Perforating branches of the ICA.
- A., artery; A.C.A., anterior cerebral artery; A.Ch.A., anterior choroidal artery; A.Co.A., anterior communicating artery; Ant., anterior; Ch., choroidal; Cin., cinereum; Co., communicating; Diaph., diaphragm; Fr., frontal; Gyr., gyrus; Hyp., hypophyseal; Infund., infundibulum; M.C.A., middle cerebral artery; Mam., mamillary; N., nerve; O., optic; Olf., olfactory; Op., ophthalmic; Ophth., ophthalmic; P.C.A., posterior cerebral artery; P.Co.A., posterior communicating artery; Perf., perforated; Subst., substance; Sup., superior; Tr., tract.
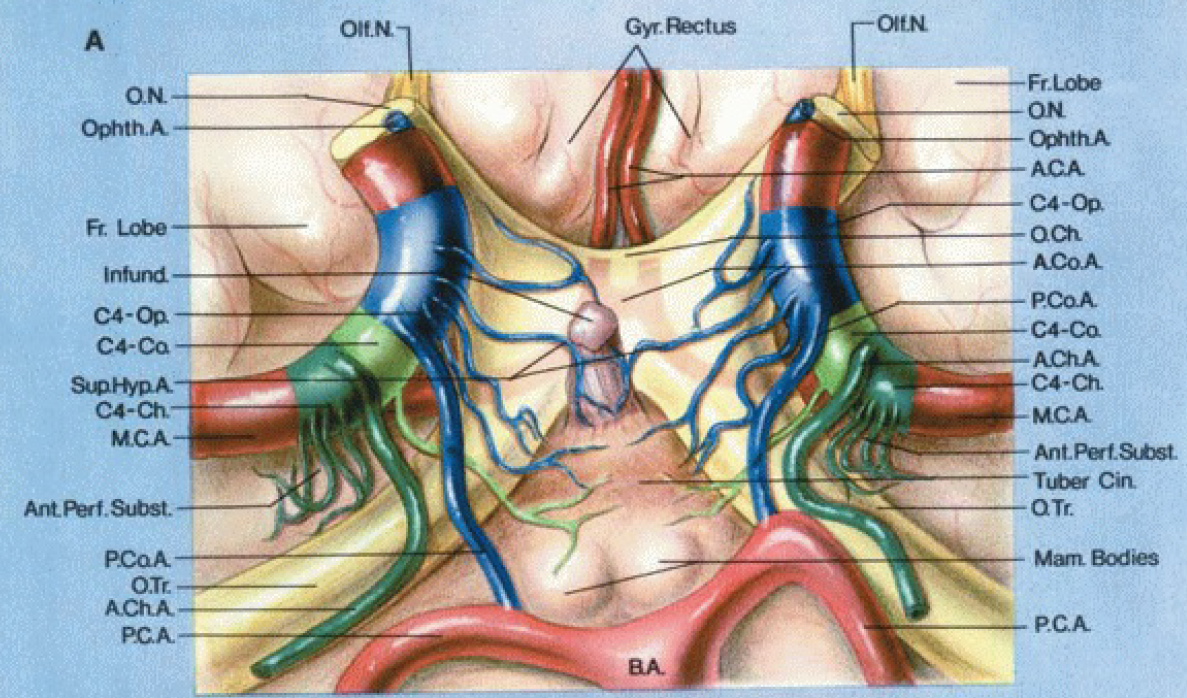
A, inferior view.
