Type of fasciculus | Name | Interconnected regions |
Association | Lateral frontoparietotemporal | |
ㅤ | Temporo-occipital | |
ㅤ | Fronto-orbital/temporomesial | |
ㅤ | Frontotemporal-(?) occipital | |
ㅤ | Medial frontoparietotemporal | |
Projection | Corticopontospinal and thalamocortical | |
ㅤ | Sagittal stratum | Thalamotemporoparieto-occipital |
ㅤ | Dorsal external capsule | Claustrocortical |
Commissural | Anterior commissure | Inferotemporal and occipital bilateral |
ㅤ | Corpus callosum—body, forceps major and minor | Frontoparietotemporo-occipital bilateral |
Association tracts
- Connects cortical areas located on the same hemisphere
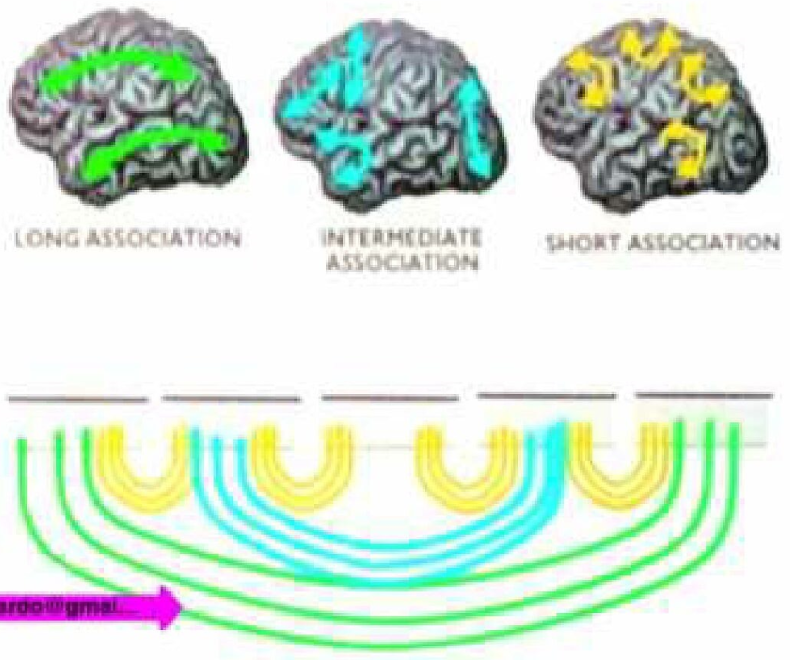
- According to their size
- Short association fibres
- U shaped
- Connects adjacent gyri
- Most superficially located
- Just under cortex
- Long association fibres
- Connects between lobes
- Classification by
- Shape
- Cingulum
- Uncinate fasciculus
- Location
- Superior longitudinal fasciculus
- Inferior longitudinal fasciculus
Projection tracts
- Connects cerebral cortex with
- Subcortical grey matter
- Basal ganglia
- Thalamus
- Brain stem nuclei
- Cerebellar cortex
- Cerebellar nuclei
- Spinal cord
- 2 functional types of fibres
- Efferent
- Afferent
- 2 anatomical types of fibers
- Frontoparietal projection fibres
- Corona radiata:
- Made up from
- Internal capsule
- External capsule
- Medial to the Superior longitudinal fasciculus
- Occipital projection fibres
- Sagittal stratum
- Medial to the
- IFOF
- Inferior longitudinal fasciculus
- Occipital extension of the Posterior limb of the anterior commissure
Commissural tract (crosses midline)
- Corpus callosum
- Anterior commissure
- Fornix
Function of white matter tracts
Function | Cortical Areas | Subcortical Pathways |
Motor function | Central region, SMA, premotor cortex | Pyramidal pathways (corona radiata, internal capsule, mesencephalic peduncles) |
Somatosensory | Central region (primary and secondary somatosensory areas), insula | Thalamocortical pathways |
Oral language | Ventral semantic stream: Posterior temporal regions, orbitofrontal and dorsolateral prefrontal areas (dorsal and ventral) | Inferior occipitofrontal fasciculus |
Oral language | Dorsal phonological stream: Posterosuperior temporal cortex, inferior frontal gyrus | Direct SLF (arcuate fasciculus) Indirect SLF III (lateral, anterior) |
Oral language | Articulatory loop: Supramarginalis gyrus, ventral premotor cortex | Operculo-insular fibers, descending pathways from the ventral premotor cortex, pyramidal tract and lentiform nucleus |
Oral language | Speech production: Dominant anterior insula (articulatory planning), ventral premotor cortex, primary sensorimotor area of the mouth | ㅤ |
Writing | Inferior and superior parietal lobules, insula, second and third frontal convolutions, SMA | SLF |
Reading | Visual cortex, visual object (word) form area | Inferior longitudinal fasciculus |
Visuospatial cognition | Visual: Temporo-parieto-occipital junction, visual cortex | Right radiations |
Visuospatial cognition | Spatial awareness: Right supramarginal gyrus, right superior temporal cortex | Right SLF |
Visuospatial cognition | Vestibular: Right inferior parietal cortex, posterior insula, superior temporal cortex | Right SLF |
Higher cognitive/executive functions | Language switching: Left inferior frontal gyrus, posterosuperior temporal area | SLF |
Higher cognitive/executive functions | Working memory: Inferior frontal gyrus, dorsal premotor cortex, supramarginal gyrus | SLF |
Higher cognitive/executive functions | Syntactic processing: Left inferior frontal gyrus, left superior temporal gyrus | SLF |
Higher cognitive/executive functions | Judgment, decision making, understanding: Left dominant prefrontal cortex, left posterior temporal cortex | Inferior occipitofrontal fasciculus |
Higher cognitive/executive functions | Selection, inhibition, attention: SMA, cingulum, frontal eye fields | Subcallosal medialis fasciculus, head of the caudate nucleus |