant. | Anterior | Hypogl. | Hypoglossal | Premeat. | Premeatal |
Atl. | Atlanto | Inf. | Inferior | Prox. | Proximal |
B.A. | Basilar artery | Int. | Intermediate | Quad. | Quadrigeminal |
Bas. | Basilar | Intermed. | Intermedius | Rec. | Recurrent |
Bivent. | Biventral | labyr. | Labyrinthine | Ro. | Rostral |
Bo. | Body | L. | Long | Rost. | Rostral |
Br. | Branch | Lat. | Lateral | S. | Short |
Bridg. | Bridging | Lig. | Ligament | S.C.A. | Superior cerebellar artery |
Ca. | Caudal | Marg. | Marginal | Seg. | Segment |
Caud. | Caudal | Meat. | Meatal | Sp. | Spinal |
Cer. | Cerebellar | Med. | Medial, median, medullary | Str. | Straight |
Cer. Med. | Cerebellomedullary | Men. | Meningeal | Suboccip. | Suboccipital |
Cer. Mes. | Cerebellomesencephalic | Mes. | Mesencephalic | Sulc. | Sulcus |
Cer. Pon. | Cerebellopontine | Mid. | Middle | Sulcare. | Sulcature |
Ch. | Choroid, choroidal | Mod. | Moderate | Sup. | Superior |
Chor. | Choroid | N. | Nerve | Tent. | Tentorial |
Circ. | Circumflex | No. | Nodular | To. | Tonsillo |
Cist. | Cistern | Nerv. | Nervus | Ton. | Tonsillar |
CN | Cranial nerve | Nucl. | Nucleus | Tr. | Trunk |
Co. | Communicating | O. | Optic | Trans. | Transverse |
Cochl. | Cochlear | Occ. | Occipital | Trig. | Trigeminal |
Coll. | Colliculus | Paramed. | paramedian | V.A. | Vertebral artery |
Cran. | Cranial | P. | Posterior | V. | Vein |
Dent. | Dentate | P.C.A. | Posterior cerebral artery | Ve. | Vermian |
Dup. | Duplicate | Pe. | Peduncular | Vel. | Velum |
F. | Foramen | Ped. | Peduncle | Vent. | Ventral, ventricle |
Fiss. | Fissure | Perf. | Perforating | Verm. | Vermian |
Fl. | Floccular | Pet. | Petrosal | Vert. | Vertebral |
Flocc. | Flocculus | P.I.C.A. | Posteroinferior cerebellar artery | Vest. | Vestibular |
For. | Foramen | Pl. | Plexus | ㅤ | ㅤ |