General
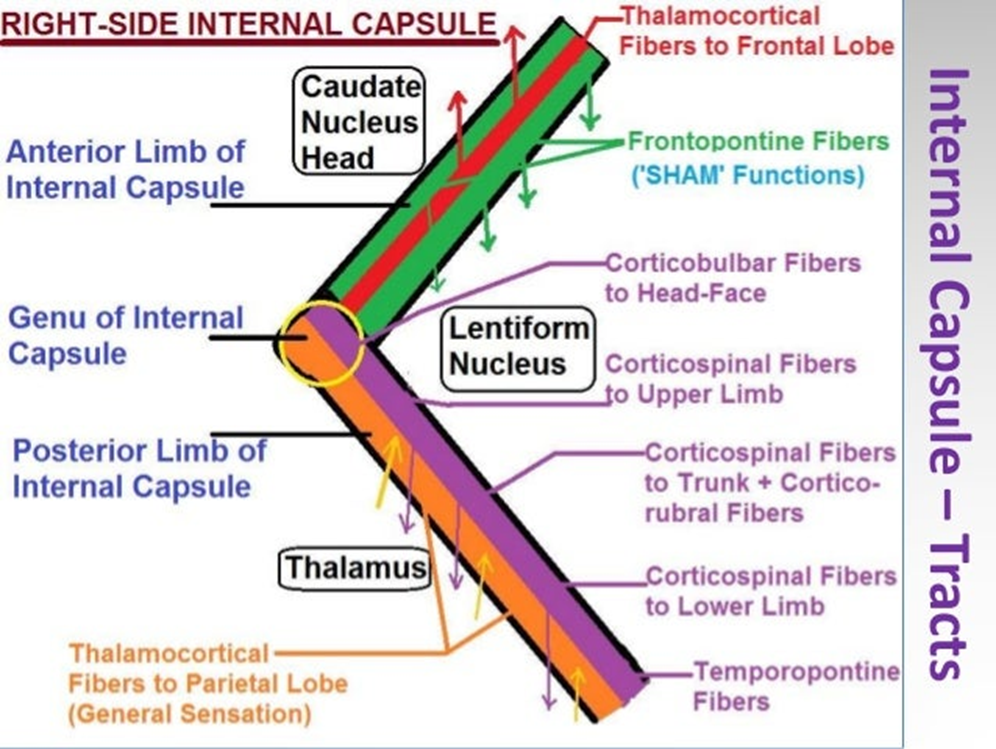
- Most important projection fibre
Composed
- Corticopontospinal fibres
- Thalamocortical fibre
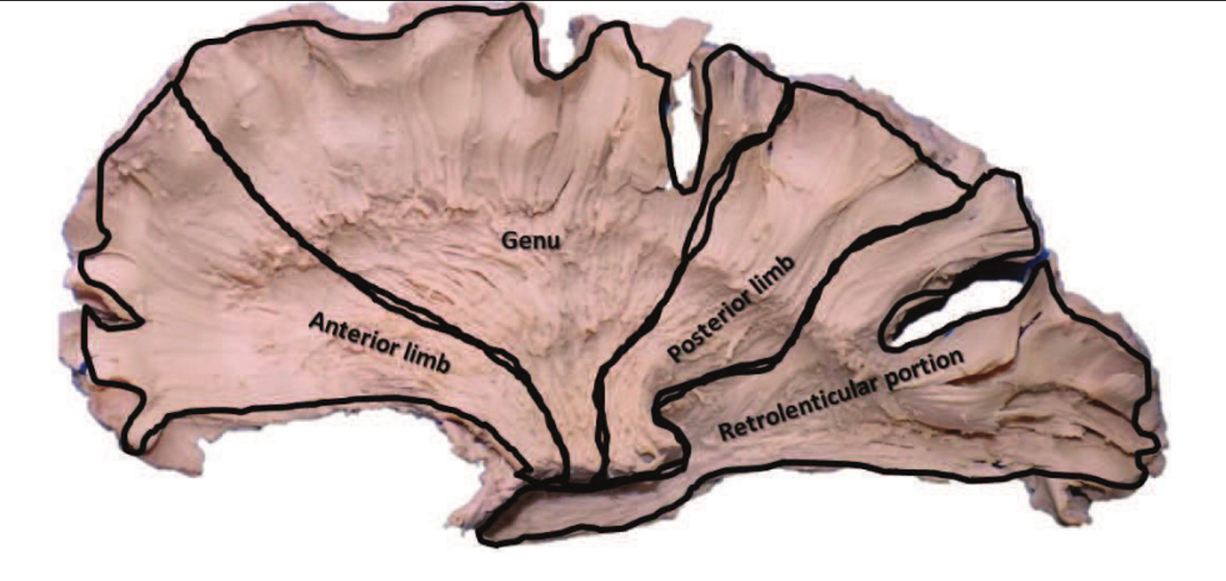
5 topographical portions
Anterior limb
- contains
- frontopontine fibres
- Anterior thalamic peduncle
- Blood supply
- Superior portion
- lenticulostriate branches of the middle cerebral artery,
- Inferior portion
- the recurrent artery of Heubner, a branch of the anterior cerebral artery
- Function
- Associated with different aspects of emotion, motivation, cognition processing, and decision-making.
