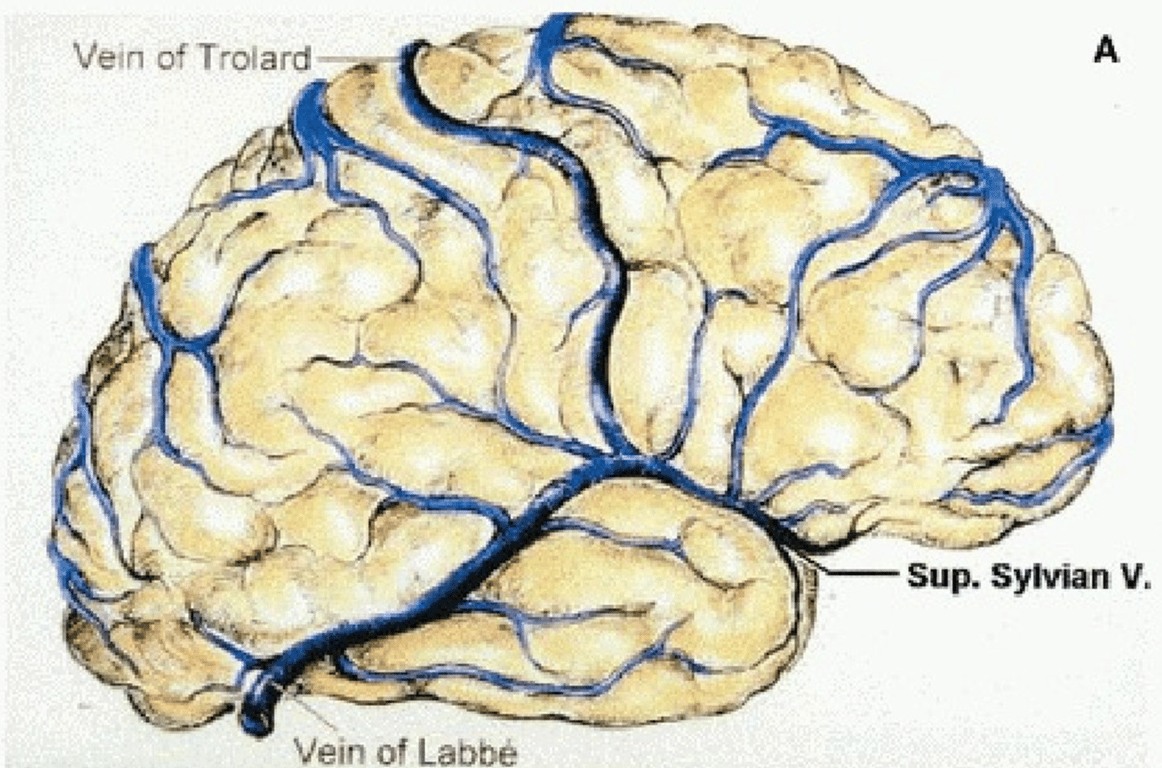
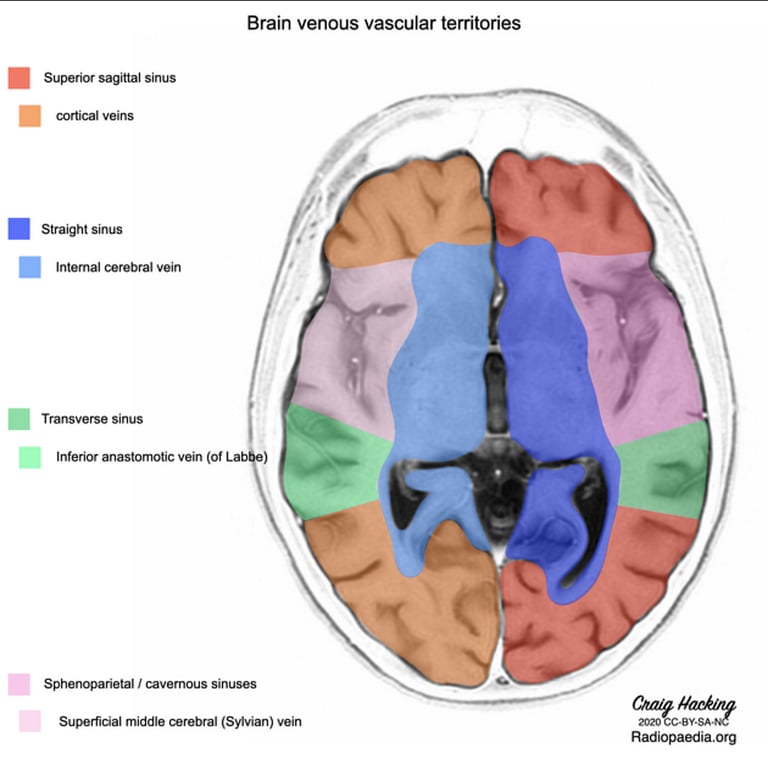
The superficial system
- Made up of numerous and variable superficial cortical veins, which typically accompany arteries travelling within the cerebral sulci.
