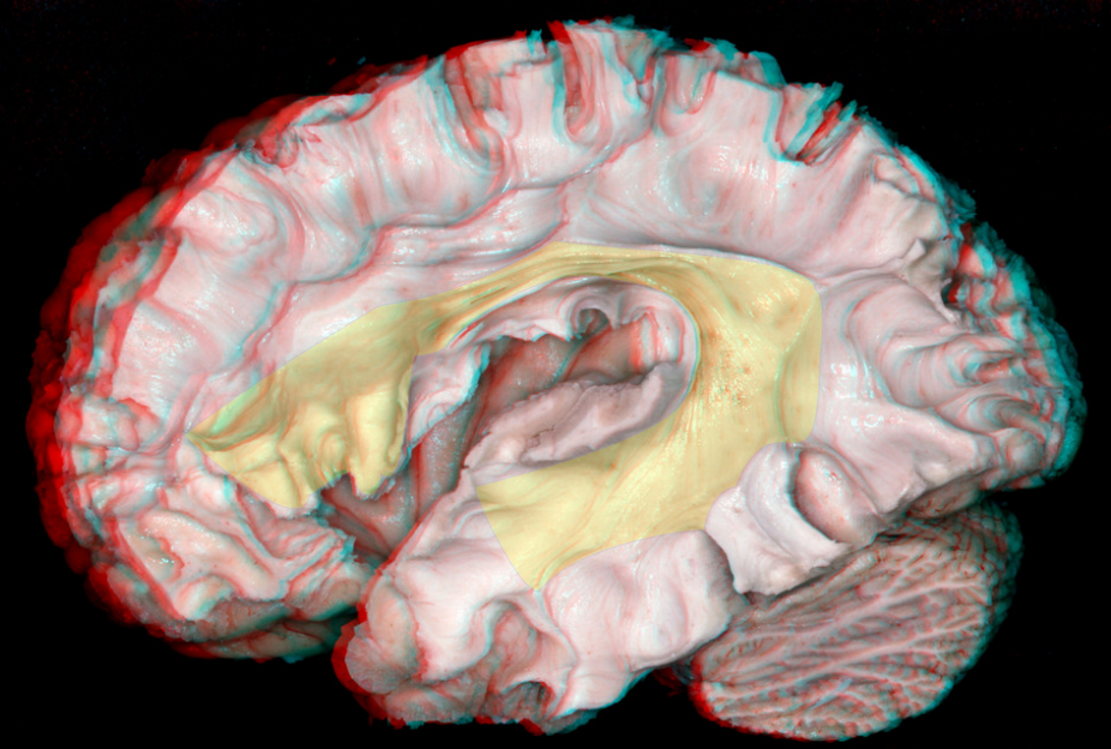
Shape
- Reversed C-shaped structure surrounding the insula
Interconnection
- Lateral frontoparietotemporal connections
- Interconnects the frontal and temporal lobes
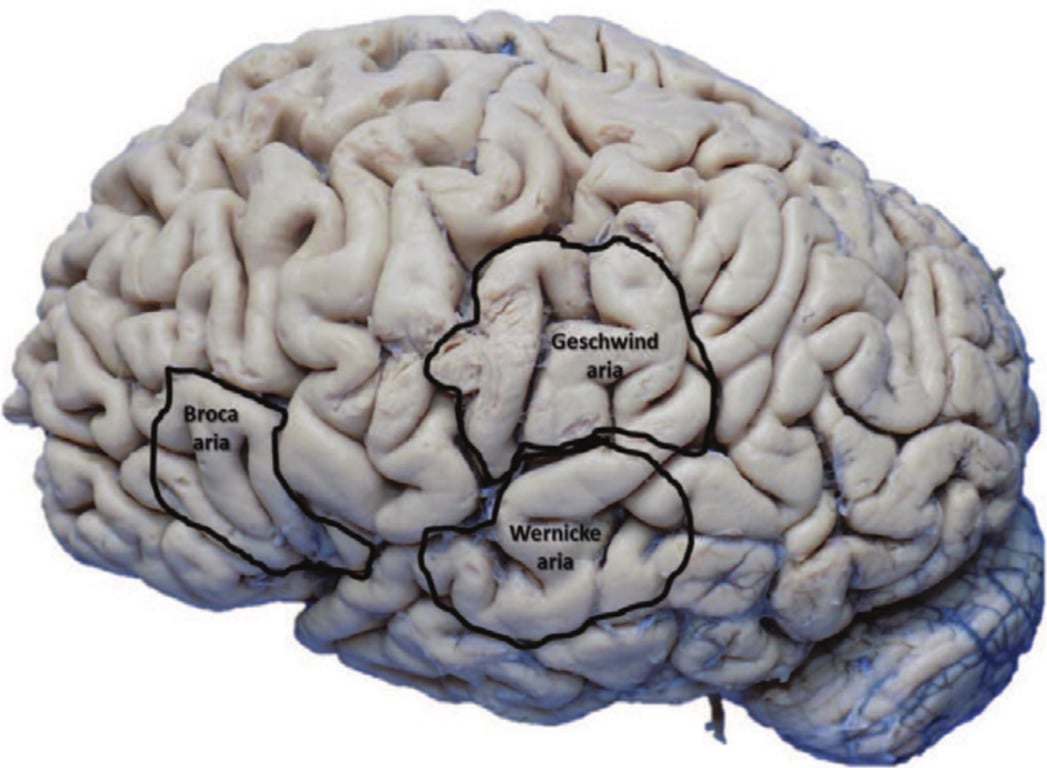
- Connects
- Broca area
- Wernicke area
- Geschwind area
Relations
- Superficial to
- The corona radiata and external capsule
- Deep to
Function
- Non dominant
- Spatial awareness
- Dominant
