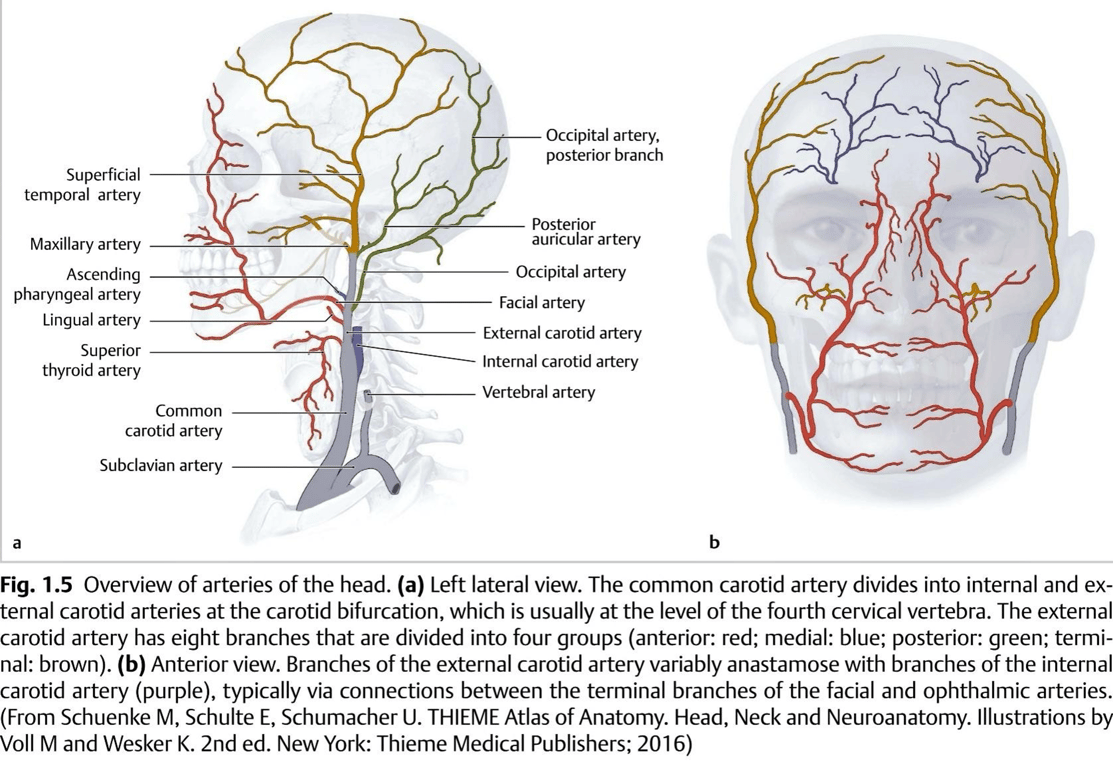
Origin
- The level of C4
- Begins at the level of the upper border of the thyroid cartilage (at the level of the fourth cervical vertebra).
Relation
- Lies anteromedial to the ICA
Location
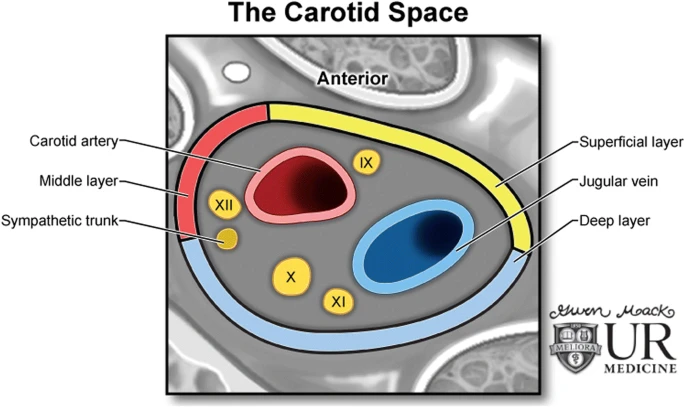
- Within carotid sheath
- Right common carotid sheath.