- Drain into a number of larger named veins, which subsequently drain into the venous sinuses:
- drains into the cavernous (or sphenoparietal) sinus
- Drains the superficial middle cerebral vein into the superior sagittal sinus
- Is the largest superficial vein on the lateral surface of the parietal or frontal lobe
- Connects the superior sagittal sinus and the superficial middle cerebral vein (of Sylvius).
- Usually runs in the post-central sulcus draining the adjacent cortex.
- Posterior anastomotic vein (of Labbé)
- drains superficial middle cerebral vein into the transverse sinus.
- There is often a reciprocal arrangement between the two anastomotic veins with Labbé larger in the dominant hemisphere and Trolard in the non- dominant.
- Clinical
- Slight difficulty with naming and had agraphia and acalculia
- Thrombosis can cause temporal lobe hemorrhagic infarction, hemorrhage, or edema.
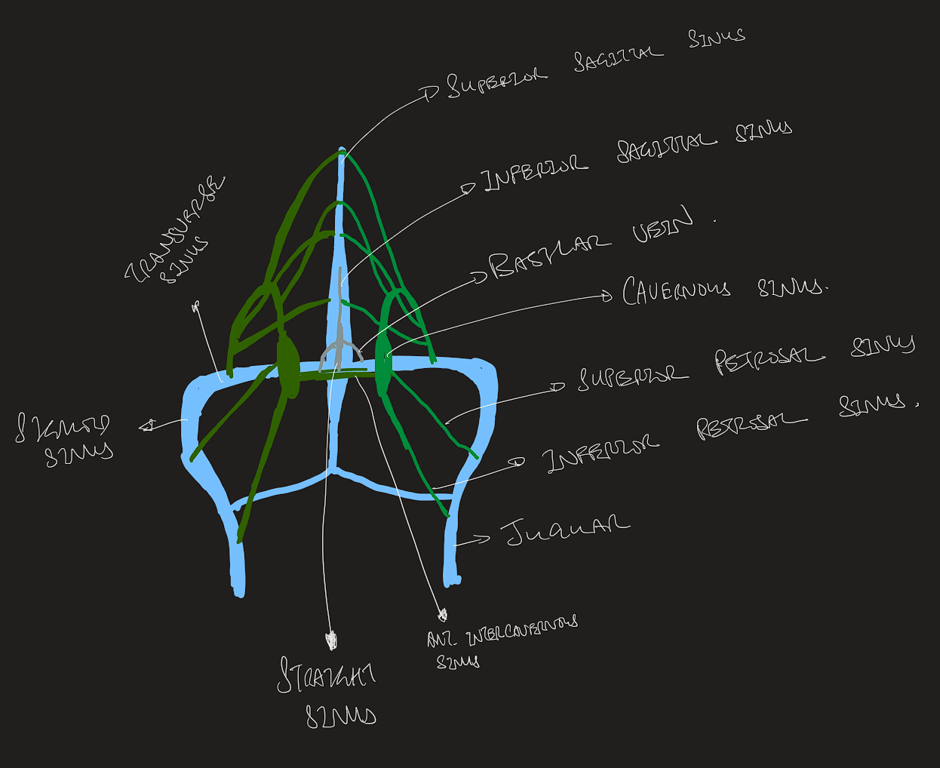
- Dural sinuses are valveless, venous channels formed from dural folds.