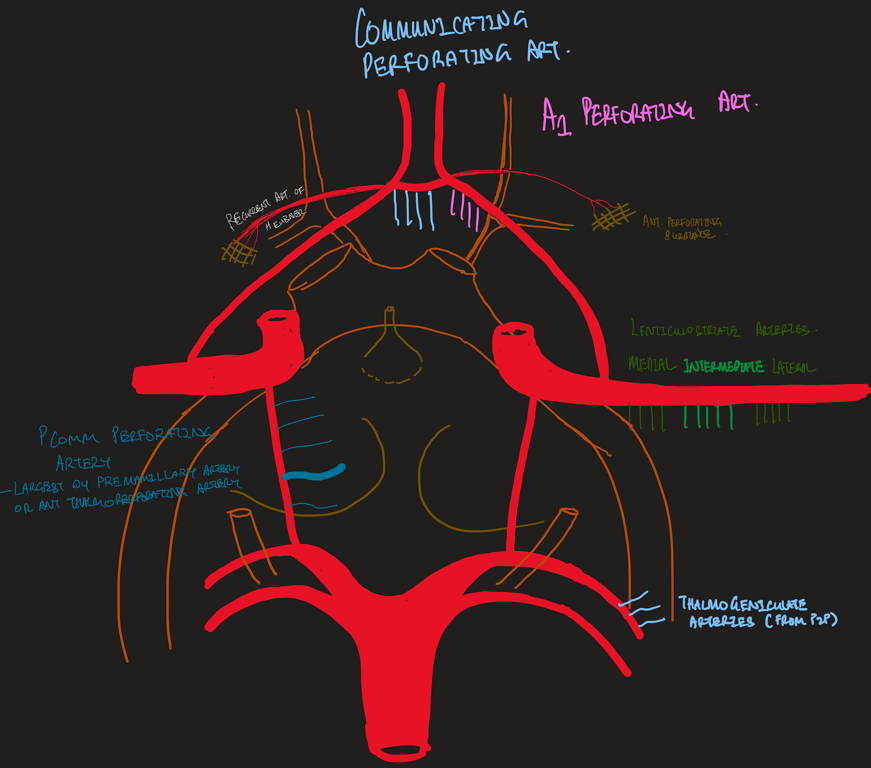
Supraclinoid portion of the ICA is divided into 3 segments
- Ophthalmic segment (C4-Op., blue)
- Extends from the origin of the ophthalmic artery to the origin of the PComA
- The perforating branches arising from the ophthalmic segment extend to the optic nerve, optic chiasm and the optic tracts, and the floor of the third ventricle around the infundibulum and tuber cinereum.
- The superior hypophyseal arteries arise from the ophthalmic segment and extend to the infundibulum of the pituitary gland.
- Communicating segment (C4-Co., light green)
- Extends from the origin of the PComA to the origin of the AChA;
The branches arising from the communicating segment reach the optic tracts, floor of the third ventricle, and the area around the mamillary bodies.
- Choroidal segment (C4-Ch., dark green)
- Extends from the origin of the AChA to the bifurcation of the ICA into the anterior and middle cerebral arteries.
- The perforating branches of the choroidal segment pass upward and enter the anterior perforated substance.
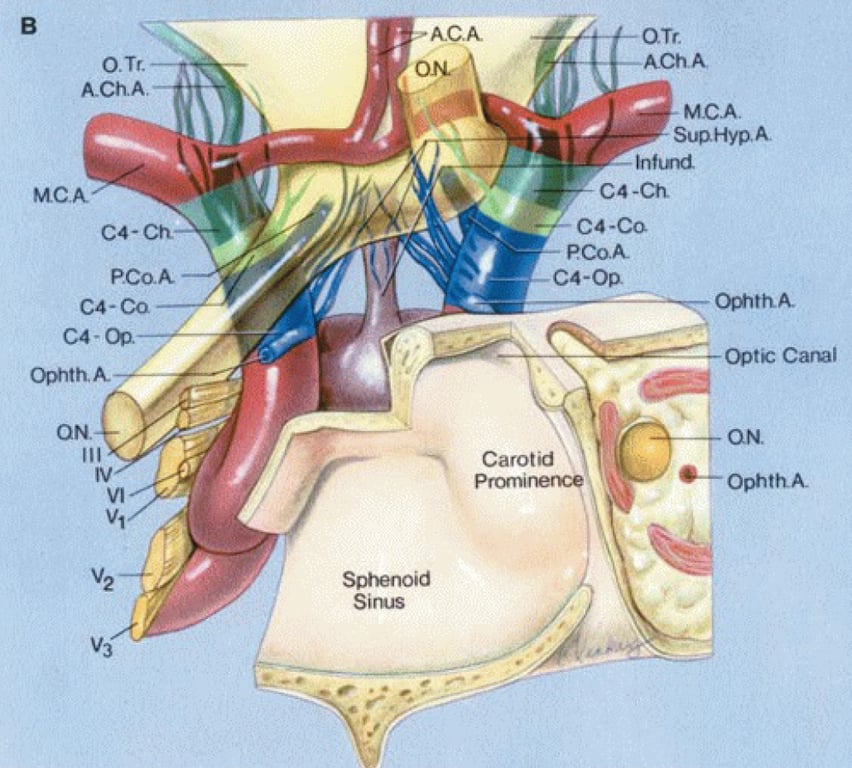
B, anterior view.
