General
- There is considerable variation in the venous system draining the cerebellum and brain stem.
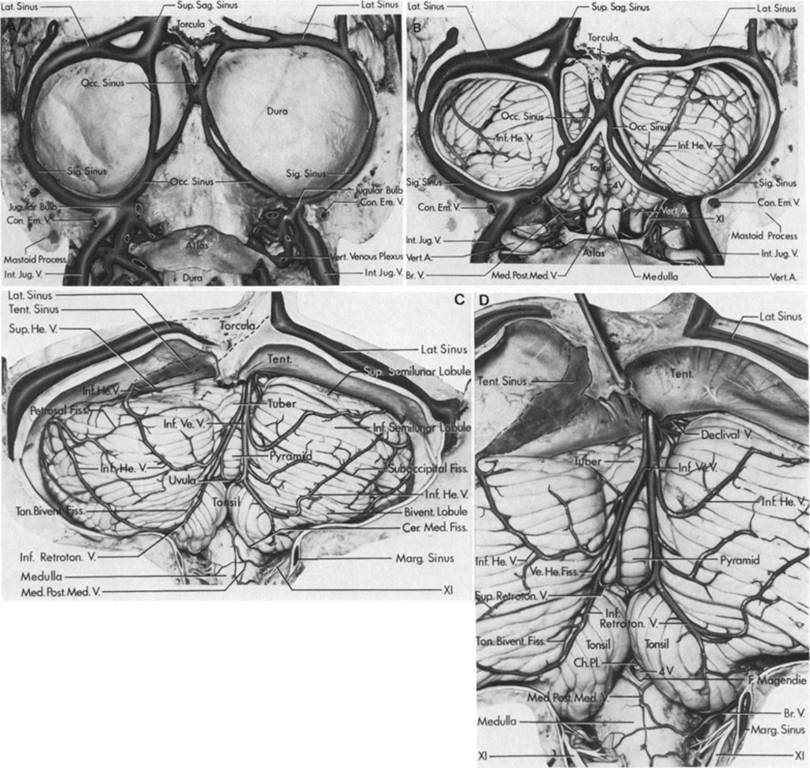
- The superficial cerebellar hemispheres drain into the nearest of the sigmoid or transverse sinuses.
- The (superior and inferior) vermian veins are the exception, which run along the vermis in the midline.
- The anterior cerebellum drains into the superior or inferior petrosal sinuses.
Brainstem veins grouping
Lateral mesencephalic vein
- Contiguous with the petrosal vein
- Is commonly present
- Runs along the lateral aspect
- Connecting superiorly the basal vein (of Rosenthal) with the superior petrosal sinus.
Anterior mesencephalic/pontomedullary/spinal vein (depending on its most adjacent structure)
- Vein running longitudinally on the anterior aspect
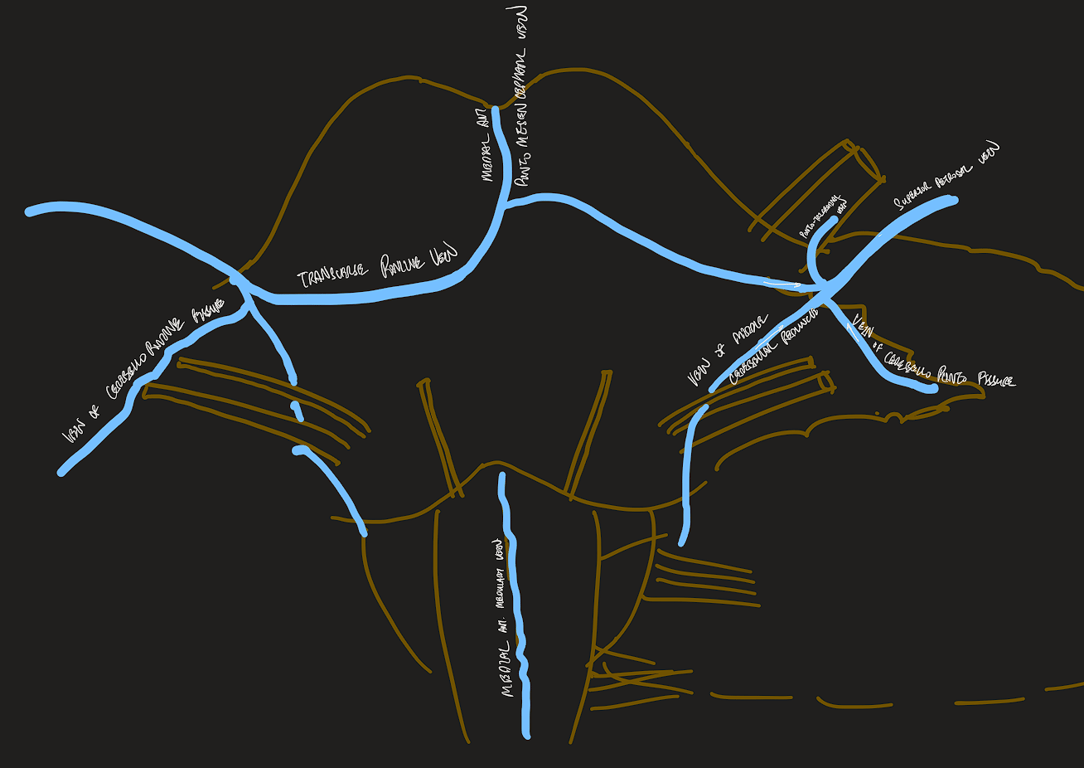
The precentral (or cerebellar) vein
- is an unpaired vein running posterior to the brainstem,
- draining into the superior vermian vein or great vein (of Galen)
- its inferior aspect marks the upper border of the fourth ventricle.
