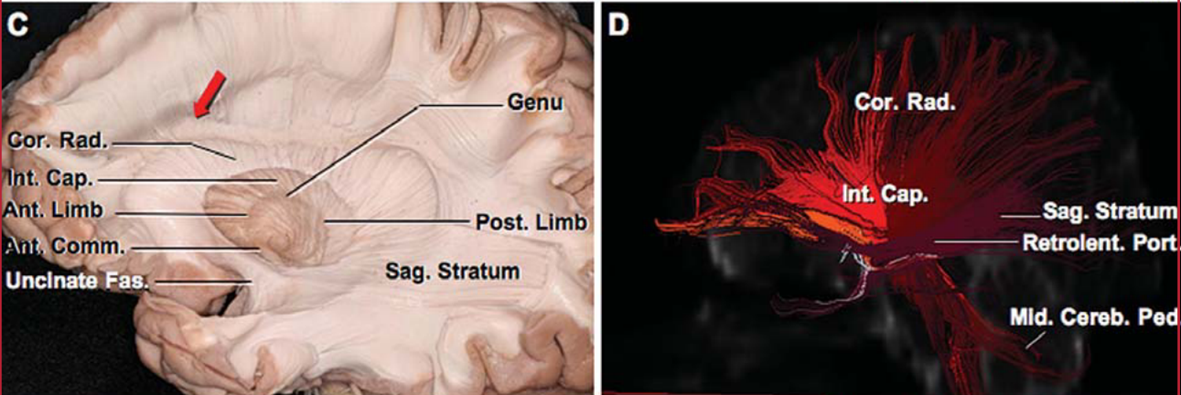
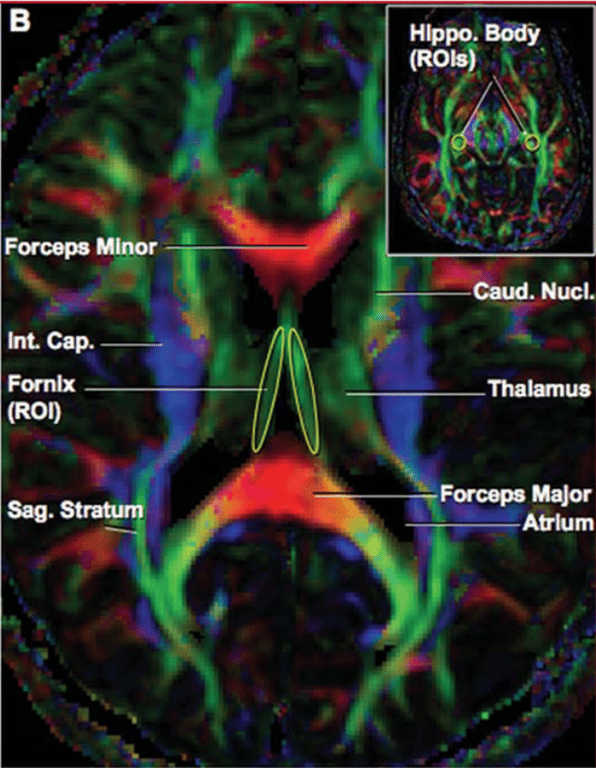
General
- A complex of sagittal fascicles
- Horizontally orientated
- Forms lateral wall of temporal horn of lateral ventricles
- A region of important cross road of major white matter tracts
Composed of
- Occipital pontine fibres
- Occipital thalamic fibres (optic radiations)
3 layers
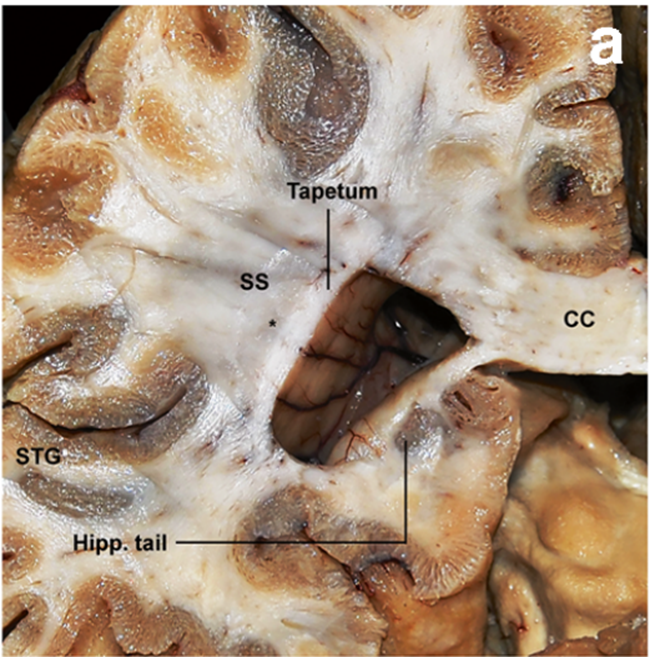
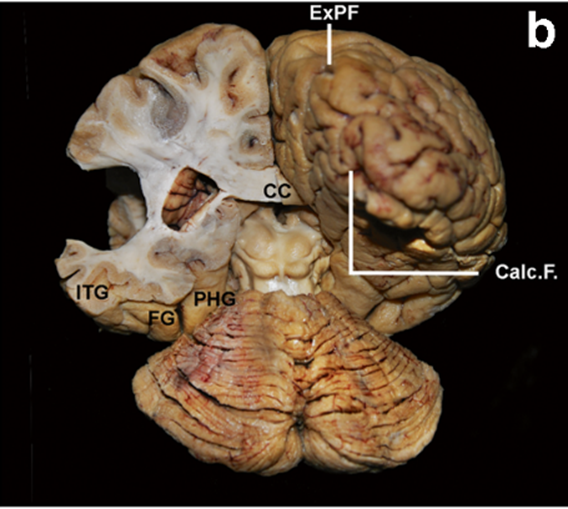
Hipp. Tail: hippocampal tail
SS: Sagittal stratum
CC: corpus callosum
ITG: inferior temporal gyrus
FG: fusiform gyrus
PHG: parahippocampal gyrus
ExPF: external perpendicular fissure
That space is the occipital horn
- At the level of the lateral wall of the atrium showing the three layers of the Sagittal stratum (SS)
- Superficial layer:
- Middle longitudinal fascicle (MdlF)
- Originate: Anterior 1/3 Superior temporal gyrus --> runs under the transverse temporal gyri in a caudocranial and lateromedial direction + passes below arcuate fasciculus of the SLF --> terminate: inferior parietal lobule (IPL)
- Inferior longitudinal fascicle (ILF)
- Connection
- occipital lobe --> anterior temporal region
- See previous
- Middle layer:
- Inferior fronto-occipital fascicle (IFOF)
- See previous
- Deep layer:
- Anterior commissure (AC):
- Yellow spots intermingling with blue (showing a mixture of the two tracts)
- See previous
- Optic radiation (OR) - Posterior thalamic peduncle
- Origin: lateral geniculate body as part of the posterior thalamic peduncle.