- Language (repetition)
Segments
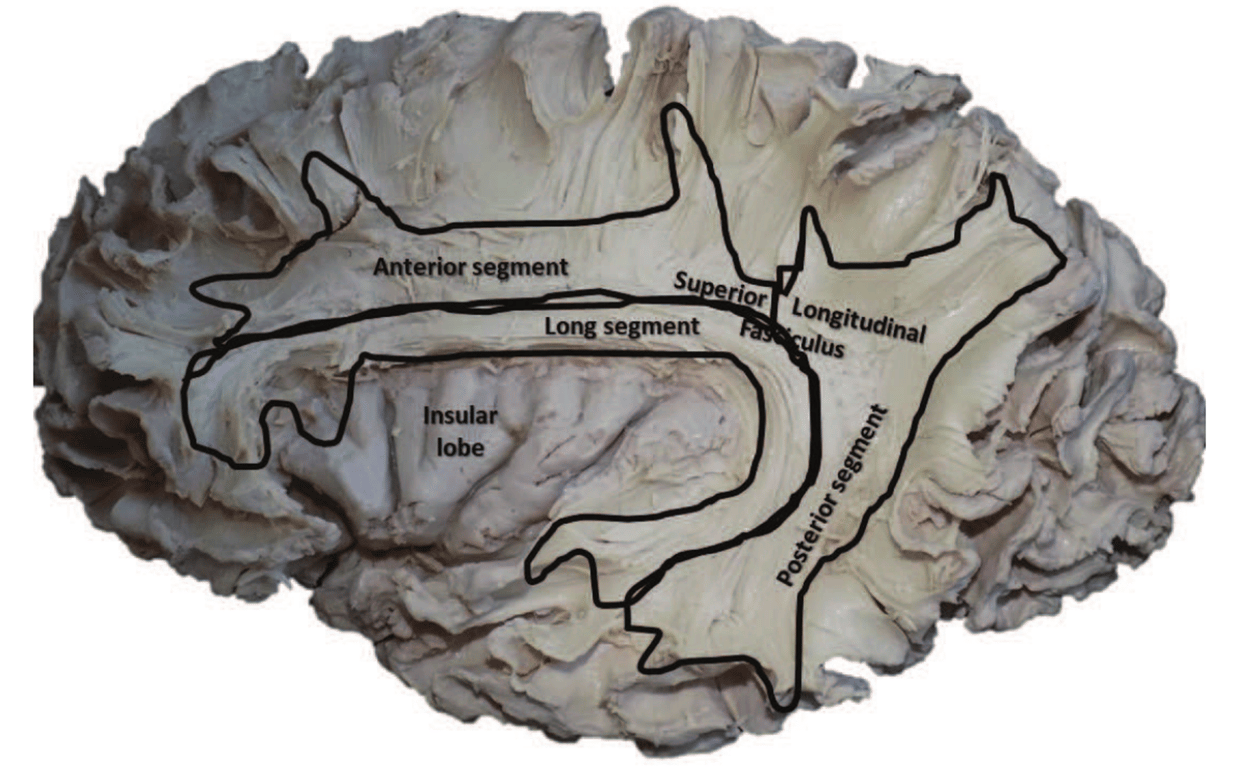
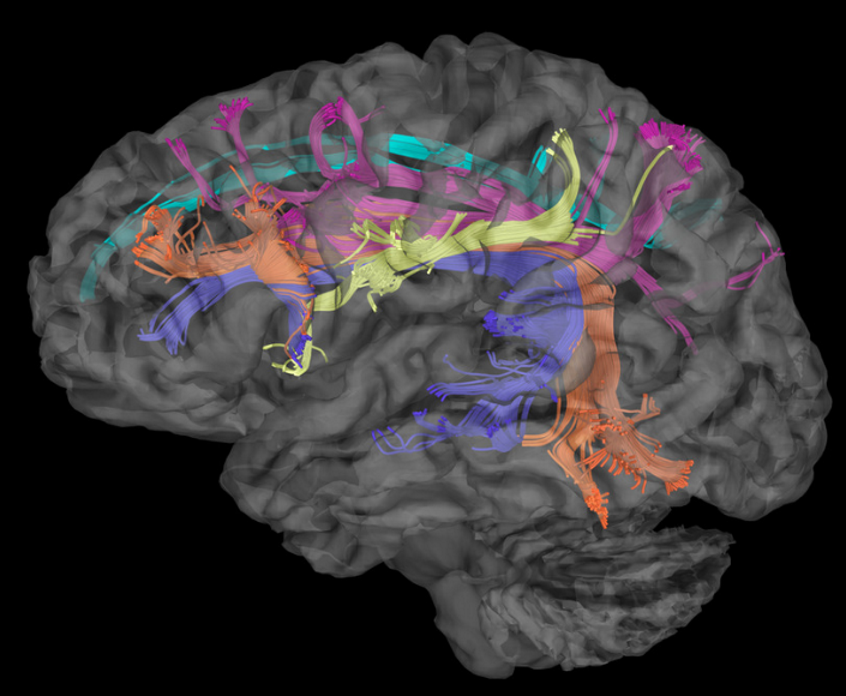
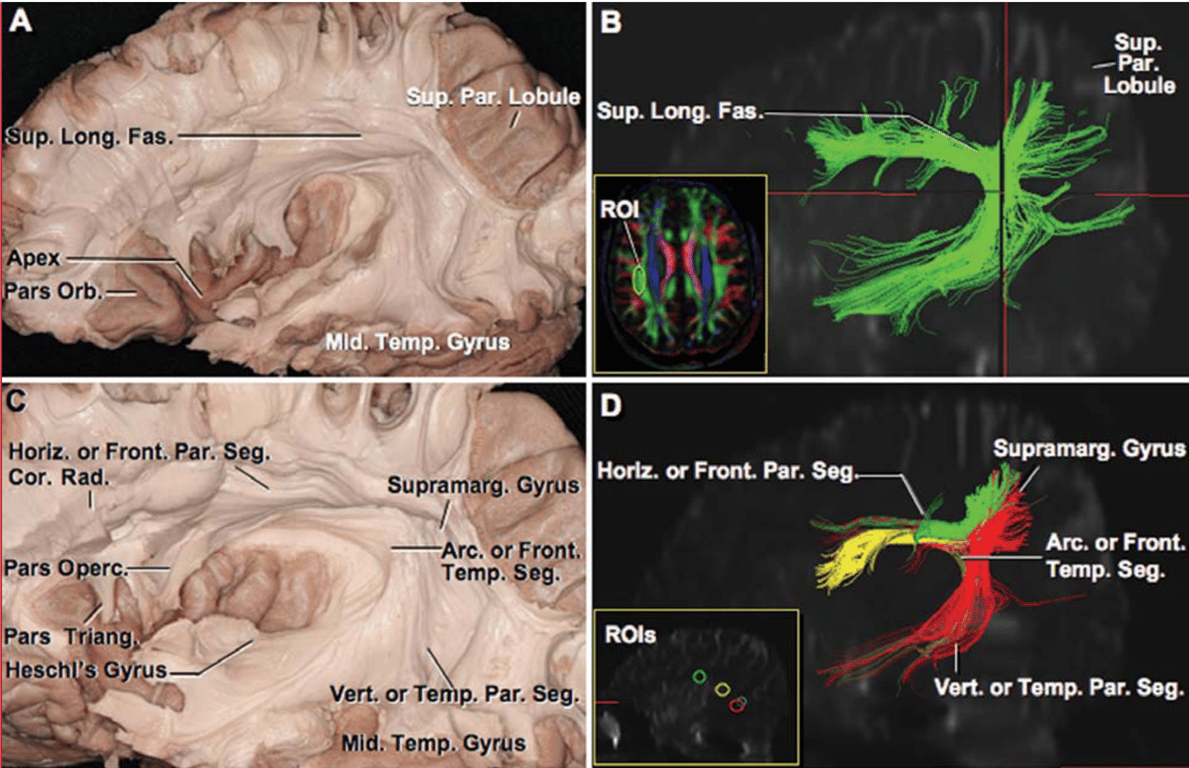
Frontoparietal segments
- Aka
- Horizontal segment
- Anterior segment
- 3 parts
- Courses within the superior bank of the cingulate sulcus
- Just above the cingulum
- Pathway
- Dorsal superior parietal lobe and the medial parietal lobe (precuneus) → through the white matter of the superior parietal and frontal regions → premotor and prefrontal cortex (dorsal parts of areas 6, 8, and 9 and the supplementary motor area)
- Extends from the inferior parietal lobe to the middle frontal gyrus
- Within Middle frontal gyrus
- Pathway
- Posterior portion of the inferior parietal lobe (angular gyrus) → through the central core of the white matter above the superior limiting sulcus of the insula → dorsal premotor and prefrontal regions.
