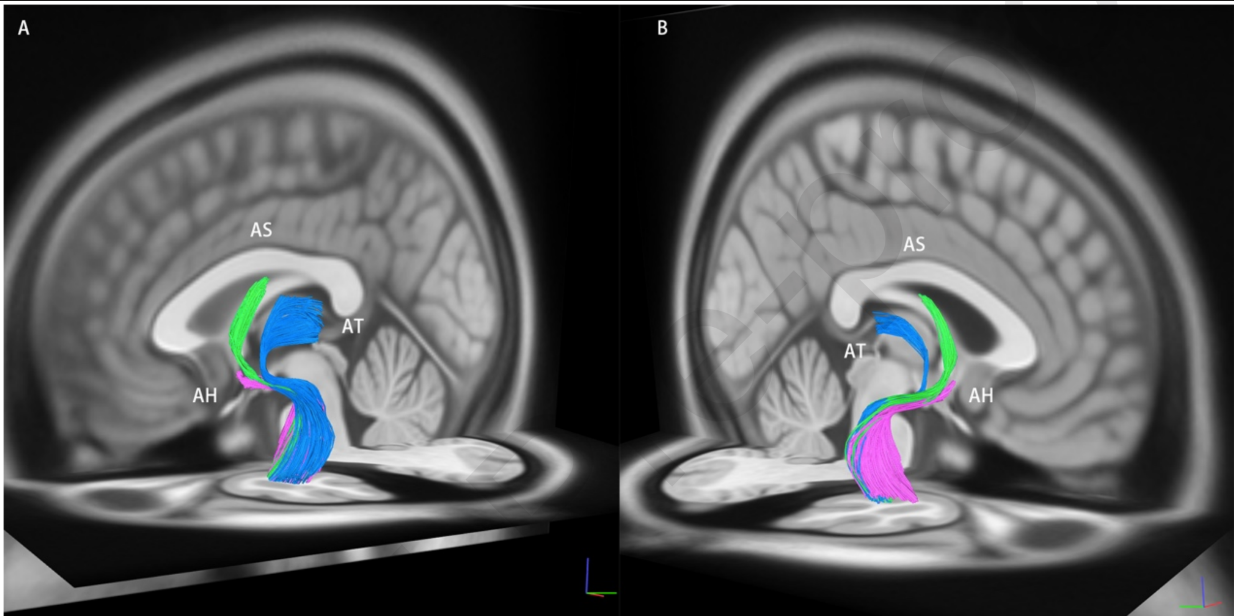
General
- Aka:
- Inferior thalamic peduncle
- Ansa peduncularis
- Part of the subthalamus
- Shaped like the letter "S"
- Located at junction between temporal pole and frontal lobe
- A limbic tract
Segments
- Temporal segment
- Frontal segment
Composed of
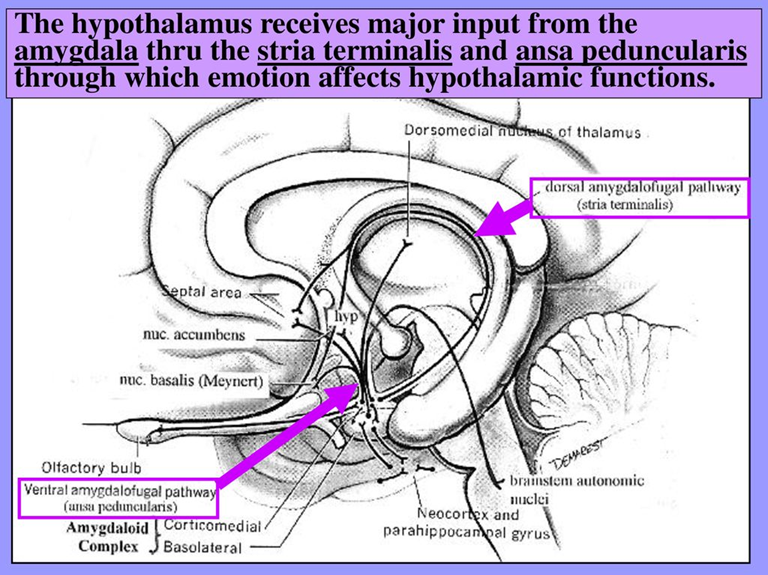
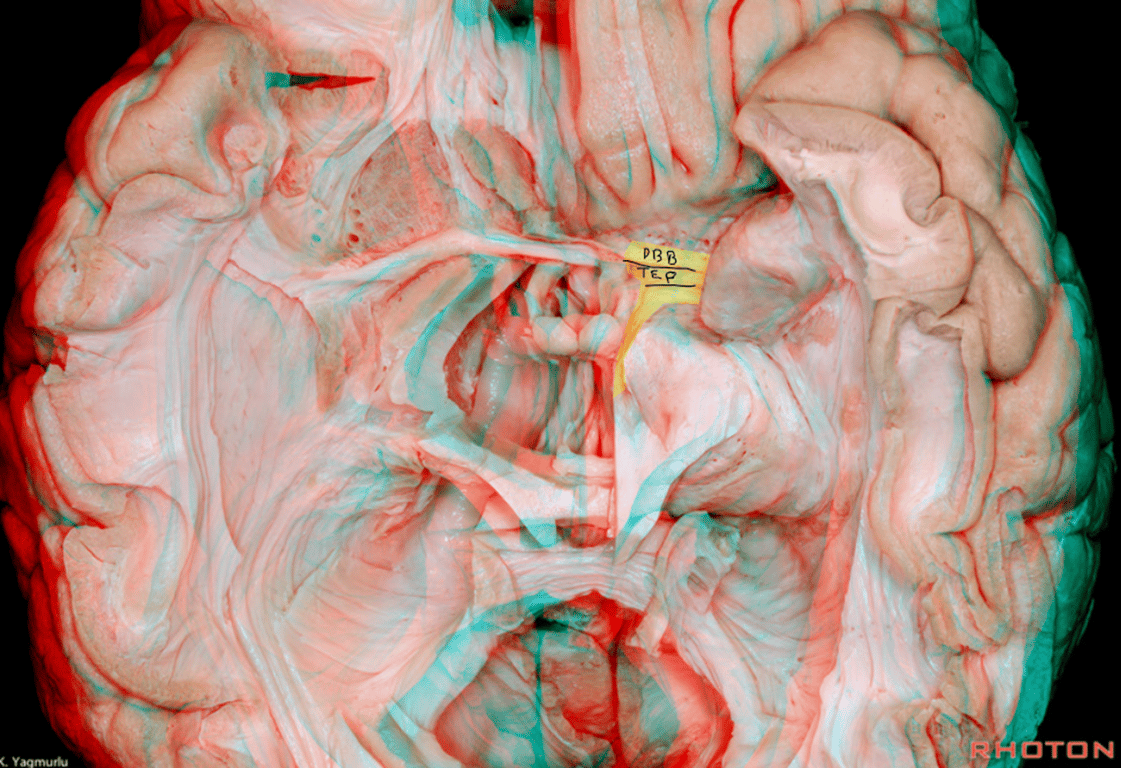
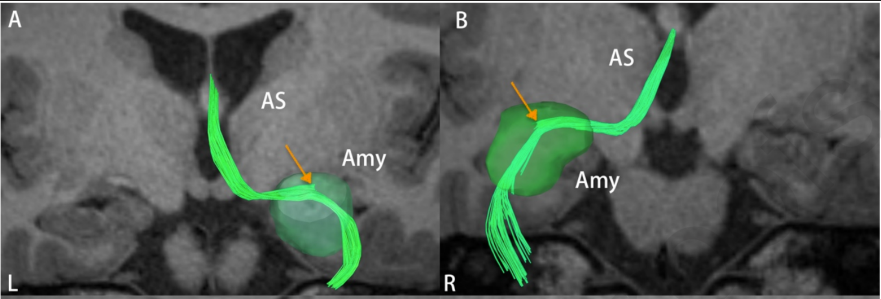
Amygdaloseptal fibres
- Aka: Horizontal limb of the Diagonal band of broca (DBB)
- Connection:
- Amygdala ↔ septal area/nucleus
- Meets the indusium griseum along the medial surface of the nucleus accumbens to form the paraterminal gyrus, which is part of the septal region at the subcallosal area