- Courses:
- posteriorly together with the auditory radiations, temporal and occipital projections (here at the lateral geniculate body) cannot be differentiated
- Anterior portion of the OR follows an anterolateral direction along the roof of the temporal horn, shifting backwards in a posterolateral course, forming the Meyer’s loop
- Termination: along the calcarine fissure and the lateral aspect of the occipital lobe
- Relationship
- Inferior: temporal horn
- Medial:
- Atrium
- Occipital horn
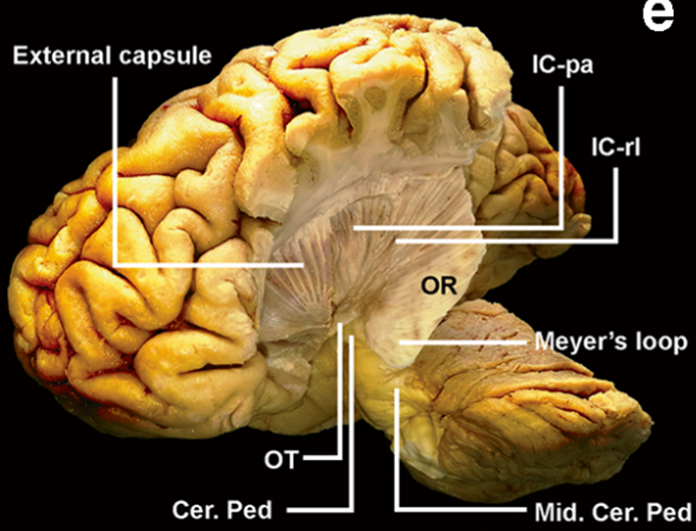
OT: optic tract
IC-PA: internal capsule posterior arm
IC-RL: internal capsule retrolenticular portion
Cer Ped: cerebral peduncle
Mid Cer Ped: middle cerebellar peduncle
Relations
- Anteriorly
- inferior limiting sulcus of the insula
- Superiorly
- Corona radiata
- Inferiorly
- Dorsolateral occipital segment of the ILF
- Medially
- Temporal horn
- Occipital horn
- Atrium of lateral ventricle
- Lateral
- IFOF
- ILF
- Occipital extension of the anterior commissure
- Arcuate fasciculus of the Superior Longitudinal Fasciculus: which is lateral to all 3
- Posteroinferiorly
- Vertical occipital fascicle
Function
- Verbal and non verbal language processing
- Reading and visual recognition
- Visual information
Deficit
- Language impairment (IFOF)
- Semantic paraphasia
- Rt IFOF (non dominant) is involved in non-verbal semantic processing and facebased mentalizing
- Reading impairment and visual agnosia (ILF)
- visuospatial processing, and it has a main role in face recognition and visual memory
- language-processing deficits (MdlF)
Images
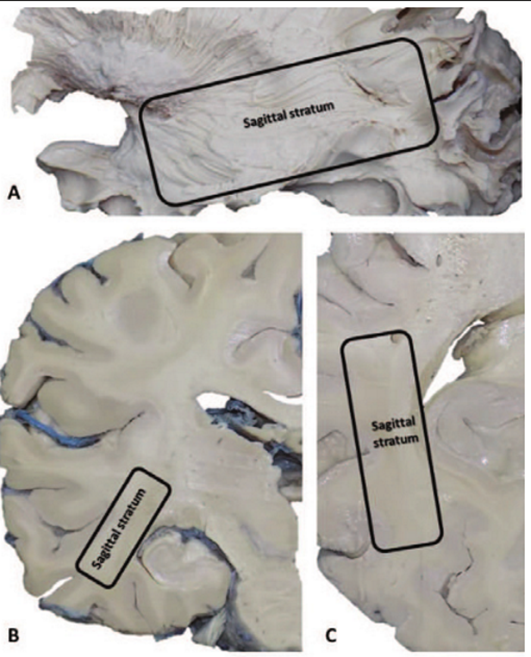
A) Lateral view
B) Coronal plane
C) Transverse plane
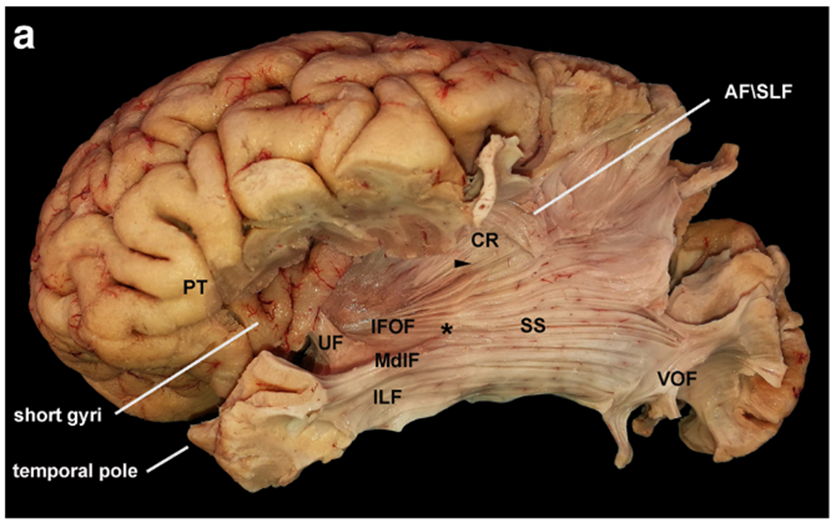
- The frontoparietal operculum and long gyri of the insula were removed to expose the IFOF at the level of the temporal stem.