- It predominantly drains the cerebellum
Upper brainstem veins
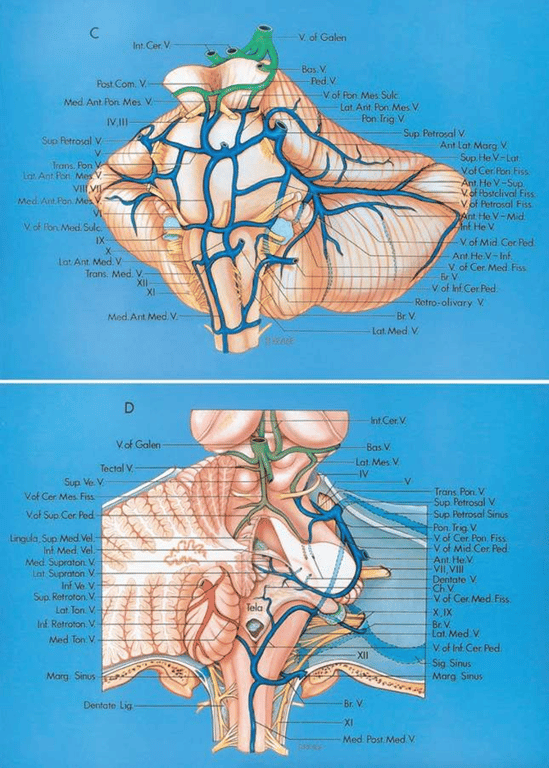
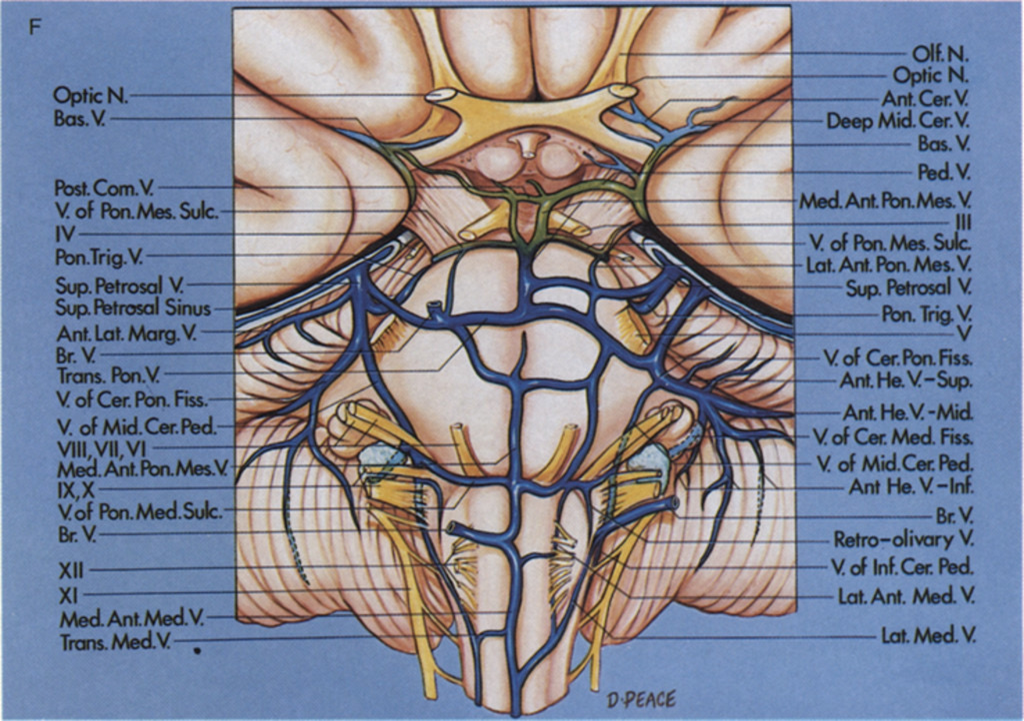
The veins on the anterior surface of the pons and medulla and the veins of the cerebellopontine fissure and their tributaries empty into the superior petrosal veins.