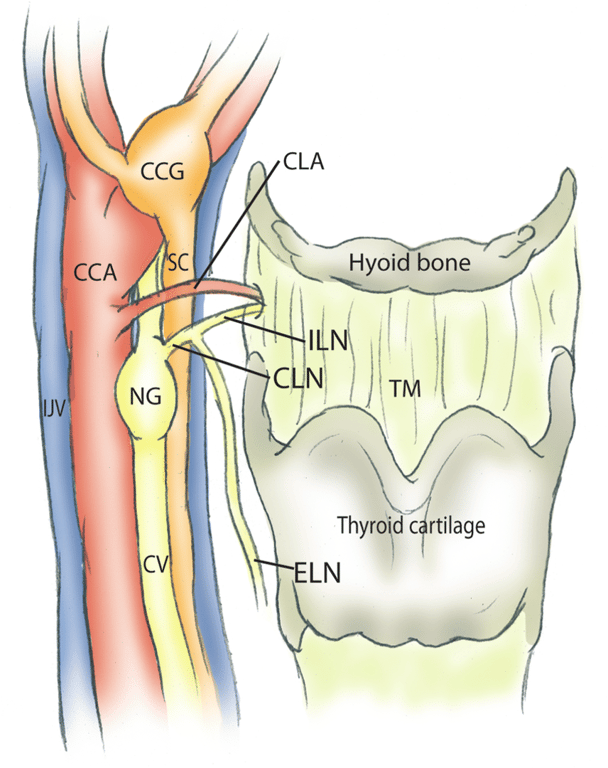
- The ventral red structure is the common carotid artery (CCA) with its 2 branches:
- Internal carotid artery (ICA)
- External carotid artery (ECA)
- The nodose ganglion (NG) and cervical vagus nerve (CV) are dorsal and medial to the CCA.
- The internal jugular vein (IJV) locates most dorsally within the sheath.
- The cervical sympathetic chain (CSC) goes cranially between the CV and IJV within the carotid sheath and then curves dorsally to the cranial laryngeal nerve (CLN), arriving at the cranial cervical sympathetic ganglion (CCG).
- The CCG lies ventral and medial to the ICA, and immediately adjacent to the bifurcation of the CCA.
- It has 2 main branches sending sympathetic fibers cranially innervating the face and cranium along the ICA and ECA separately.
- The bifurcation of the CCA is at the level of the great cornu of the hyoid bone.
Branches
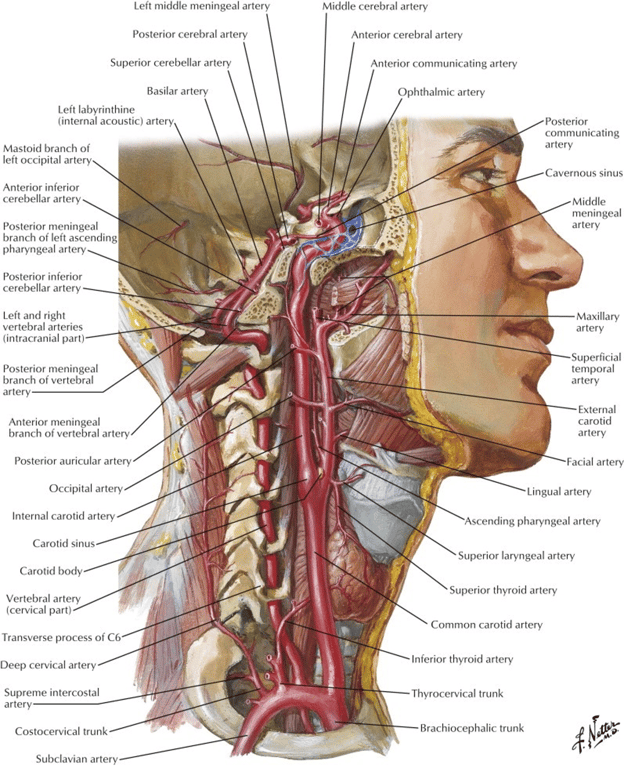
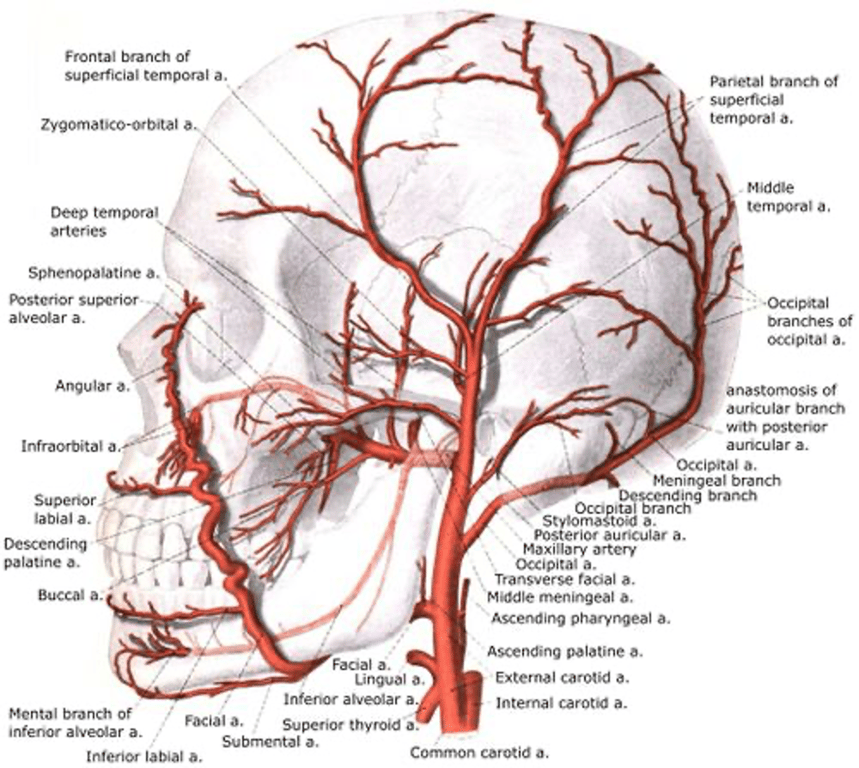
- Classically eight branches are described (can vary): Some Anatomists Like Freaking Out Poor Medical Students
Superior thyroid artery
Ascending pharyngeal artery
- Supplies Glomus Jugulare tumours
Lingual artery
Facial artery
Occipital artery
Posterior auricular artery
Internal maxillary artery (terminal)
- First (mandibular) part: Five branches, each of which enters a bony foramen:
- Deep auricular artery (enters squamotympanic fissure)
- Anterior tympanic artery (enters petrotympanic fissure)
- Middle meningeal artery (enters foramen spinosum)
- Accessory meningeal artery (enters foramen ovale)
- Inferior alveolar artery (enters mandibular foramen)
- Artery to mylohyoid