- The image shows the intersection between the MdlF and the IFOF (*) posteriorly to the inferior limiting sulcus of the insula.
- This point is the anterior limit of the SS.
- The dorsolateral occipital segment of the ILF originates from the anterior temporal region and is the inferior portion of the SS.
- Postero-inferiorly, the VOF intersects the stratum before its cortical termination into the occipital cortex. Superiorly, the SS is contiguous to the corona radiata at the level of the posterior insular point (arrowhead), and it runs below the AF\SLF complex directed to the posterior aspect of the parietal lobe
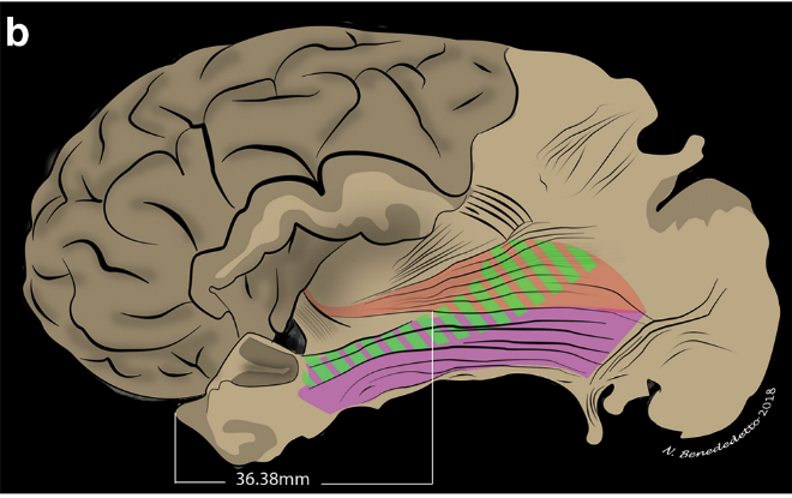
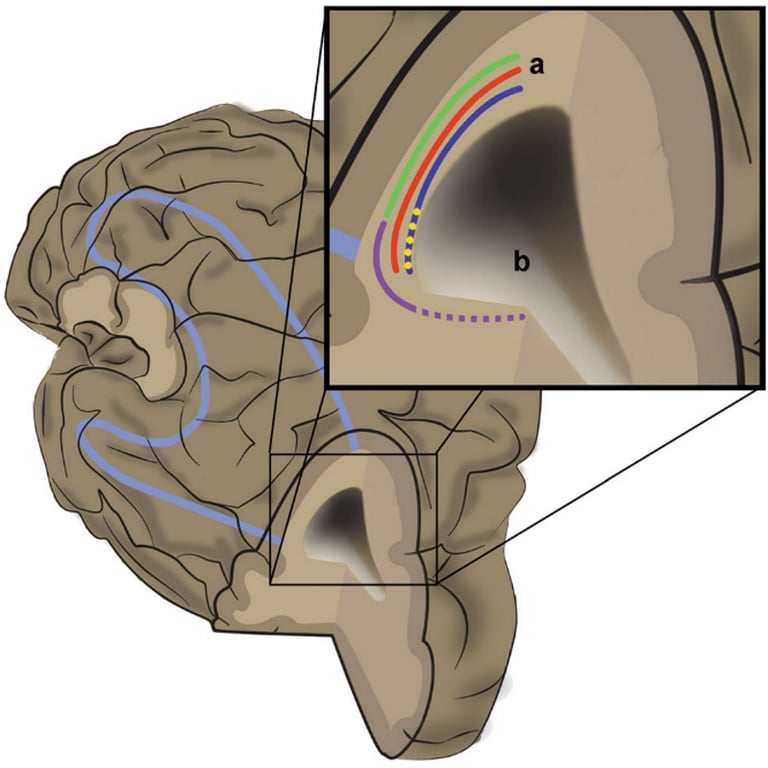
Schematic representation of the anterior limit of the stratum:
- the IFOF and the MdlF cross each other at the mean distance of 36.38 mm from the temporal pole (*).
- The dorsolateral occipital portion of the ILF and the MdlF is partially overlapped.
