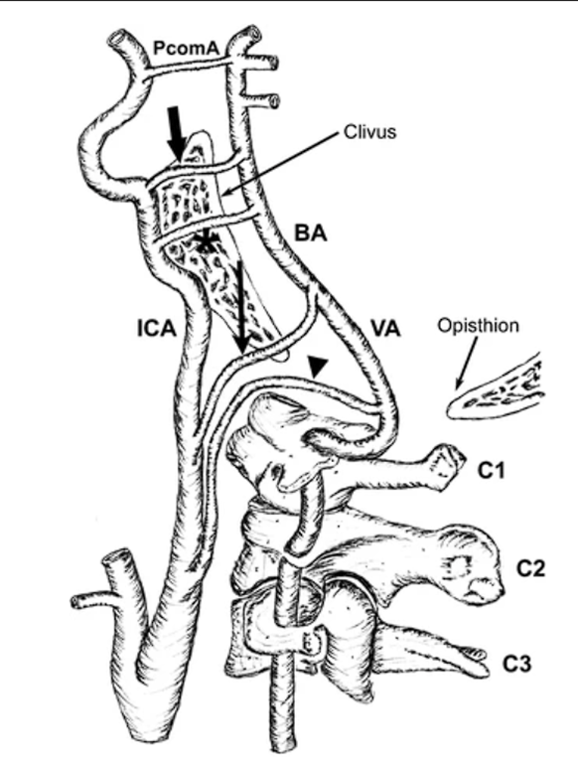
4 Embryonic connections between the carotid and basilar arteries exist that can persist into adulthood.
Trigeminal artery (Top fat arrow),
- Most common
- Intracavernous portion of the carotid artery ↔ basilar artery
- Purely subarachnoid
- Associated with an increased incidence of cerebral aneurysms
- In utero, the trigeminal artery supplies the basilar artery before the development of the posterior communicating and vertebral arteries.
Otic artery (Asterik)
- Intrapetrous carotid artery ↔ midportion of the basilar artery
- Partly intrapetrous coursing through the vidian canal to become subarachnoid
Hypoglossal artery (Long arrow)
- Extracranial ICA ↔ intracranial vertebral artery
- Enter skull via Hypoglossal canal.
- thereby representing a single artery supplying the brainstem and cerebellum.
- Associated with an increased incidence of cerebral aneurysms
Proatlantal intersegmental artery (arrowhead)
- Extracranial ICA ↔ extracranial vertebral artery
- Entirely extra cranial