- Left optic nerve divided near entrance into optic canal and elevated for a clearer view of perforating branches.
- Ophthalmic artery arises above the cavernous sinus.
- Carotid artery courses through the cavernous sinus, then laterally, producing a prominence in the wall of the sphenoid sinus before giving rise to the ophthalmic artery.
- Oculomotor, trochlear, abducens, and the ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular divisions of the trigeminal nerve pass lateral to the sphenoid sinus in the walls of the cavernous sinus.
- Superior hypophyseal arteries arise from the ophthalmic segment.
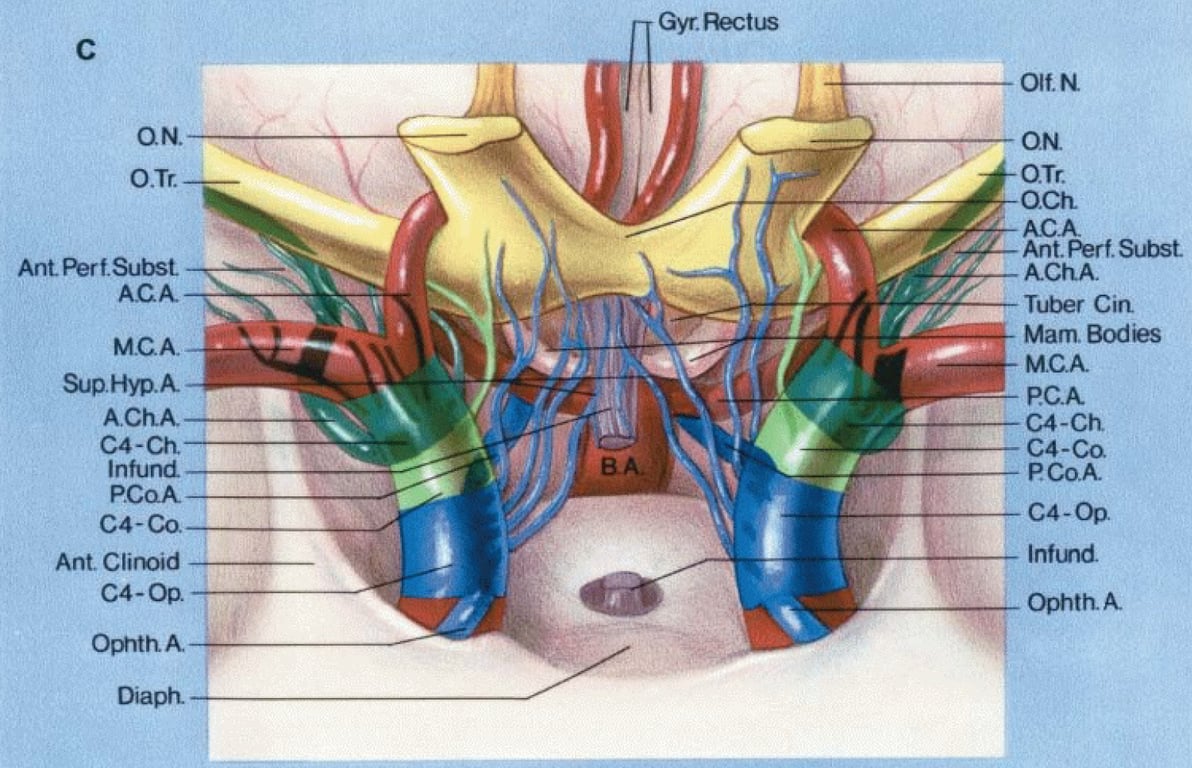
Continued C
- anterior view with both optic nerves divided and elevated to show the lower surface of the floor of the third ventricle and the perforating branches passing to it.