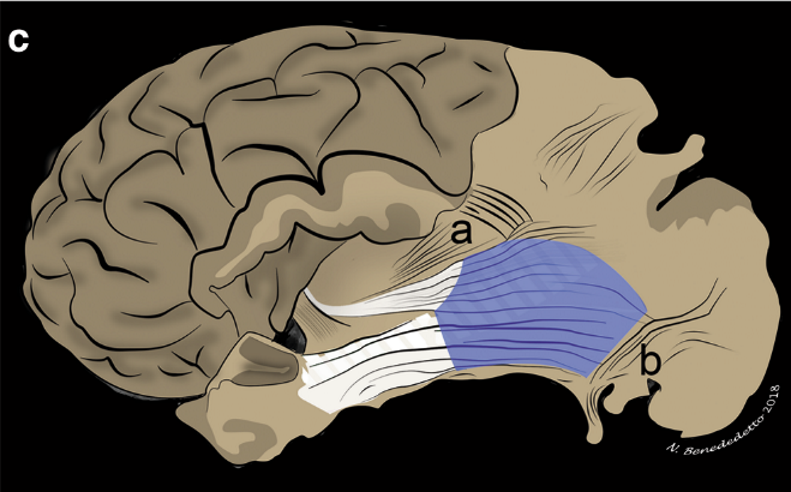
The SS presents a polygonal shape and is limited by the corona radiata (a) superiorly and the VOF (b) posteroinferiorly.
Keys:
AF, arcuate fascicle;
CR, corona radiata;
IFOF, inferior fronto-occipital fascicle;
ILF, inferior longitudinal fascicle;
MdlF, middle longitudinal fascicle;
Pip, posterior insular point;
PT, pars triangularis;
SLF, superior longitudinal fascicle;
SS, sagittal stratum;
UF, uncinated fascicle;
VOF, vertical occipital fascicle.
CR, corona radiata;
IFOF, inferior fronto-occipital fascicle;