- Second (pterygoid or muscular) part: Five branches although pterygoid branches are irregular in their number and origin:
- Anterior, middle and posterior deep temporal branches
- Pterygoid branches
- Masseteric artery
- Buccinator artery
- Third (pterygopalatine) part: Six branches including the terminal branch:
- Posterior superior alveolar artery
- Infraorbital artery (enters inferior orbital fissure)
- Artery of the pterygoid canal
- Pharyngeal artery (enters palatovaginal canal)
- Descending palatine artery (enters greater palatine foramen)
- Sphenopalatine artery - terminal branch (enters sphenopalatine foramen)
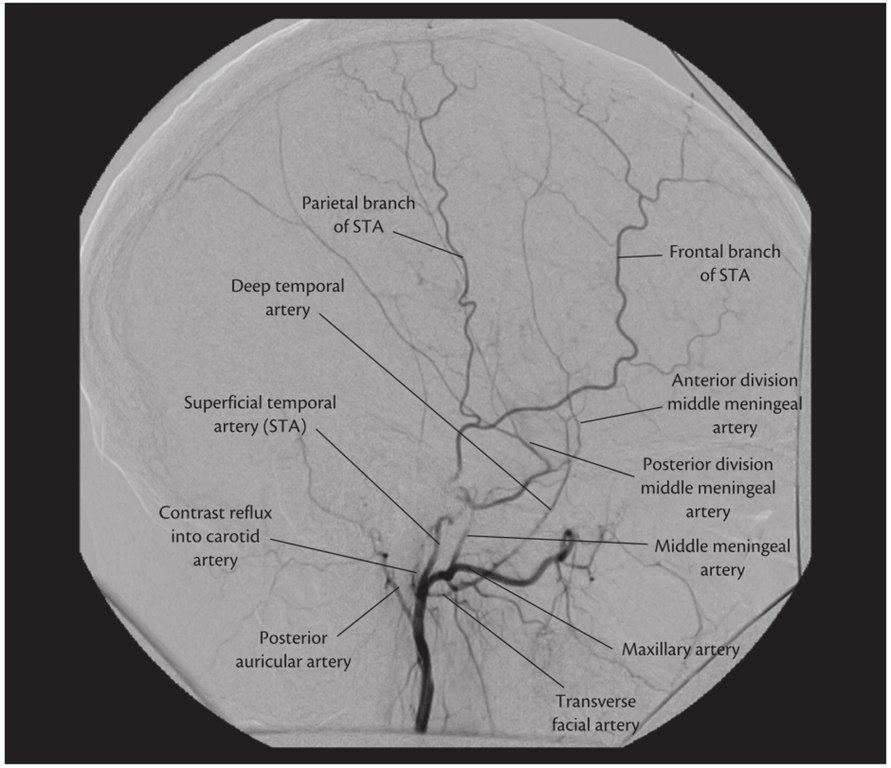
Superficial temporal artery (Terminal)
- Pinar 2006
- Originates from the external carotid at the level of the parotid gland.
- It crosses very superficially over the posterior third of the zygomatic process
- Divides in its frontal and parietal branches.
- Is located
- 1.6 cm anterior to tragus
- 2cm anterior to pinna
- Clinical
- Posterior part of the Superficial temporal artery is sacrificial able
- Can be used for bypass in Moyamoya
- The temporal artery can be injured at the most caudal part of the skin incision during pterional craniotomy
- Blunt dissection down to the level of the temporalis fascia is used in this region to preserve the superficial temporal artery.
- The skin flap is elevated and retracted anteriorly and the superficial temporalis fascia is exposed
- Sacrificing the superficial temporal artery can compromise the vascularization of the skin flap. A well-vascularized skin flap is important to achieve good cosmetic results and is also important in those cases when adjuvant radiotherapy will be needed.
Anastomosis
