
Benner 2021: Magnified sagittal view of the skull base with arterial cerebrovascular structures illustrated to highlight the arterial eponyms:
A, Artery of Salmon
B, Artery of Wollschlaeger and Wollschlaeger
C, Artery of Davidoff and Schechter
D, Artery of Bernasconi and Cassinari
- aka
- Marginal tentorial artery
- Artery of the free margin of the tentorium
- Artery of Bernasconi and Cassinari
- May have different origins
- Lacrimal artery (LA) within the orbit, through the superficial recurrent ophthalmic artery (SRecOA)
- Inferolateral trunk (ILT)
- Meningohypophyseal trunk (MHT)
- Course
- Posterolaterally along the free margin of the tentorium.
- Note a 3D-DSA reconstruction of a rare case of MTA (highlighted in red) origin from the OA.
- The MTA exits the orbit through the superior orbital fissure (SOF) and is directed posteriorly to feed an arteriovenous malformation. DRecOA indicates deep recurrent ophthalmic artery .

- Arise from cavernous portion of ICA
- Supplies
- Tent
- Meningiomas
E, Artery of Percheron
F, Arteria termatica of Wilder
G, Vidian artery
H, Recurrent artery of Heubner
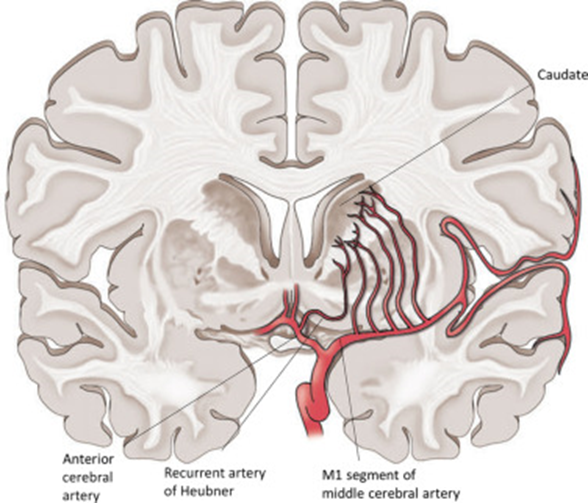
- AKA medical distal striate artery
- This artery is the largest of the perforating branches of the ACA
- Course generally follows the A1 laterally
- Arises anywhere near A1-Acom-A2 J(x): most common @ proximal A2
- Enters anterior perforating substance
- Supplies:
- Head of caudate
- Anterior limb of internal capsule
- Anterior putamen + Globus pallidus
- Septal nuclei
- Inferior frontal lobe
- Easily clipped accidentally when targeting AComA → pure motor stroke
- Unilateral
- Weakness contralateral arm
- Weakness contralateral face
- Dysarthria
- Hemichorea
- Bilateral: akinetic mutism
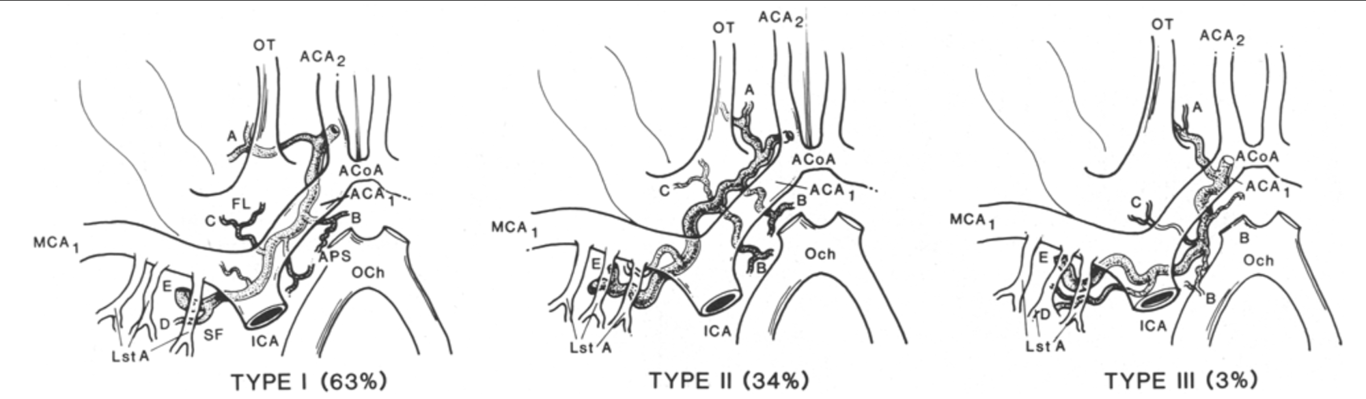
- 3 variation in the course
- (A); anterior perforated substance (APS) branches (B); frontal branches (C); Sylvian fissure branches (D); and terminal branches (E).
- ICA = internal carotid artery; MCA~ = proximal middle cerebral artery; ACA~ = proximal anterior cerebral artery; ACA2 = distal anterior cerebral artery; ACoA = anterior communicating artery; FL = frontal lobe; SF = Sylvian fissure; OT = olfactory tract; Lst A = lenticulostriated arteries; OCh = optic chiasm.
I, McConnell's capsular arteries
- Aka
- Medial trunk
- McConnell's capsular arteries
- Supplies
- Sellar region, in particular, to the sella dura mater and the anterior pituitary capsule
- Branches into
- Anterior capsular artery
- Inferior capsular artery
- Courses inferior
- Least constant of the three major branches (30% present) of the intercavernous ICA