- The principal dural sinuses are the
- Superior sagittal
- Start
- Crista galli
- Ends
- Torcular Herophili
- It can also divide prior to the torcula, where it usually meets the transverse sinuses, leading clinically to misdiagnosis of superior sagittal sinus thrombosis.
- Inferior sagittal sinus
- lies in the free margin of the falx cerebri
- drains tributaries from the corpus callosum and cingulate gyrus,
- itself drains into the straight sinus at the venous confluence.
- It is typically not visible radiologically
- Transverse sinus
- Are commonly asymmetric
- Usually with a dominant right side which receives the majority of the blood from the superior sagittal sinus at the torcula.
- Become the sigmoid sinuses at the posterior petrous edge, which then continue to the jugular bulb.
- Sigmoid sinus
- Can vary in size compared to the transverse sinus, particularly when receiving large flow from the posterior anastomotic vein (of Labbé) into its proximal part.
- Straight sinus
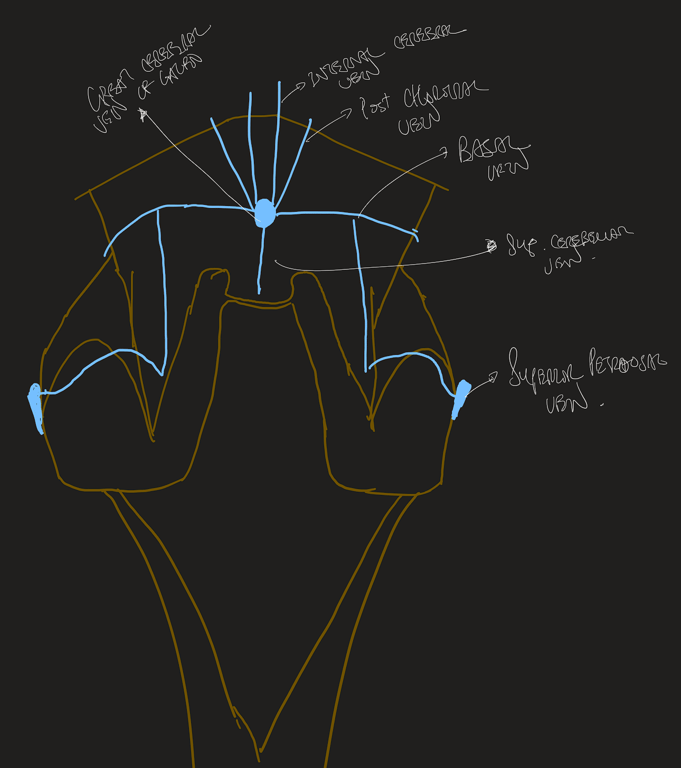
- Superior and inferior petrosal sinus
- Cavernous sinus
- Receives flow from the
- Superficial middle cerebral (Sylvian) veins,
- Ophthalmic veins
- Sphenoparietal sinus (itself sometimes draining the Sylvian veins).
- Outflow from the cavernous sinus is through the
- Superior petrosal sinuses
- connecting to sigmoid sinus
- Inferior petrosal sinuses
- Connecting to jugular foramen
- Contralateral cavernous sinus
- Pterygoid and clival venous plexuses.
- Sphenoparietal sinus
- Occipital sinus
- Varyingly present
- More common in children,
- may run from the torcula in the midline to the foramen magnum and can be the source of significant bleeding in an otherwise straightforward midline posterior fossa approach.