- Medially, this bundle may continue with the precommissural fornix at the septal region and laterally reach the amygdala and anterior temporal cortex.
- Location:
- Dorsal to the amygdalohypothalamic pathway within the ansa peduncularis
- Fx:
- The amygdala may influence the septal nucleus directly through amygdaloseptal pathway and affect the hypothalamus, midbrain and hippocampus indirectly by the septal nucleus.
Amygdalohypothalamic fibres
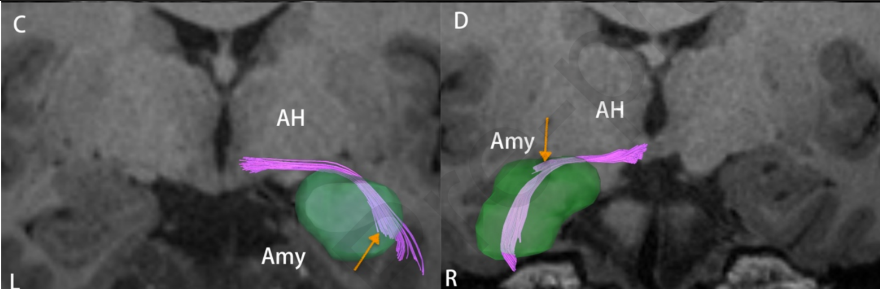
- Connection:
- Amygdala ↔ hypothalamus
- Runs ventrally to the amygdaloseptal pathway and enters the anterior hypothalamus
- Fx
- Amygdala to control the hypothalamus and influence the endocrine function and automatic nervous system indirectly.