The median anterior medullary vein and median anterior pontomesencephalic veins course in the midline, but often do not extend along the full length of the pons and medulla.
The vein of the pontomesencephalic sulcus and the transverse pontine veins are transversely oriented.
The veins of the cerebellomedullary fissure join the veins of the middle cerebellar peduncle, which ascends to join the veins of the cerebellopontine fissure.
The veins in the crural and ambient cistern join the basal vein, which empties into the vein of Galen in the quadrigeminal cistern. The basal vein also drains the walls of the temporal horn, which has been opened on the right. An internal occipital vein passes from the calcarine sulcus and occipital lobe to the vein of Galen.
The inferior ventricular vein from the temporal horn and the lateral atrial vein join the basal vein, which also drains the walls of the crural and ambient cisterns. The cerebellomesencephalic fissure, an inferior extension of the quadrigeminal cistern, is drained by tributaries of the vein of Galen.
The veins in the medial portion of the cerebellomesencephalic fissure empty into the vein of Galen and those from the lateral part may join the superior petrosal veins. In this case, the vein of the cerebellomesencephalic fissure is small, resulting in most of the fissure’s drainage being directed laterally through a pontotrigeminal vein, which passes above the trigeminal nerve to empty into a superior petrosal vein formed by a superior hemispheric and transverse pontine vein and the vein of the cerebellopontine fissure.
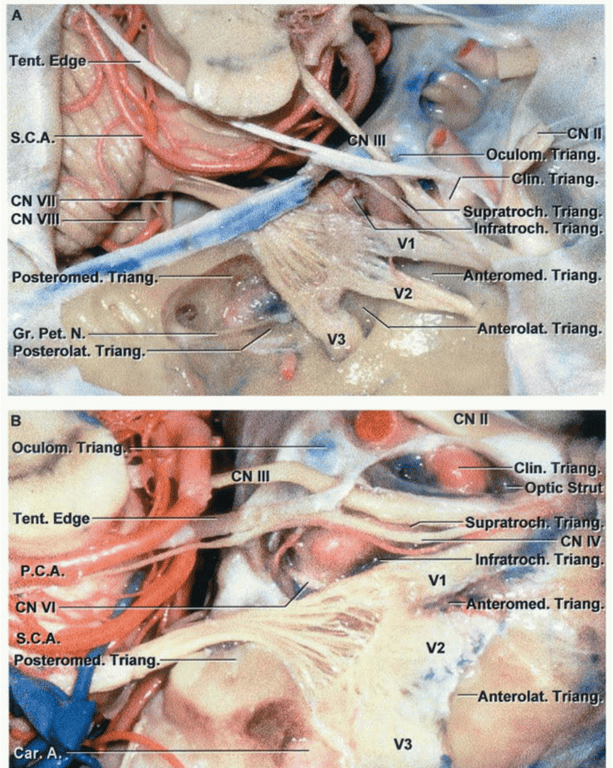
Brainstem and petrosal surface
The vertebral and basilar arteries and their branches course superficial to the veins. The veins on the anterior surface of the pons and medulla and the petrosal surface drain predominantly into the superior petrosal veins, which empty into the superior petrosal sinuses.
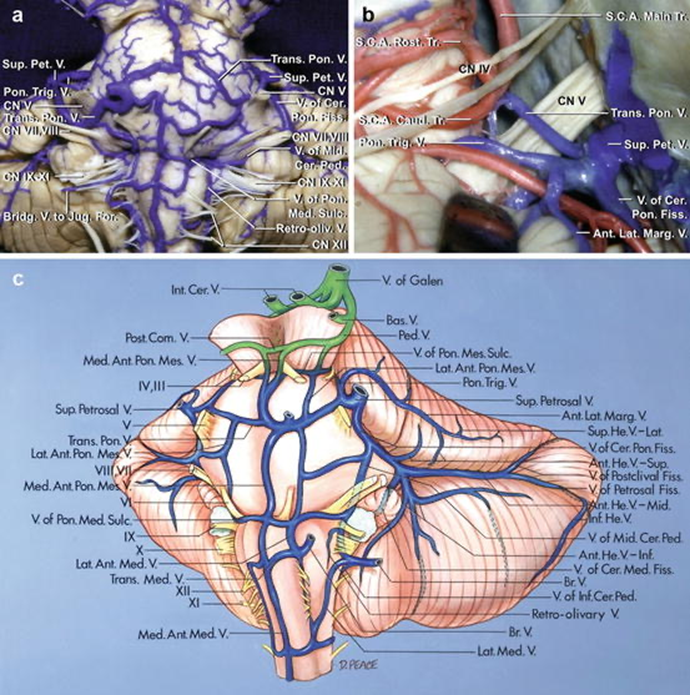
The arteries have been removed. The median anterior pontomesencephalic and median anterior medullary veins ascend on the front of the brainstem. The transverse pontine and transverse medullary veins run transversely across the pons and medulla surfaces. The anterior hemispheric veins drain the petrosal surface and commonly empty into the vein of the cerebellopontine fissure, which ascends to join the superior petrosal veins. The vein of the pontomedullary sulcus passes across the pontomedullary junction.