Genu
- Corticonuclear fibres
- Thalamoprecentral fibres
Posterior limb
- Superior thalamic peduncle
- Corticospinal
- Corticopontione
- Cortoctegmental fibres
Retrolentiform components
- Parietopontine fibers:
- The acoustic radiation from the medial geniculate body to the superior temporal and transverse temporal gyri, and fibers connecting the thalamus with the temporal lobe and insula.
- Occipitopontine fibers
- Occipitocollicular fibers
- Occipitotectal fibers
- Posterior thalamic radiation
- Optic radiation
- Most important neurosurgical connection
- Roof of temporal horn as a lateral extension of the thalamus
- Starts from lateral geniculate body → occipital lobe
- Can be damaged if you enter the temporal horn from the roof in the transslyvian approach or in standard temporal lobectomy
- The roof of the temporal horn should not be removed too medially because of the risk of damaging the thalamus
- Interconnections between the occipital and parietal lobes and caudal parts of the thalamus
Sublentiform components
- Temporopontine fibers
- Meyer's loop
- Parietopontine fibers:
- The acoustic radiation from the medial geniculate body to the superior temporal and transverse temporal gyri, and fibers connecting the thalamus with the temporal lobe and insula.
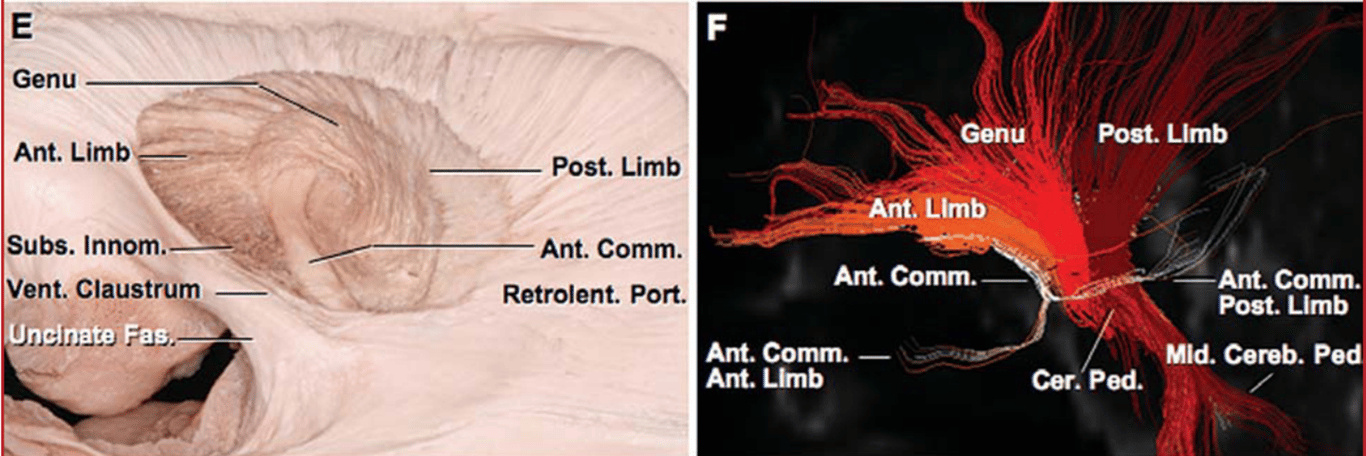
Relations
- Medial:
- Rostrally
- Caudate nuclei
- Retrolenticular portion
- Thalamus
- Occipital horn
- Lateral:
- Lentiformis nucleus
- Inferior occipitofrontal fasciculus