- Medial: Corona radiata
- Within the frontoparietal operculum
- Pathway
- Anterior portion of the inferior parietal lobe (supramarginal gyrus) → through the opercular white matter of the parietal and frontal lobes → ventral premotor and prefrontal cortex (Broca’ s territory)
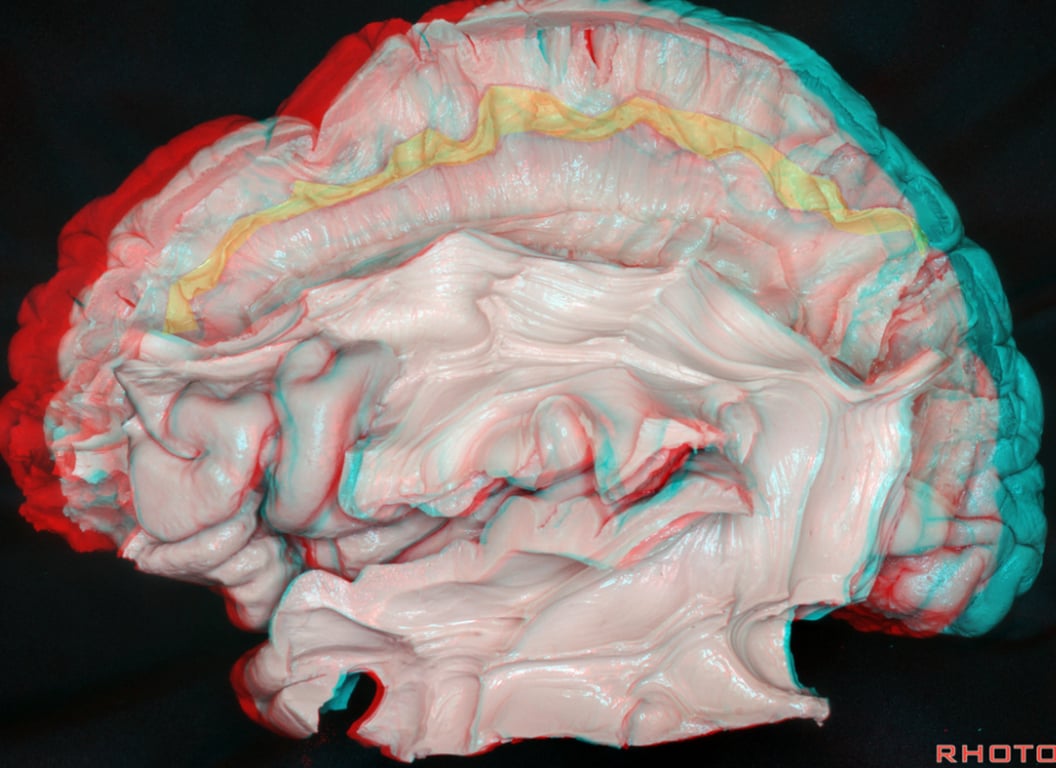
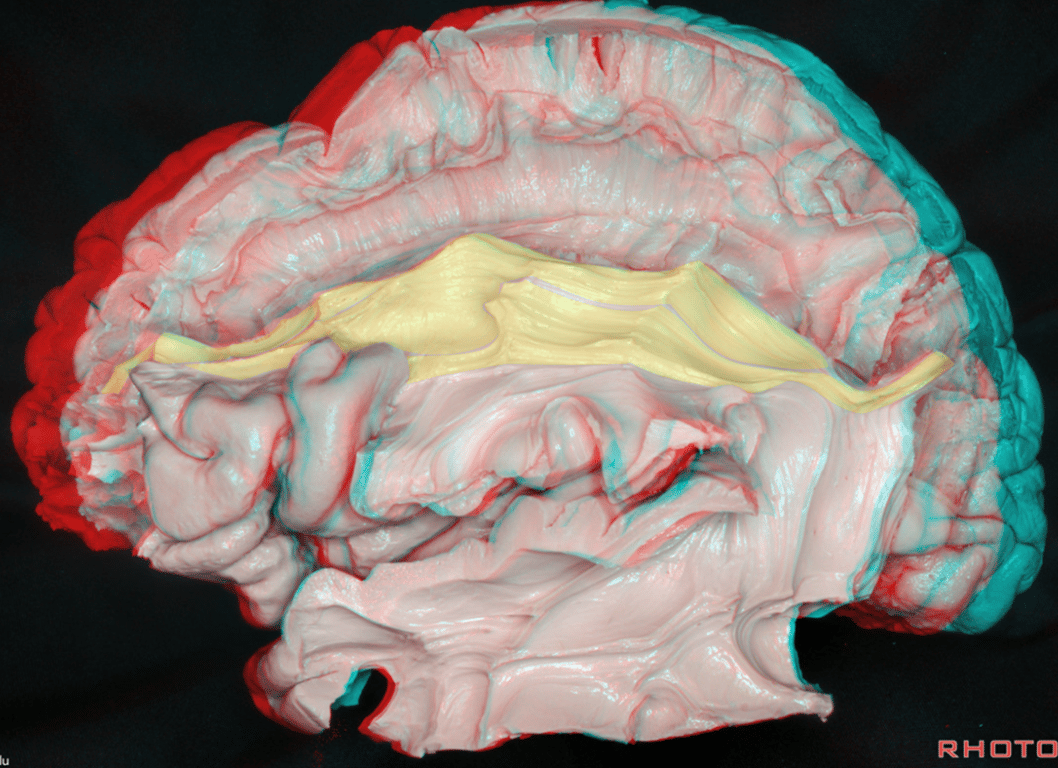
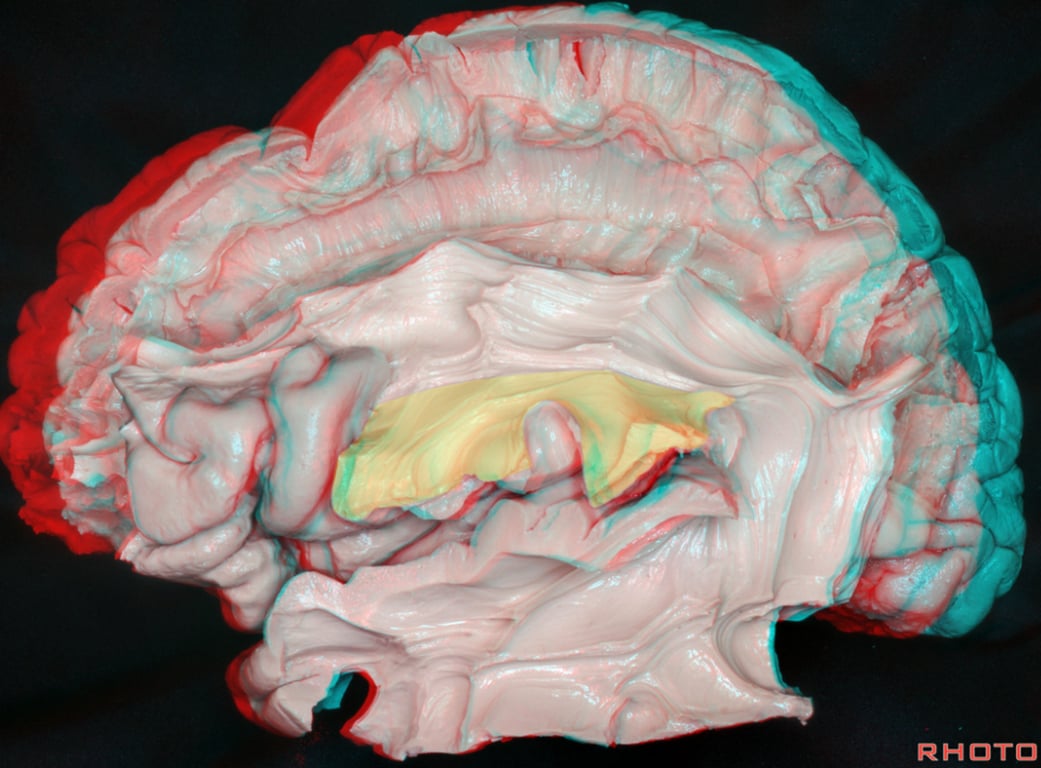
- Function a high order multisensory associative system → deficits
- Rt hemisphere: Visual spatial processing → Left spatial hemineglect
- Lt hemisphere: Dorsal phonological pathway (motor language) → Phonological apraxia
Temporoparietal segment
- Aka
- Vertical segment
- Posterior segment
- Craniocaudally orientated
- Runs parallel and lateral to arcuate fasciculus