- The infundibulum has been divided above the diaphragma sellae.
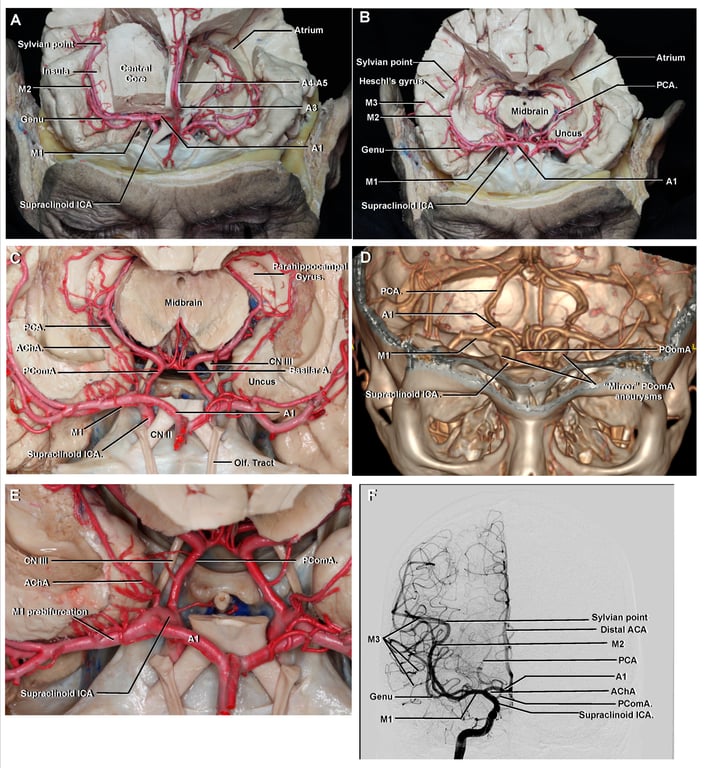
Anterior and anteroinferior views of the supraclinoid portion of the internal carotid artery.
- A., artery; A.C.A., anterior cerebral artery; A.Ch.A., anterior choroidal artery; Ant., anterior; B.A., basilar artery; C.A., carotid artery; Ch., choroidal; Ch., chiasm, chiasmatic; Co., communicating; Diaph., diaphragm; Falc., falciform; Hyp., hypophyseal; Infund., infundibulum; M.C.A., middle cerebral artery; N., nerve; O., optic; Op., Ophth., ophthalmic; P.C.A., posterior cerebral artery; P.Co.A., posterior communicating artery; Perf., perforated; Post., posterior; Subst., substance; Sulc., sulcus; Sup., superior; Temp., temporal; Tr., tract
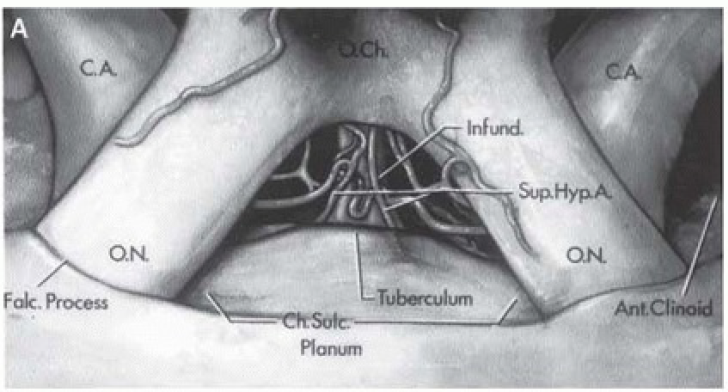
A. Anterior View
- Optic nerves enter optic canals medial to anterior clinoid processes.