- External capsule
- Superior longitudianl fasciculus
- Anteriorly
- Anterior commissure
- Nucleus accumbens
- Posteriorly
- Arcuate fibres of occipital lobe
- Superiorly
- Cerebral cortex and the short association fibres
- Inferiorly
- Root of the internal capsule is at the cerebral peduncle
- Brainstem nuclei and fascicles
- Corpus callosum intersection area:
- Where the internal capsule fibres intersect with the horizontally crossing corpus callosum fibres
Function
- Sensitive pathways
- Auditive pathway
- Visual pathway
- Motor system
Deficit
- Hypo/anesthesia
- Deafness
- Visual field defects
- Paresis/paralysis
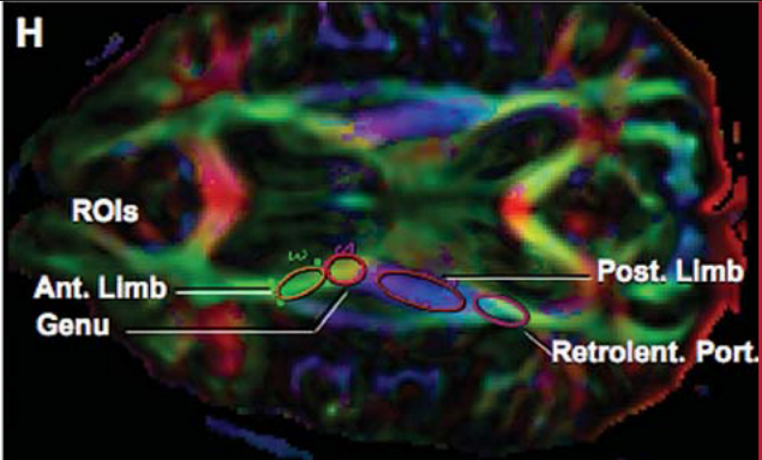
Images
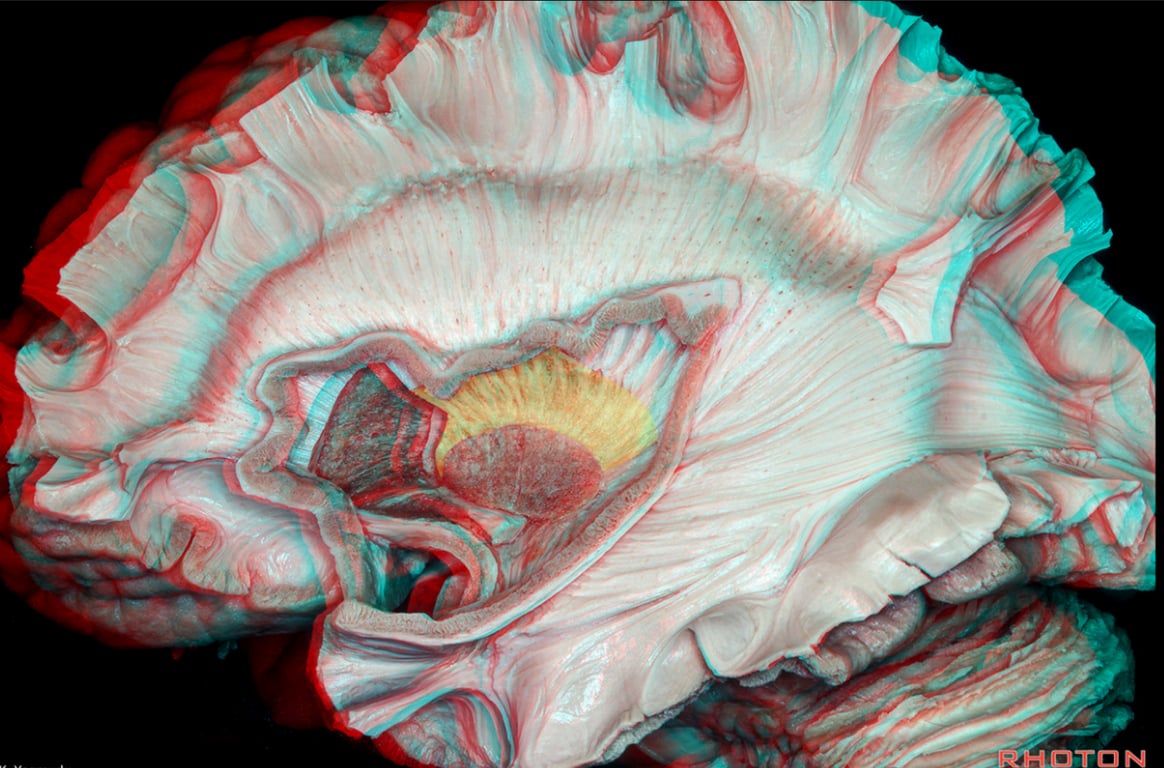
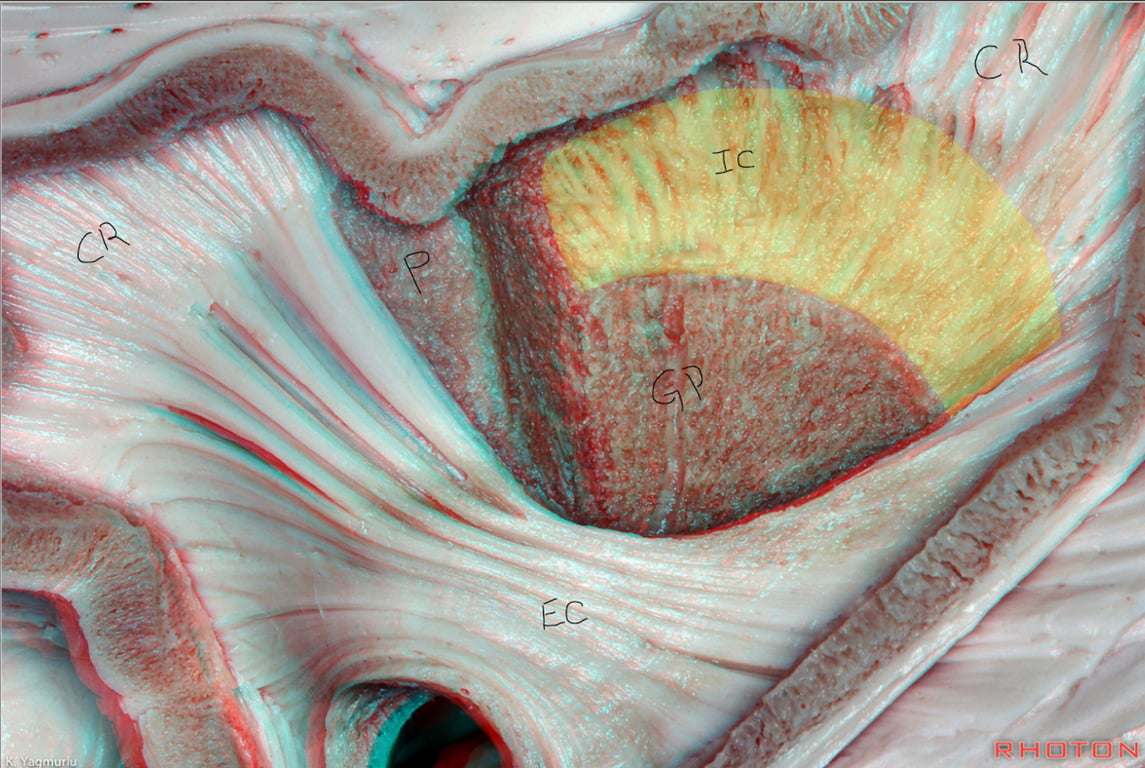