- Pathway
- Posterior part of the superior and middle temporal gyrus (wernicke's area) → Inferior parietal lobe
- Function → deficits
- Audiospatial processing → vestibular symptoms
- Sensitive language (auditory comprehension) → sensitive aphasia
Frontotemporal segment
- Aka
- Arcuate segment
- Arcuate fasciculus
- Long segment
- Two parts
- Originates
- Wernicke's area (posterior parts of the superior, middle and inferior temporal gyri)
- Arches around the caudal end of the Sylvian fissure, running within the white matter of the parietal and frontal operculi
- Runs
- Parallel and medial to the two other SLF tracts
- Lateral to the corticospinal tract
- Terminates (controversial)
- Precentral gyrus
- Broca's areas (Posterior two-thirds of the inferior frontal gyrus) composed of
- Pars opercularis
- Pars triangularis
- Function → deficits
- Visu-audio spatial → Vestibular symptoms (?)
- Repetition → conductive aphasia
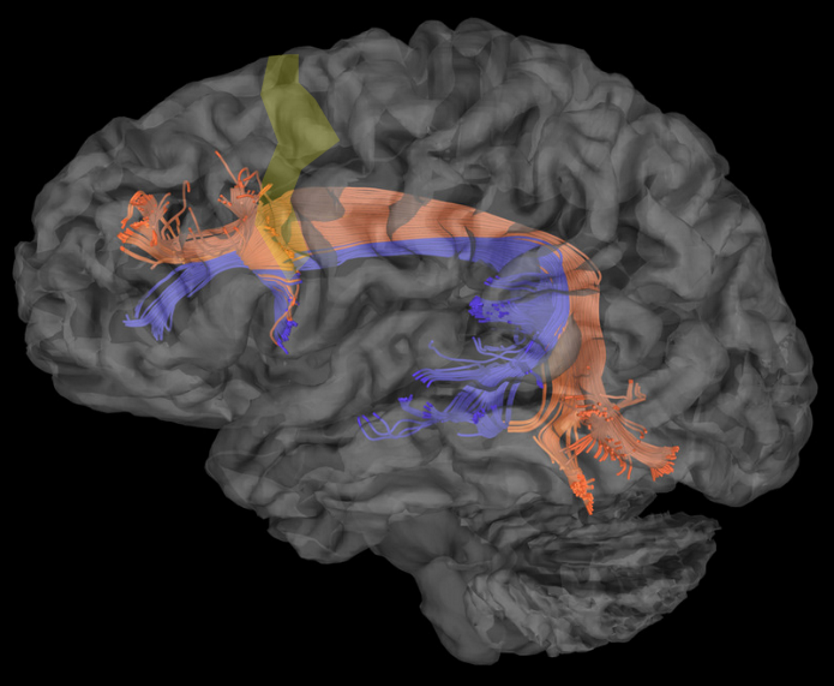
Clinical
Segment of SLF | Functional Role | Disconnection Syndrome |
Frontoparietal segment | Visuospatial processing | Left spatial hemineglect |
ㅤ | Dorsal phonological pathway (motor language) | Phonological apraxia |
Temporoparietal segment | Audiospatial processing | Vestibular symptoms |
ㅤ | Sensitive language (auditory comprehension) | Sensitive aphasia |
Frontotemporal or arcuate segment | Visu-audiospatial (?) | Vestibular symptoms (?) |
ㅤ | Repetition | Conductive aphasia |
Images