- Infundibulum passes inferiorly below optic chiasm to pituitary gland.
- Carotid arteries are posterior to optic nerves.
- Planum sphenoidal is anterior to chiasmatic sulcus and tuberculum sellae.
- Perforating branches of carotid artery pass medially in subchiasmatic space.
- Superior hypophyseal arteries arise from carotid artery and pass to infundibulum.
- Falciform process is a fold of dura mater passing above optic nerve proximal to optic foramen.
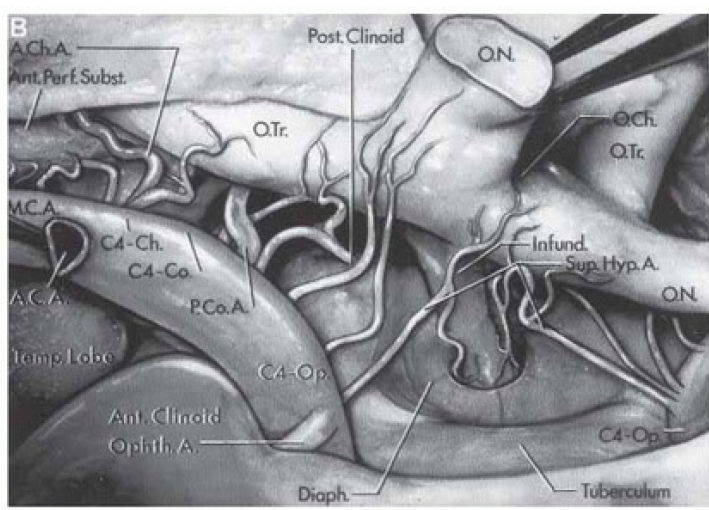
B. Perforating Branches of Carotid Arteries
- Right optic nerve divided at optic foramen and elevated to show perforating branches.
- Right anterior cerebral artery divided at origin to elevate optic nerve and chiasm.
- Carotid artery gives rise to multiple branches: ophthalmic, posterior communicating, anterior choroidal, and middle cerebral arteries.
- Supraclinoid portion of ICA is divided into three segments:
- Ophthalmic segment (C4-Op): From origin of ophthalmic artery to PComA.
- Communicating segment (C4-Co): From PComA to AChA.
- Choroidal segment (C4-Ch): From AChA to carotid bifurcation.
- Perforating branches:
- From ophthalmic segment: Pass to optic nerve, chiasm, infundibulum, and floor of third ventricle.
- From communicating segment: Pass to optic tract and floor of third ventricle.
- From choroidal segment: Pass upward through anterior perforated substance.
- Diaphragma sellae surrounds infundibulum above pituitary gland.
- Temporal lobe is below middle cerebral artery.
C. Elevated Optic Nerves and Chiasm
- Left optic nerve divided at optic foramen; anterior cerebral artery divided near origin.
- Both optic nerves and chiasm elevated to show perforating branches of carotid artery.
- Liliequist membrane is posterior to infundibulum and hides basilar artery but not posterior cerebral artery.
- Perforating branches of ophthalmic segment pass upward to infundibulum, optic nerve, chiasm, and tract.
D. Under Optic Chiasm
- Both optic nerves, both anterior cerebral arteries, and infundibulum divided.
- Optic nerves and chiasm elevated with forceps to view under optic chiasm.
- Diaphragma sellae and dorsum exposed to upper part of basilar artery and oculomotor nerves.
- Oculomotor nerves pass forward below posterior cerebral arteries (PCAs).
- Perforating branches of supraclinoid segment of carotid artery pass upward to supply infundibulum, optic chiasm and tracts, and floor of third ventricle.
- Some branches enter the brain through anterior perforated substance.
- Right anterior choroidal artery (AChA) is very large.