ILF, inferior longitudinal fascicle;
MdlF, middle longitudinal fascicle;
Pip, posterior insular point;
PT, pars triangularis;
SLF, superior longitudinal fascicle;
SS, sagittal stratum;
UF, uncinated fascicle;
VOF, vertical occipital fascicle.
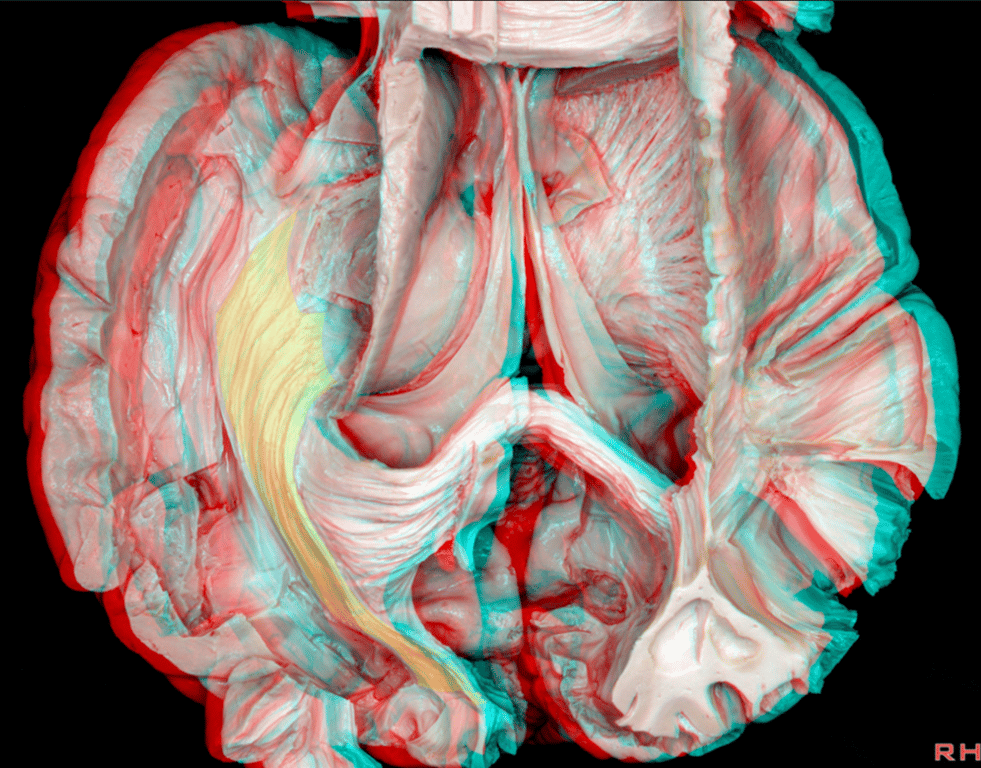
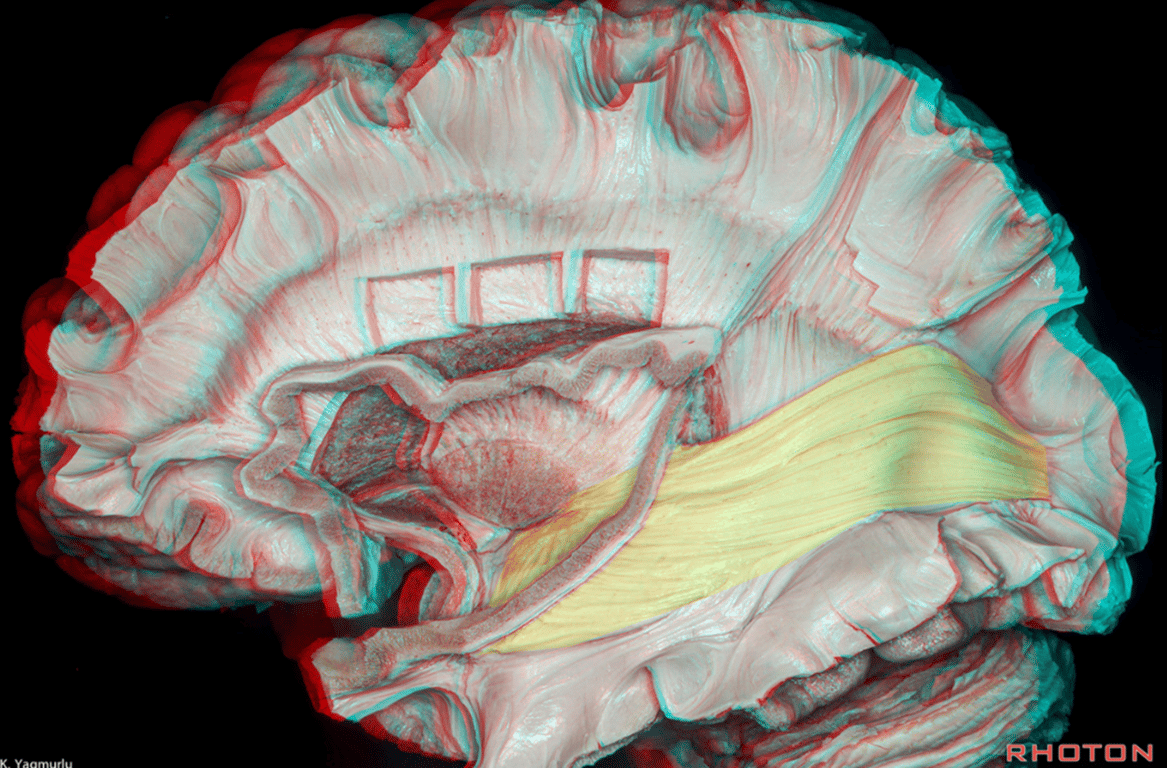
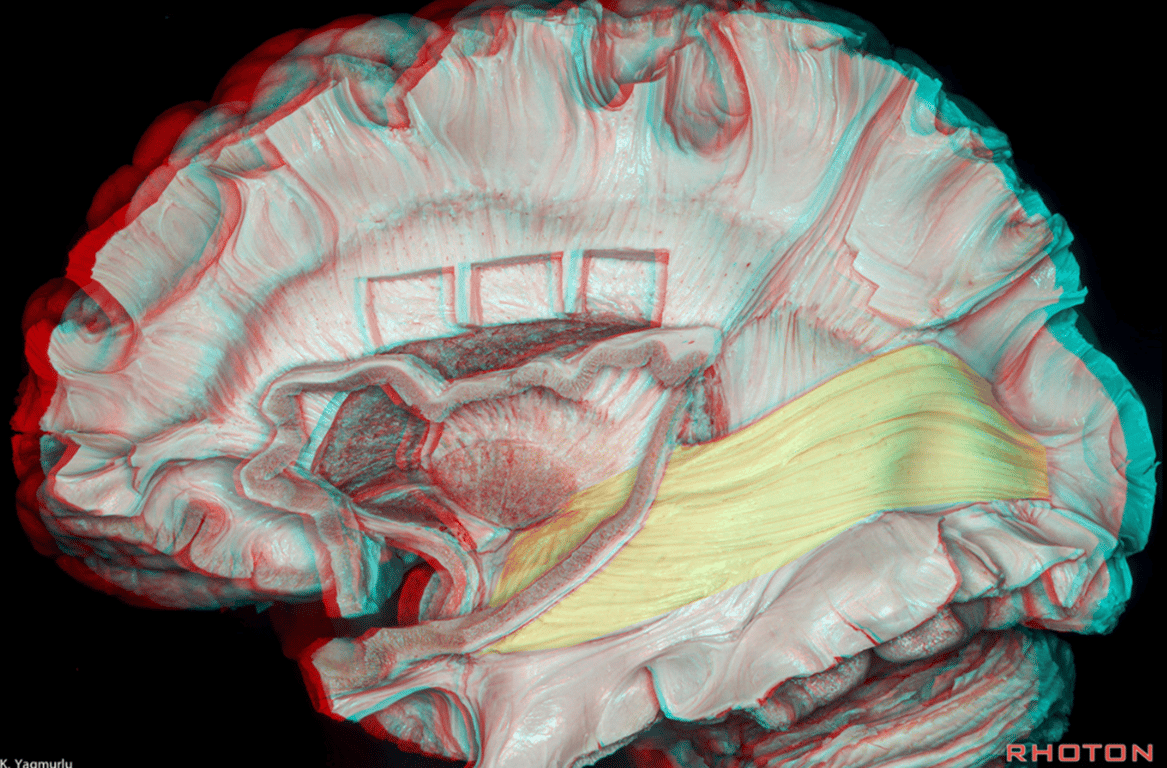
Superior view Tapetum (T), Sagittal Striatum (SS), FM (Forceps Major)
Step wise dissection of SS
- infra-parietal sulcus is represented as a blue dotted line after removal of the inferior parietal lobule.