- The dural venous sinuses also communicate with the extracranial venous system through valveless emissary veins, which can serve as a route for the introduction of intracranial infection
Superficial middle cerebral vein
Great anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
Dural venous sinus
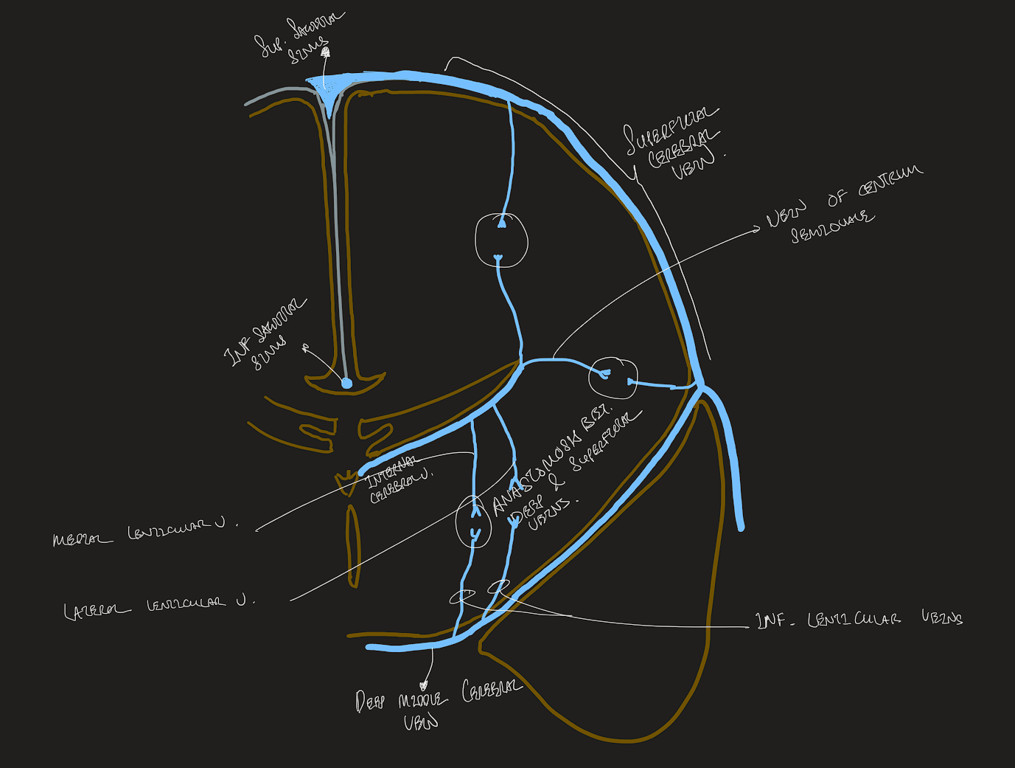
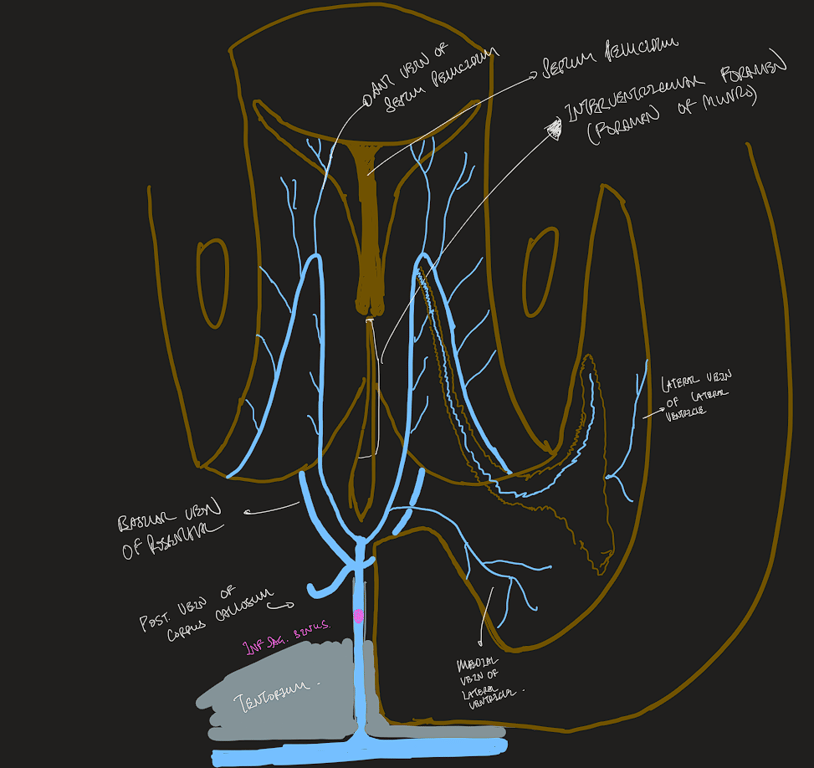
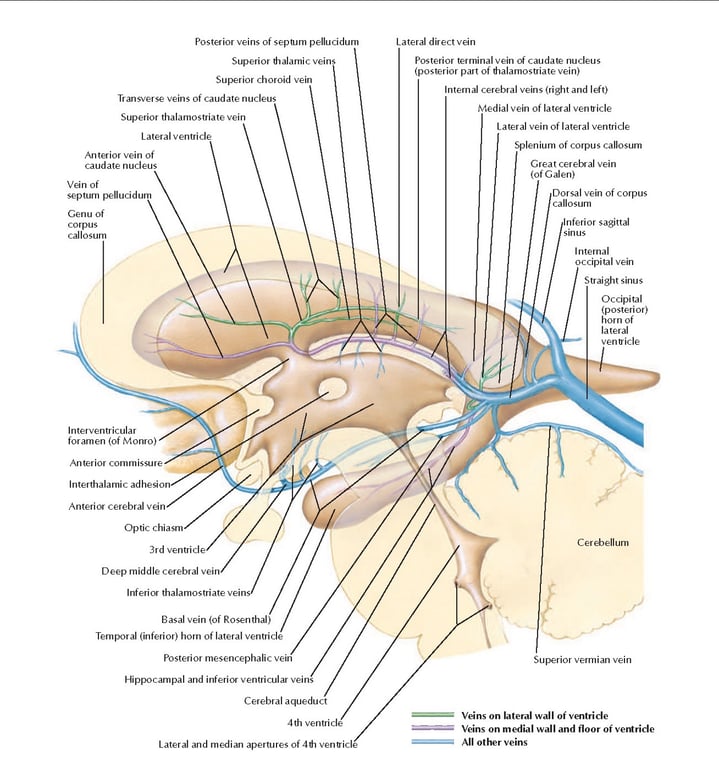
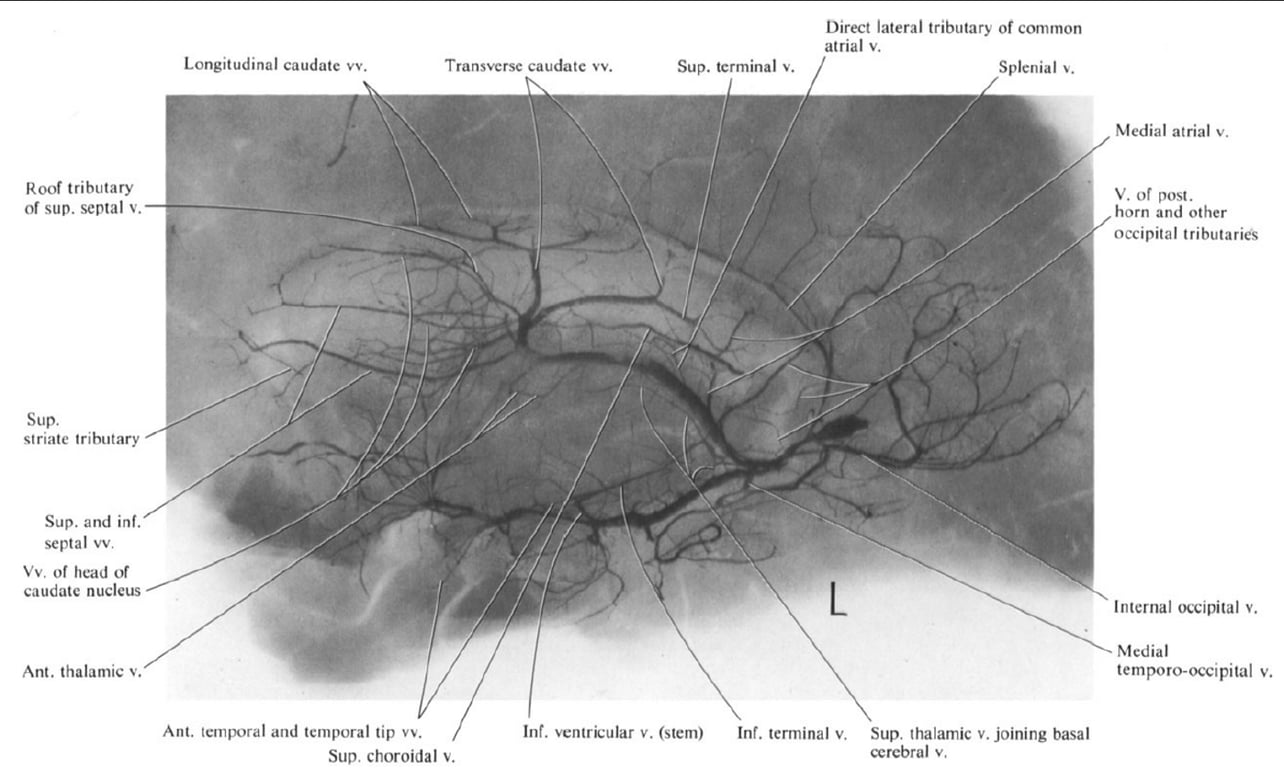
The deep system