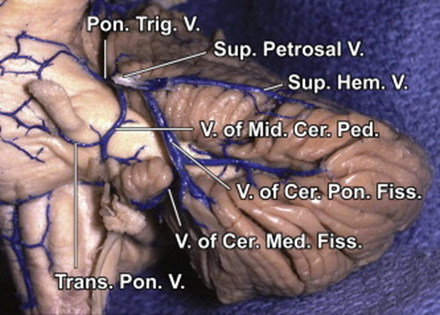
The anterior hemispheric veins drain the petrosal surface and pass forward to empty into the vein of the cerebellopontine fissure or a superior petrosal vein. The vein of the cerebellopontine fissure arises at the lateral apex of the cerebellopontine fissure and crosses the middle cerebellar peduncle, where it is joined by a large transverse pontine vein.
The vein of the cerebellopontine fissure arises from the union of the anterior hemispheric veins at the apex of the cerebellopontine fissure and ascends to be joined by a superior hemispheric vein from the lateral part of the tentorial surface before emptying into the superior petrosal sinus.
The cerebellum has been removed to expose the veins of the superior, inferior, and middle cerebellar peduncles. The vein of the superior cerebellar peduncle ascends to join the vein of the cerebellomesencephalic fissure. The vein of the inferior cerebellar peduncle crosses the peduncle at the inferolateral margin of the fourth ventricle and passes around the lateral recess to join the veins in the cerebellopontine angle. The veins of the cerebellopontine fissure and middle cerebellar peduncle and a transverse pontine vein join to form a superior petrosal vein. The vein of the cerebellomedullary fissure empties into the vein of the middle cerebellar peduncle.
The vein of the cerebellomedullary fissure passes laterally across the lateral recess and empties into the vein of the middle cerebellar peduncle. The latter vein and the vein of the cerebellopontine fissure join to form a large superior petrosal vein. A large anterior hemispheric vein ascends along the petrosal surface.
Images
Abbreviation
Abbreviation | Full Form | Abbreviation | Full Form | Abbreviation | Full Form |
A. | Artery | Int. | Internal | Quad. | Quadrigeminal |
A.I.C.A. | Anteroinferior cerebellar artery | Interped. | Interpeduncular | Retrot. | Retrotonsillar |
Ant. | Anterior | Jug. | Jugular | Sag. | Sagittal |
Atr. | Atrial | Lat. | Lateral | S.C.A. | Superior cerebellar artery |
Bas. | Basilar | Lig. | Ligament | Seg. | Segment |
Bivent. | Biventral | Marg. | Marginal | Sig. | Sigmoid |
Br. | Bridging | Med. | Medial, medullary | Str. | Straight |
Carotid | Carotid | Mes. | Mesencephalic | Sulc. | Sulcus |
Cav. | Cavernous | Mid. | Middle | Sup. | Superior |
Cer. | Cerebellar, cerebellum | N. | Nerve | Supracol. | Supracolliculate |
Cer. Med | Cerebellomedullary | Occip. | Occipital | Supraton. | Supratonsillar |
Cer. Mes. | Cerebellomesencephalic | Olf. | Olfactory | Temp. | Temporal |
Cer. Pon. | Cerebellopontine | P.C.A. | Posterior cerebral artery | Tent. | Tentorial |
Ch. | Choroidal | Ped. | Peduncle | Ton. | Tonsillar |
Cist. | Cistern | Pet. | Petrosal | Trans. | Transverse |
CN | Cranial nerve | P.I.C.A. | Posteroinferior cerebellar artery | Trig. | Trigeminal |
Comm. | Communicating | Pon. | Pontine, ponto | V. | Vein |
Condylar | Condylar | Pon. Med. | Pontomedullary | Ve. | Vermian |
Em. | Emissary | Pon. Mes. | Pontomesencephalic | Vel. | Velum |
Fiss. | Fissure | Pon. Trig. | Pontotrigeminal | Vent. | Ventricle |
Hem. | Hemispheric | Post. | Posterior | Vert. | Vertebral |
Inf. | Inferior | ㅤ | ㅤ | ㅤ | ㅤ |