- AF, arcuate fascicle; AG, angular gyrus; CS, central sulcus; ExPF, external perpendicular fissure; Hipp., hippocampus; ILF, inferior longitudinal fascicle; IFOF, inferior fronto-occipital fascicle; IPS, infra-parietal sulcus; ISJ, intermediate sulcus of Jensen; limit., limiting; MdlF, middle longitudinal fascicle; MOG, middle occipital gyrus; SF, Sylvian fissure; SLF, superior longitudinal fascicle; SMG, supramarginal gyrus; SS, sagittal stratum; STG, superior temporal gyrus; STS, superior temporal sulcus; sup., superior; UF, uncinate fascicle
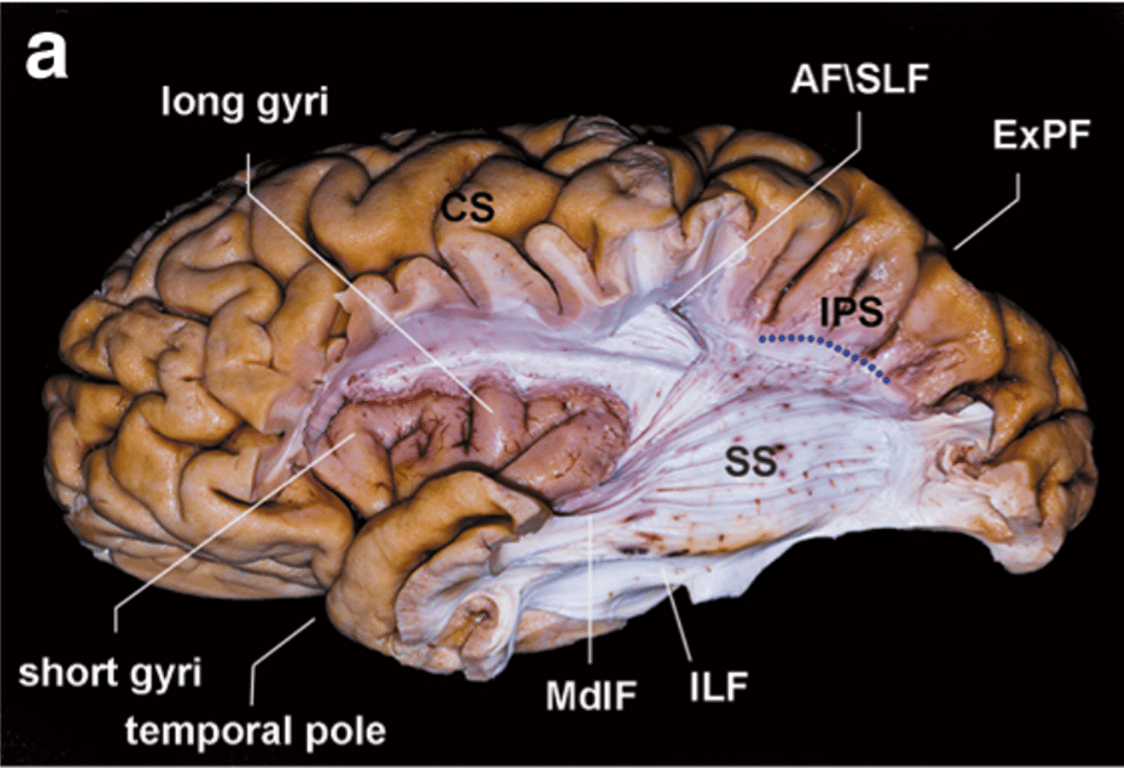
The frontoparietal operculum was removed to expose the insula and the dissected temporal lobe.
The IPS was the superior limit of the dissection.
After removal of the “U” fibers, the AF/SLF complex was peeled away exposing the superficial layer of the SS (MdlF and ILF).
The IPS was the superior limit of the dissection.
After removal of the “U” fibers, the AF/SLF complex was peeled away exposing the superficial layer of the SS (MdlF and ILF).
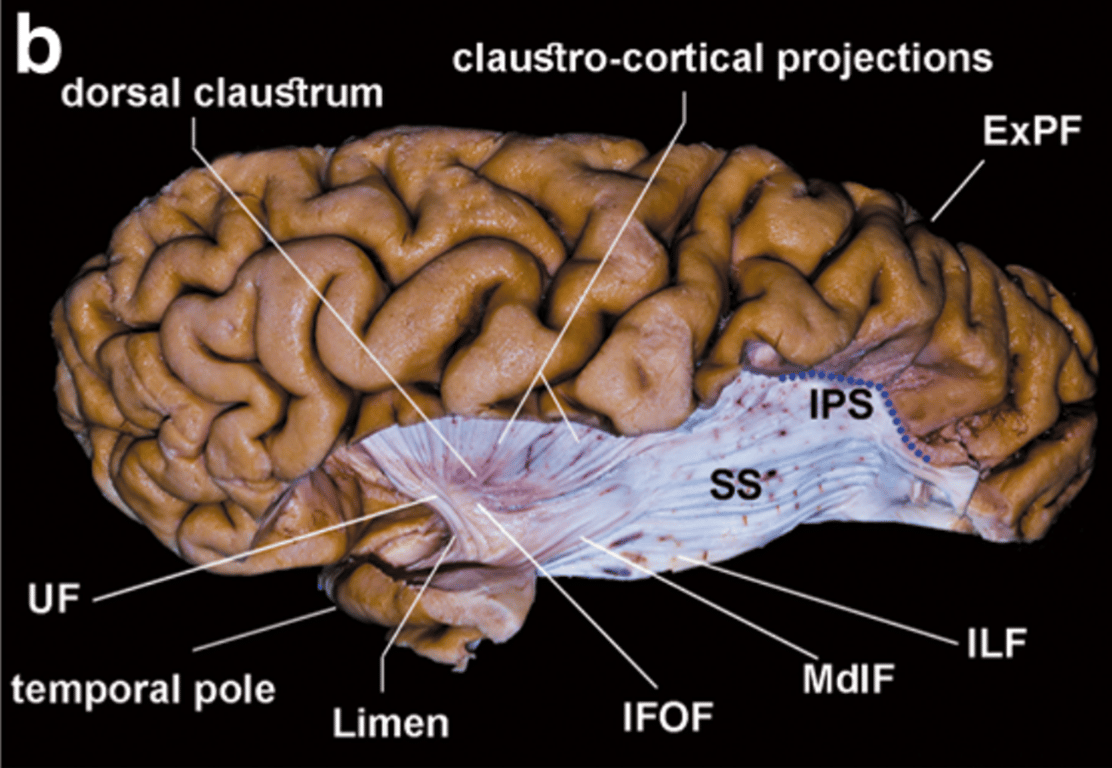
The insular cortex and extreme capsule were removed. The IFOF and the MdlF cross each other defining the anterior limit of the stratum.