- The deep venous system drains the deep white and grey matter surrounding the lateral and third ventricle and basal cisterns.
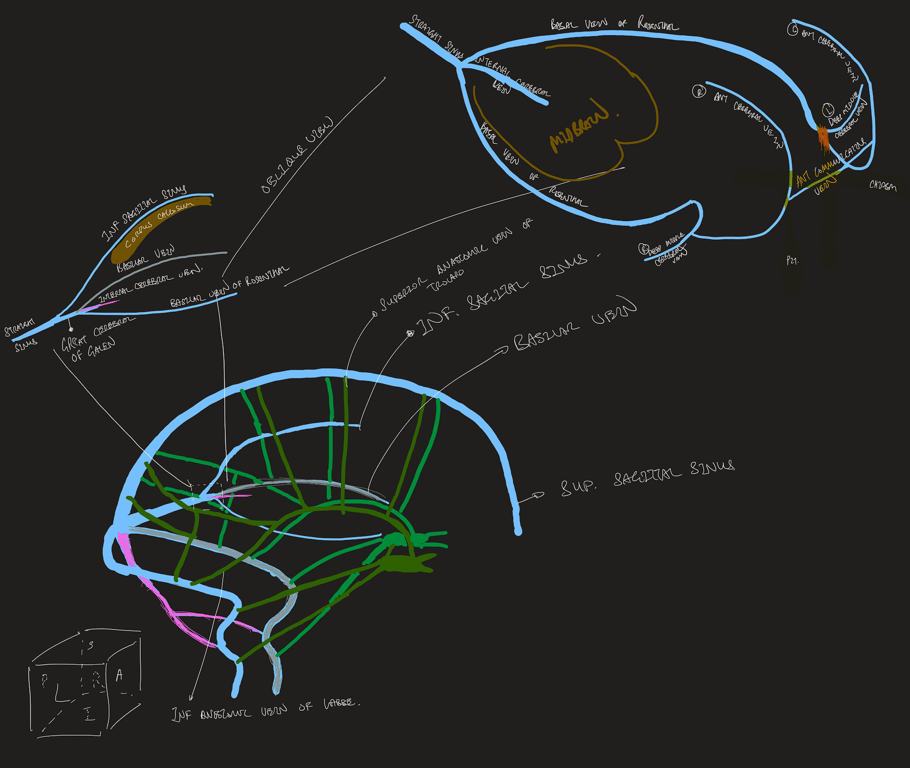
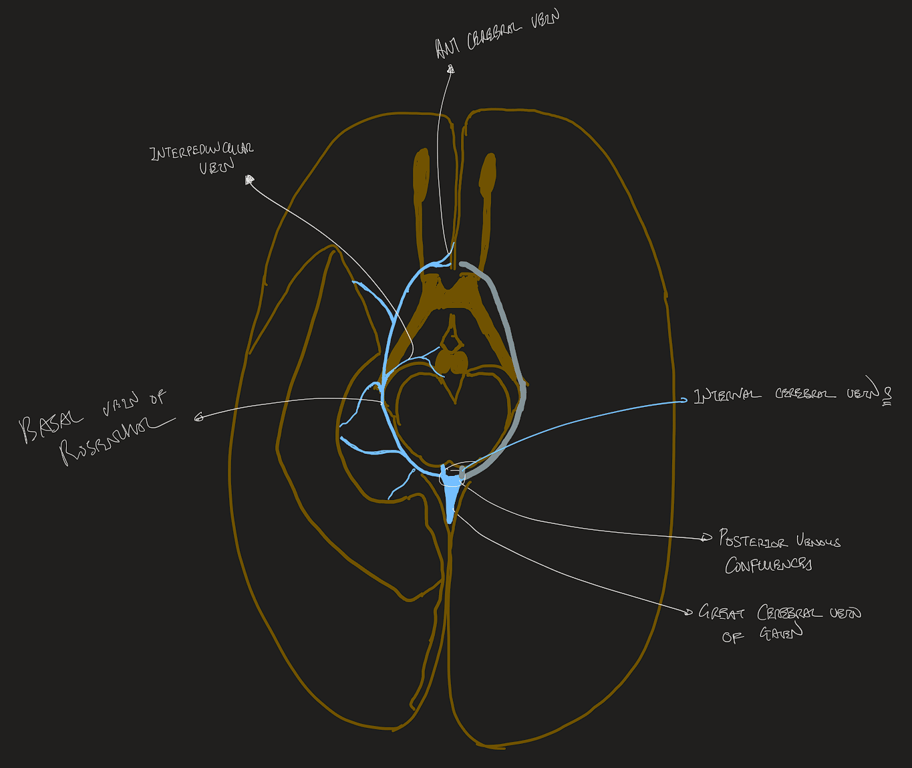
The great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- found below the splenium of the corpus callosum
- a short, single midline vessel.
- formed by
- joining of the two internal cerebral veins,
- two basal veins (of Rosenthal)
- occipital veins draining the medial and inferior occipital lobes.
- Drains into the venous confluence where it is joined by the inferior sagittal sinus to form the straight sinus.
The basal veins (of Rosenthal)
- Originates on the surface of the anterior perforated substance
- arise at the anterior perforated substance on the medial aspect of the temporal lobe
- run posteriorly and medially.
- They travel laterally around the midbrain through the ambient cistern
- Drain the hypothalamus, midbrain, and medial and inferior portions of the frontal and temporal lobes, including the insula and operculum.
- The internal cerebral veins,
- situated in the velum interpositum (roof of the third ventricle),
- formed by the union of the choroidal and thalamostriate veins.
- The choroidal vein
- drains the choroid plexus of the lateral ventricle.
- Tributaries draining into the thalamostriate vein include the
- transverse caudate veins,
- anterior terminal vein (draining the ventricular surface of the caudate nucleus)
- septal vein (draining the corpus callosum and deep frontal white matter).