- Several anastomoses exist between ECA branches and both ICA and vertebral artery branches.
- Ascending pharyngeal artery branches anastomose with cavernous ICA branches and meningeal vertebral artery branches;
- The facial artery with branches of the ophthalmic artery and the occipital artery with vertebral artery branches (and also superficial temporal artery branches).
Clinical
- Dural supply from ECA branches have relevance to dural fistula diagnosis and management, for example,
- Ascending pharyngeal artery and occipital artery supply to the posterior fossa dura or
- Middle meningeal and accessory meningeal branches of the maxillary artery supplying supratentorial dura.
- Paragangliomas
- Blood supply is ascending pharyngeal
- Meningiomas supply
- Clinoidal meningiomas
- Anterior dural branches of MMA
- Meningo-orbital branches of MMA
- Posterior ethmoidal branch of ophthalmic artery branch of ICA
- Superficial recurrent ophthalmic artery
- Sphenoid wing meningiomas
- Branches from middle cerebral artery
- Branches from middle meningeal artery
- Relations
- Anteriorly (i.e. ECA is crossed by these structures)
- Upper root of ansa cervicalis
- Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- Posterior belly of digastric muscle
- Stylohyoid muscle and ligament
- Facial nerve (CN VII) (within the parotid gland)
- Retromandibular vein (within the parotid gland)
- Passing between ECA and ICA
- Pharyngeal branch of vagus nerve (CN X)
- Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- Stylopharyngeus muscle
- Styloglossus muscle
- Posteriorly (i.e. ECA lies on these structures)
- Pharyngeal wall
- Superior laryngeal branch of vagus nerve (CN X)
- Deep lobe of the parotid gland
Image