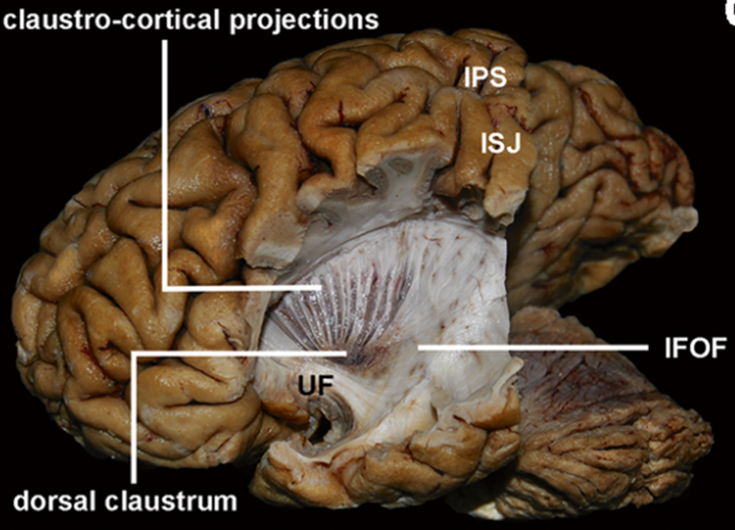
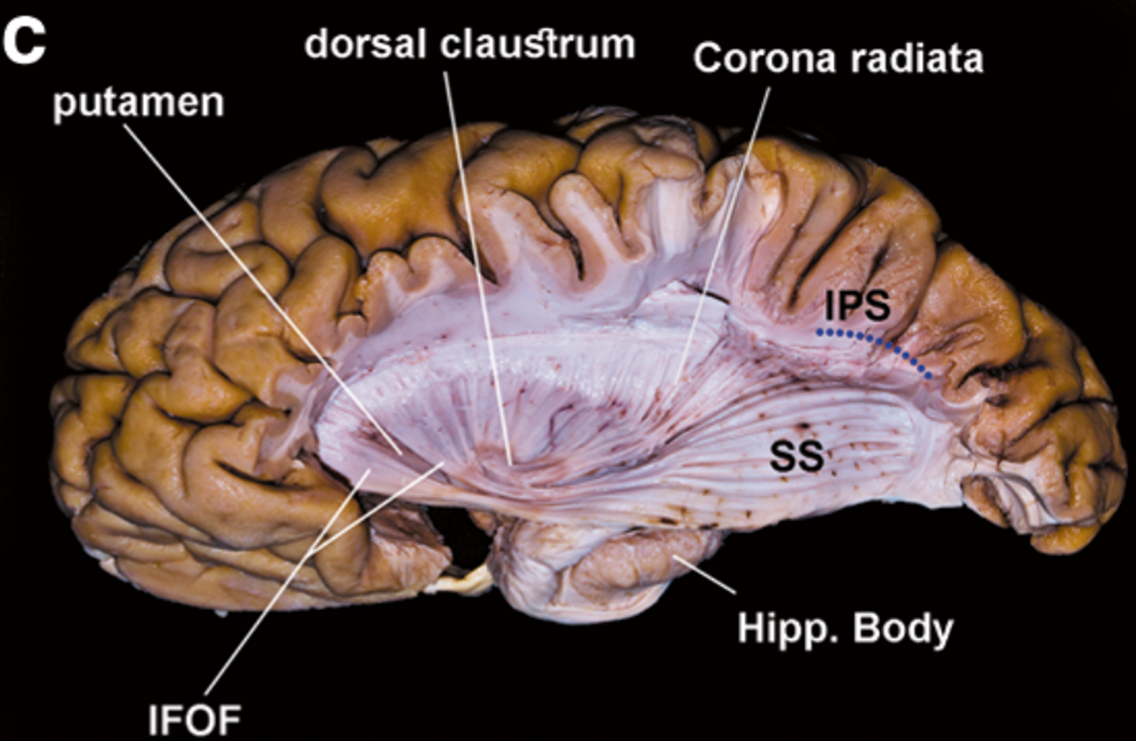
The middle layer of the SS is exposed.
The IFOF, after passing into the temporal stem, joins the SS directed toward the temporo-parieto-occipital cortex.
The IFOF, after passing into the temporal stem, joins the SS directed toward the temporo-parieto-occipital cortex.