Amygdalothalamic fibres
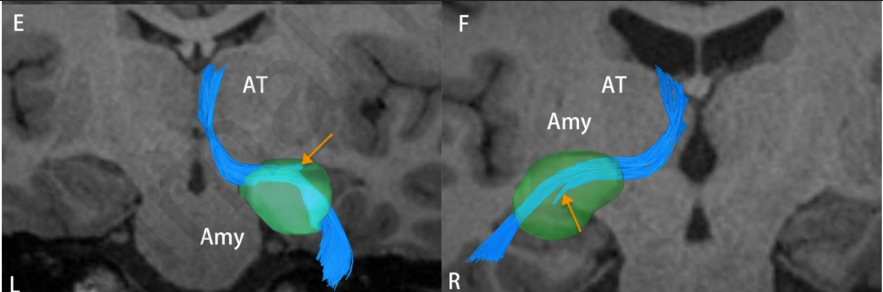
- Aka: medial forebrain bundle
- Inferior thalamic peduncle
- Extracapsular thalamic peduncle
- Connects the anterior temporal cortex + amygdala ↔ medial thalamus ↔ prefrontal and orbitofrontal cortex.
- Relation:
- Posterior to the amygdaloseptal pathway
- Dorsal to the hypothalamuss
- Fx
Connections
- Amygdala → Nucleus accumbens/ Subgenual part of cingulate gyrus/Gyrus rectus
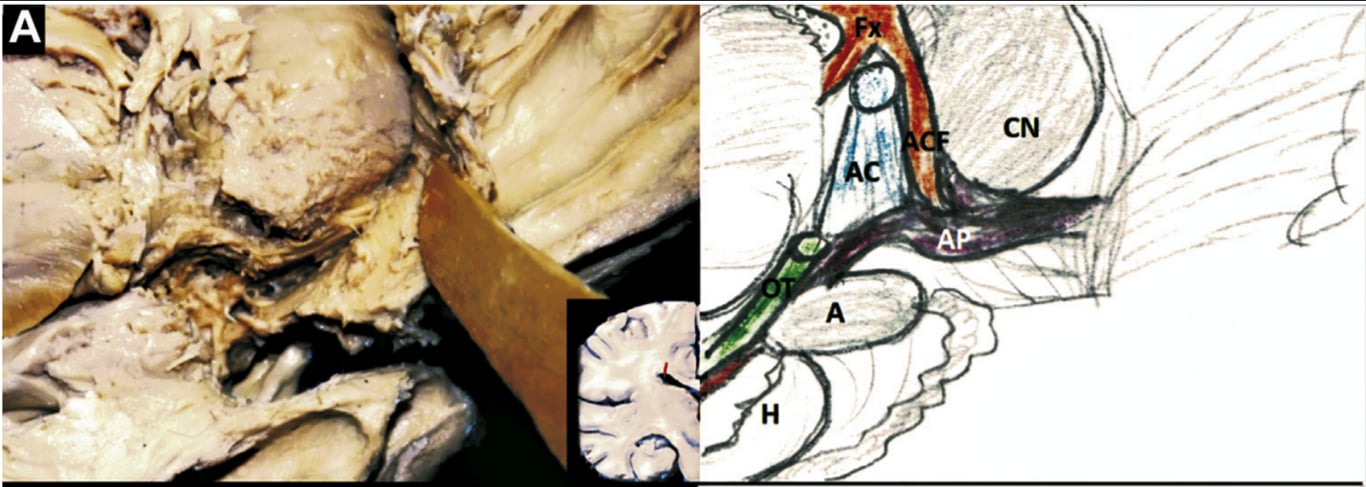
Relations
- Superior:
- Anterior perforating substance
- Inferior:
- Optic tract
- Medially
- Columns of Fx
- Rostrum of corpus callosum
- Laterally
- Caudate nucleus
- Temporal radiations of the uncinate fasciculus
- Anterior commissure
- Have a parallel direction with the anterior commissure and optic tract
- The anterior commissure, which crosses the AP being anterior to the temporal segment and posterior to the frontal segment of AP.
Function
- Multimodal sensory integration
- Behavioural inhibition
Deficits
- Impaired modulation of social behaviour
- Learning and recall deficits