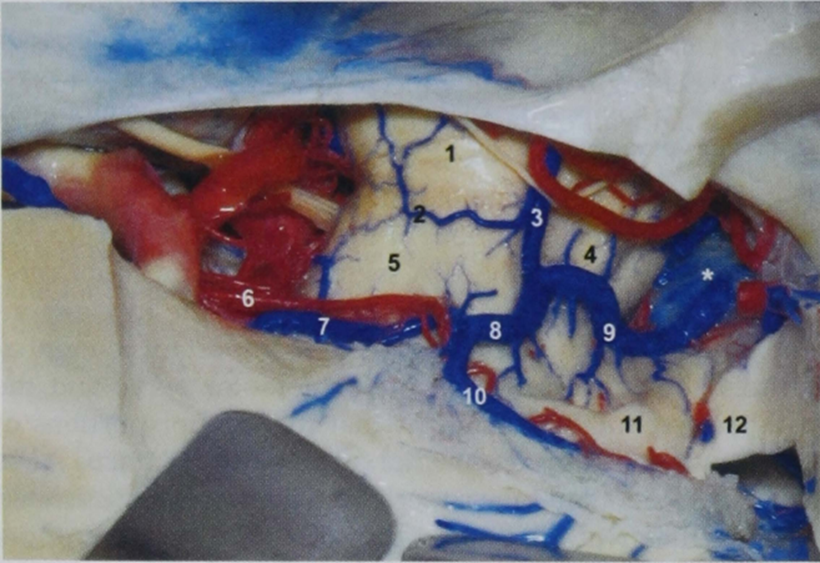
1, pons;
2, pontomesencephalic sulcus and vein;
3, lateral mesencephalic vein;
4, tegmentum of the mesencephalon;
5, crus cerebri;
6, anterior choroidal artery (cisternal segment);
7, anterior peduncular segment of the basal vein;
8, posterior peduncular segment of the basal vein;
9, posterior mesencephalic segment of the basal vein;
10, inferior ventricular vein and plexal segment of the anterior choroidal artery;
11, pulvinar of the thalamus;
12, tail of the hippocampus;
*, vein of Galen.
2, pontomesencephalic sulcus and vein;
3, lateral mesencephalic vein;
4, tegmentum of the mesencephalon;
5, crus cerebri;
6, anterior choroidal artery (cisternal segment);
7, anterior peduncular segment of the basal vein;
8, posterior peduncular segment of the basal vein;
9, posterior mesencephalic segment of the basal vein;
10, inferior ventricular vein and plexal segment of the anterior choroidal artery;
11, pulvinar of the thalamus;
12, tail of the hippocampus;
*, vein of Galen.
Images
Abbreviation
Abbreviation | Full Form | Abbreviation | Full Form | Abbreviation | Full Form |
A. | Artery | Int. | Internal | Quad. | Quadrigeminal |
A.I.C.A. | Anteroinferior cerebellar artery | Interped. | Interpeduncular | Retrot. | Retrotonsillar |
Ant. | Anterior | Jug. | Jugular | Sag. | Sagittal |
Atr. | Atrial | Lat. | Lateral | S.C.A. | Superior cerebellar artery |
Bas. | Basilar | Lig. | Ligament | Seg. | Segment |
Bivent. | Biventral | Marg. | Marginal | Sig. | Sigmoid |
Br. | Bridging | Med. | Medial, medullary | Str. | Straight |
Carotid | Carotid | Mes. | Mesencephalic | Sulc. | Sulcus |
Cav. | Cavernous | Mid. | Middle | Sup. | Superior |
Cer. | Cerebellar, cerebellum | N. | Nerve | Supracol. | Supracolliculate |
Cer. Med | Cerebellomedullary | Occip. | Occipital | Supraton. | Supratonsillar |
Cer. Mes. | Cerebellomesencephalic | Olf. | Olfactory | Temp. | Temporal |
Cer. Pon. | Cerebellopontine | P.C.A. | Posterior cerebral artery | Tent. | Tentorial |
Ch. | Choroidal | Ped. | Peduncle | Ton. | Tonsillar |
Cist. | Cistern | Pet. | Petrosal | Trans. | Transverse |
CN | Cranial nerve | P.I.C.A. | Posteroinferior cerebellar artery | Trig. | Trigeminal |
Comm. | Communicating | Pon. | Pontine, ponto | V. | Vein |
Condylar | Condylar | Pon. Med. | Pontomedullary | Ve. | Vermian |
Em. | Emissary | Pon. Mes. | Pontomesencephalic | Vel. | Velum |
Fiss. | Fissure | Pon. Trig. | Pontotrigeminal | Vent. | Ventricle |
Hem. | Hemispheric | Post. | Posterior | Vert. | Vertebral |
Inf. | Inferior | ㅤ | ㅤ | ㅤ | ㅤ |