IC: internal capsule
EX: External capsulee
CR: Corona Radiata
GP: Globus pallidus
P: Putamen
EX: External capsulee
CR: Corona Radiata
GP: Globus pallidus
P: Putamen
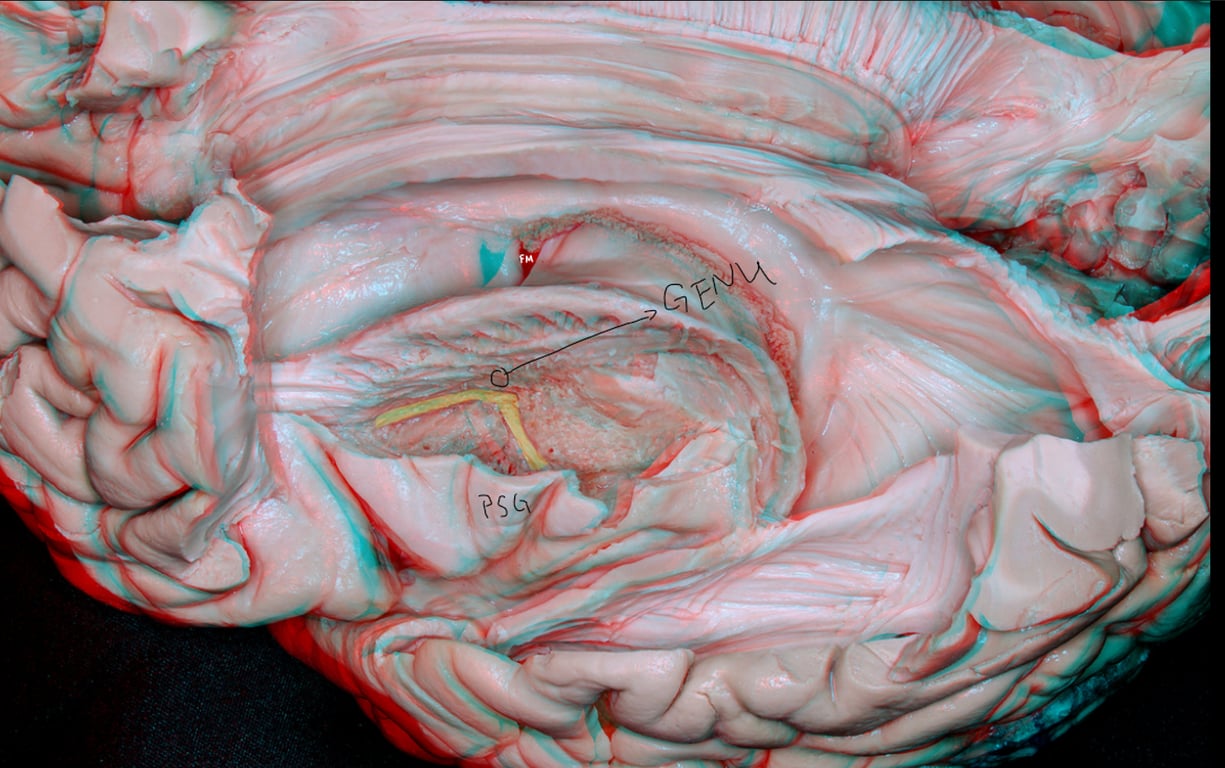
Genu of internal capsule
- Same coronal plane level as
- posterior short gyrus of insula (PSG),
- Foramen Magnum (FM)
- Behind: Ant. Commissure (yellow),
- Splenium of the corpus callosum
- Head of the caudate nucleus
- Thalamus
- Genu of the internal capsule
- Anterior limb of the internal capsule
- Posterior limb of the internal capsule
- Calcar avis
- Glomus (choroid plexus)
- Retrolentiform part of the internal capsule
- Lentiform nucleus
- Collateral trigone
- Sublentiform part of the internal capsule and roof of the temporal horn