Hartel's triangle
- The three points
- 2.5 cm lateral to the angle lip
- Corresponds to the location of the skin puncture:
- On the inferior edge of the zygomatic arch, 3 cm anterior to the external auditory canal.
- On the line joining the first point to the pupil on the inferior edge of the orbit
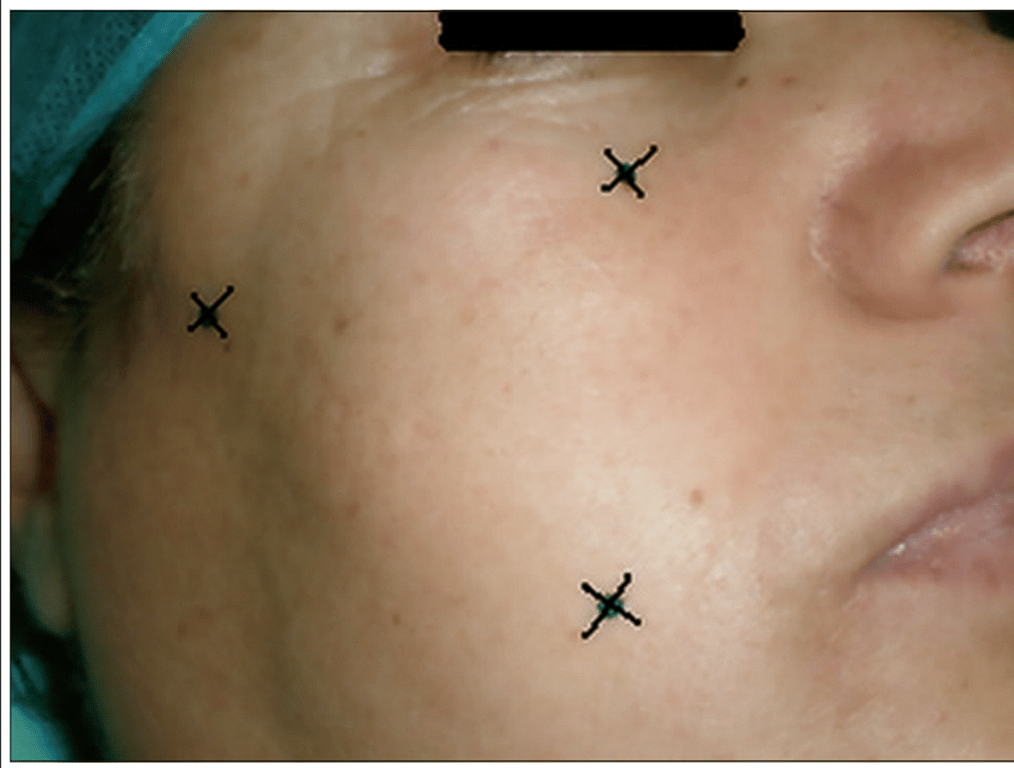
- Suttner
- Mid pupillary line plane
- 2.5cm from tragus
- 2.5cm from angle of mouth
Steps
- Performed under general anaesthesia + tracheal intubation
- X- ray guidance of a No. 4 Fogarty catheter through the foramen ovale
- Balloon should be driven inside the walls of the MC
- Appropriate placement is confirmed by the pear- shaped aspect of the balloon inflated with metrizamide.
- Compression is maintained for approximately five ± 2 minutes according to authors. Bradycardia may happen during compression. (trigeminocardiac reflex)
- Appropriate placement is confirmed by the pear- shaped aspect of the balloon inflated with metrizamide.
- Compression is maintained for approximately five ± 2 minutes according to authors. Bradycardia may happen during compression.
Cannulating the foramen ovale
- Three anatomical structures will be successively traversed: The cheek, then the pterygo maxillary fossa, and finally the FO.
- Neurosurgeon’s index was in close contact with the internal side of the cheek. It guided the introducer in order to avoid the penetration of the oral cavity.
- However, bleeding can happen deeper in the pterygo-maxillary fossa through the HI or within the cheek.
- This is due to the injury of branches of internal maxillary artery or of the veins of the pterygoid venous plexus. → the procedure should be stopped, whereas the haemostasis is obtained by external compression of the cheek → the surgery is re‑performed 1-2 weeks later
- Trigeminocardio reflex.
- Want to get to the Inferior medial limit of the foramen Ovale
- If too lateral and anterior then will get into the nerve
Balloon shape
- Pear shape: Normal
- Dumb bell: located in pre pontine cistern
- Damage to CN6
- Round: Located above into tent
- Damage to CN3
Risk of
- Infection
- CSF leak
- Bleeding
- Corneal keratosis
- Due to CN V numbness
- Death
- Diplopia
- Jaw weakness