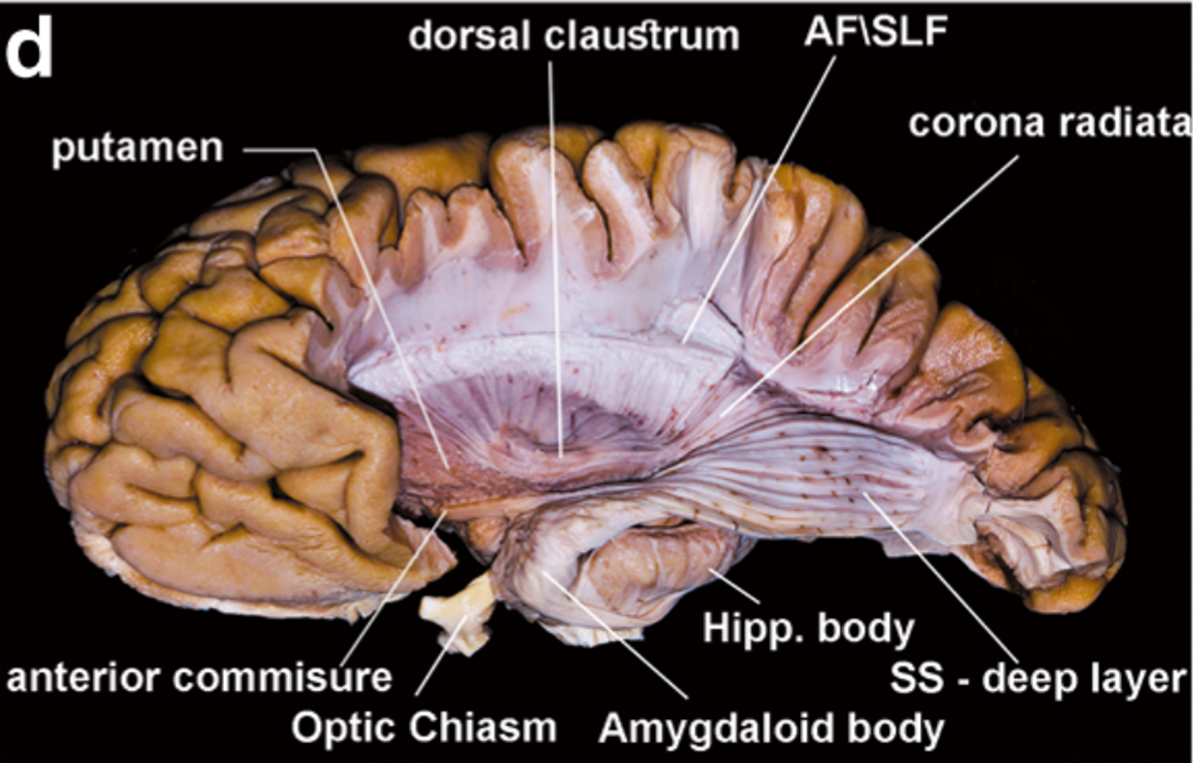
The substantia innominate was removed exposing the AC and its lateral extension.
This fascicle passes through the basal portion of the putamen and the globus pallidus within the temporal stem, and joins the deep layer of the SS, intermingled with the OR.
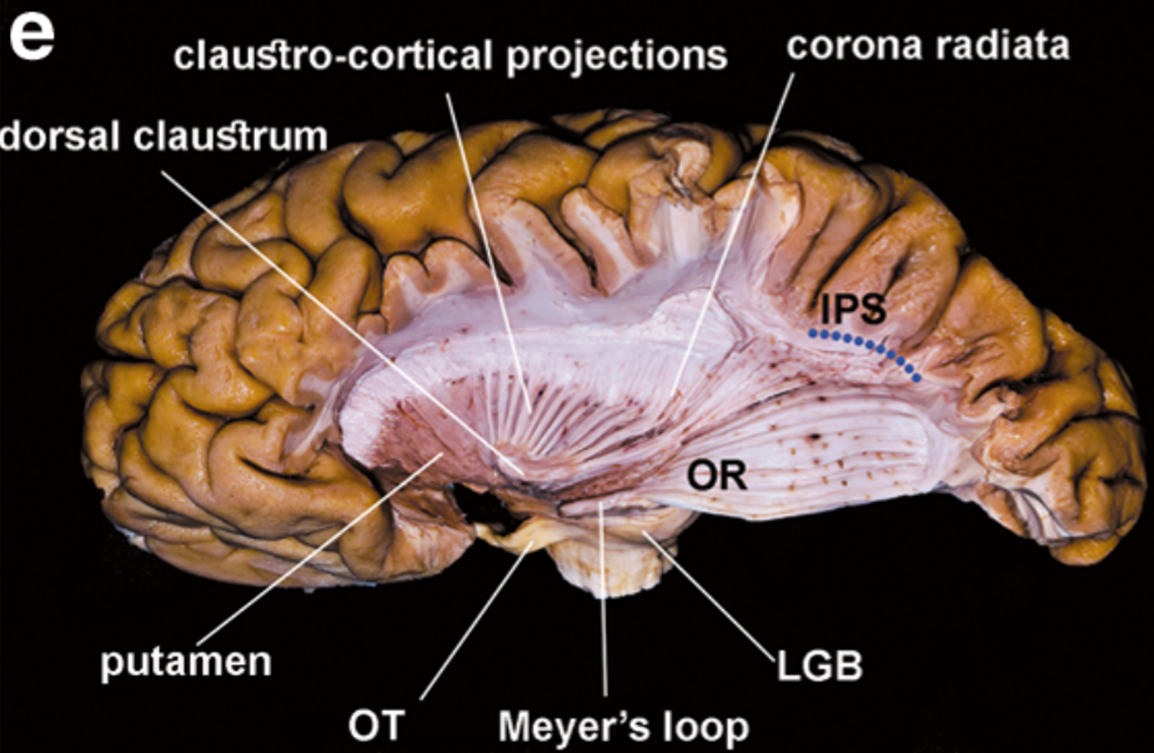
The last step of the dissection shows the LGB and the course of the OR directed toward the occipital cortex. AF, arcuate fascicle; AG, angular gyrus