Location
- Almost always dorsal,
- With a ventral cyst, consider a neurenteric cyst (see below).
- Most common in thoracic spine.
- Extradural
- Sometimes referred to as arachnoid diverticula—these may be associated with kyphoscoliosis in juveniles or with spinal dysraphism.
Clinical features
- Asymptomatic, even if large.
Aetiologies
- Congenital
- Posttraumatic
- Post-infectious
Evaluations
T1
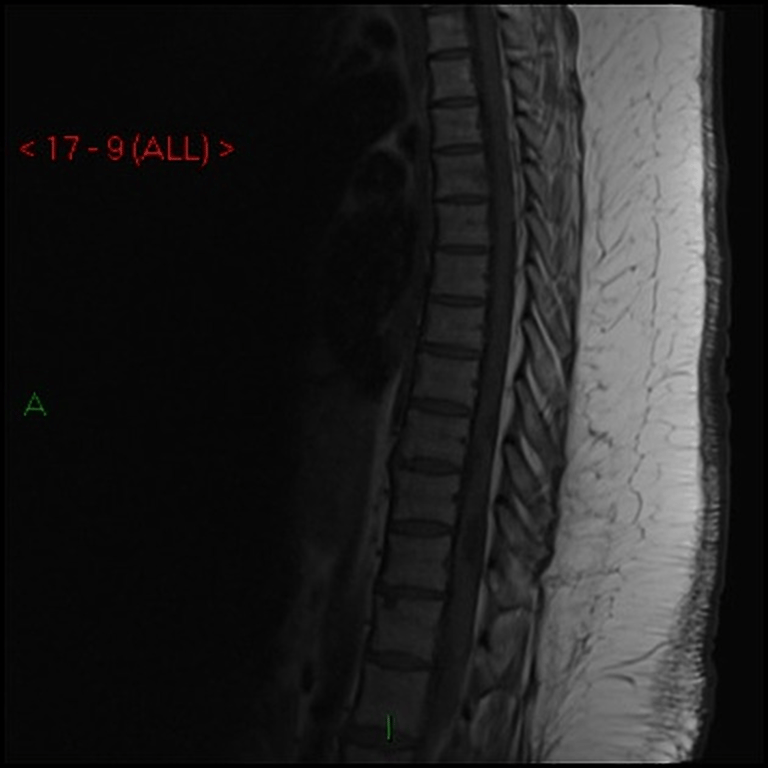
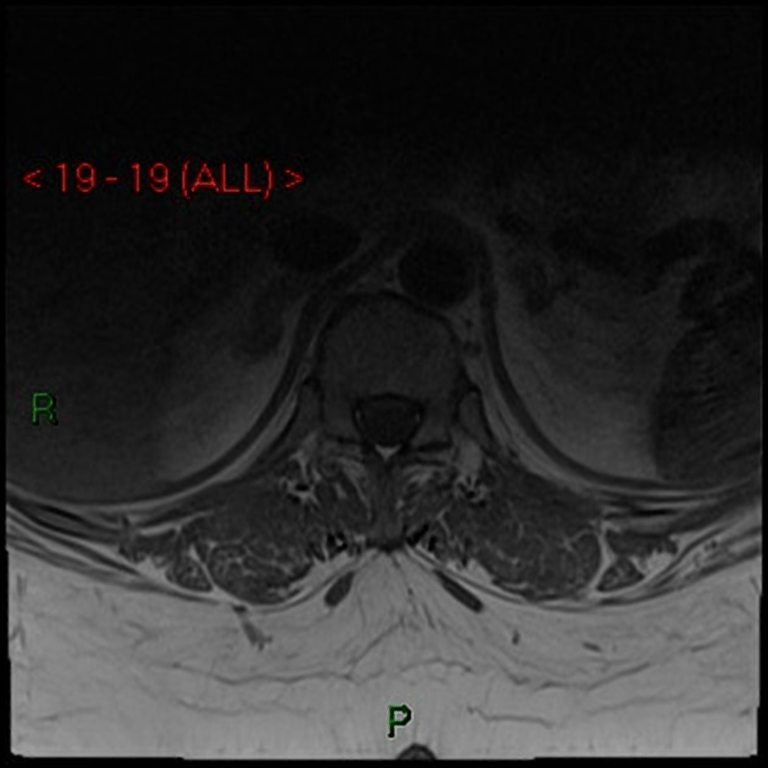
T1C
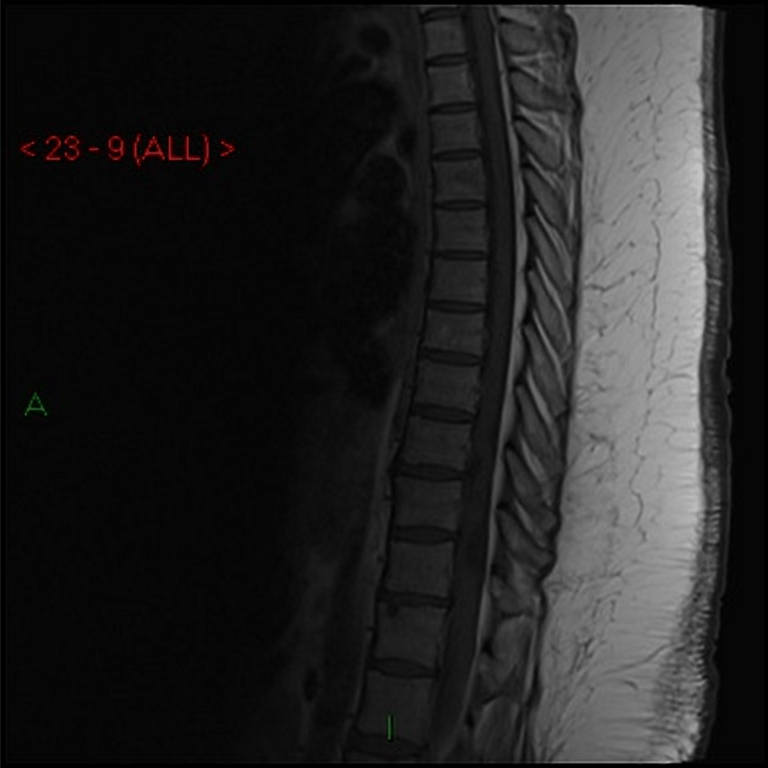
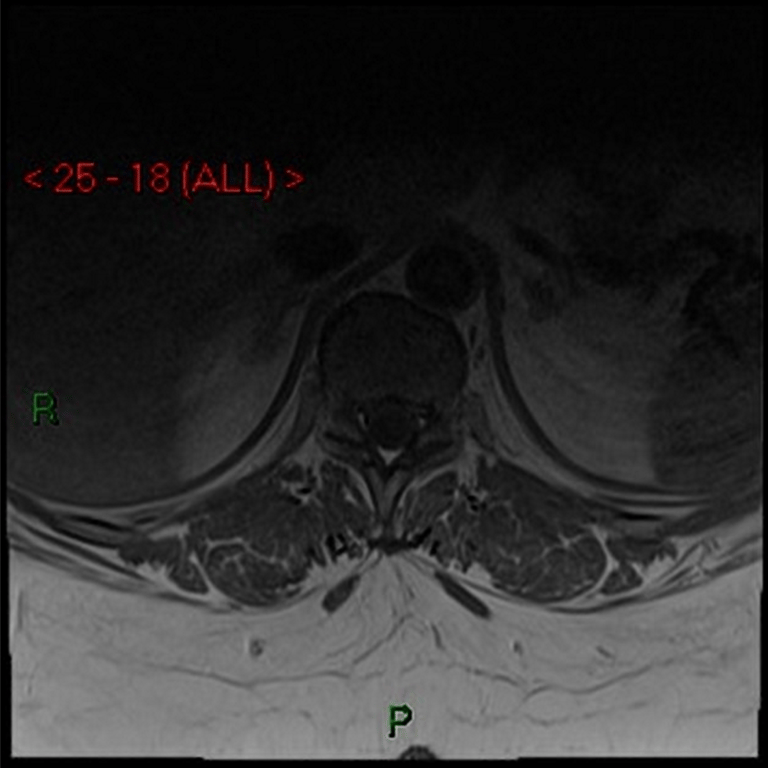
No contrast enhancement
T2
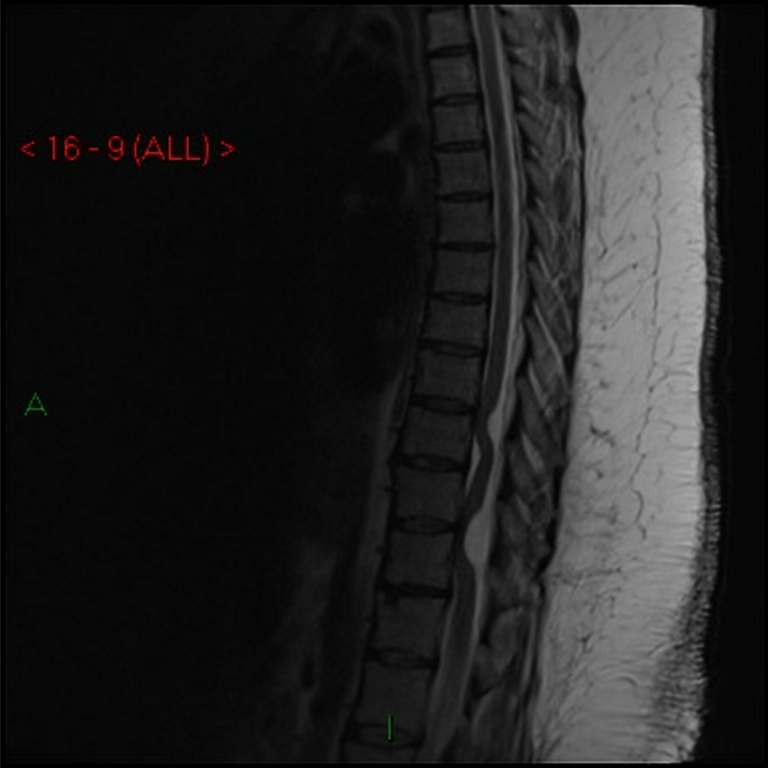
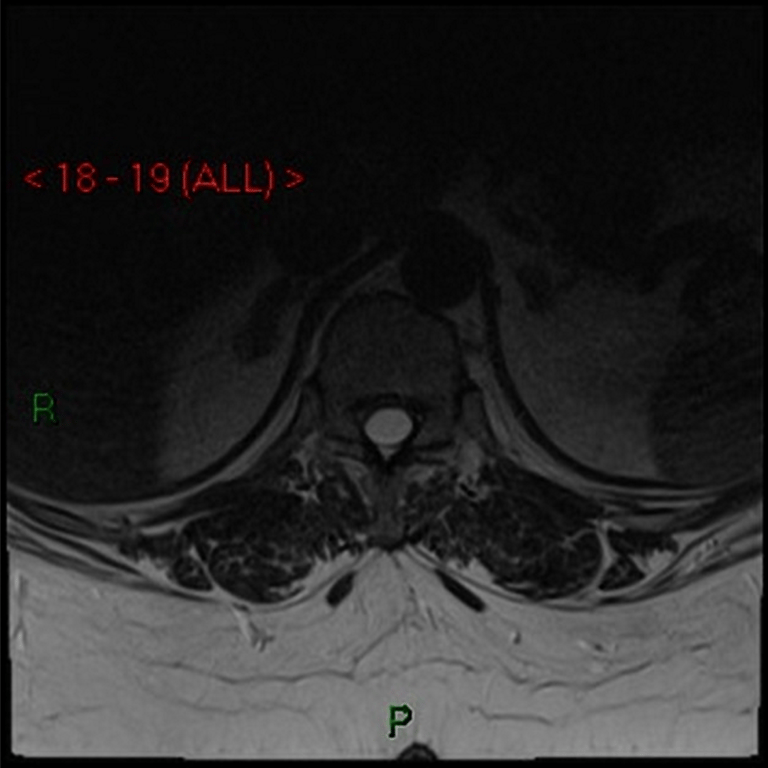
CSF signal
Treatment
- Indications for surgery
- Symptomatic lesions
- Myelopathy
- Pain is a soft indication as it may be difficult to determine if the pain is due to the lesion.
- Surgical options
- Percutaneous procedures: MRI or CT guidance.
- CT guidance usually requires use of intrathecal contrast to delineate the cyst
- Needle aspiration
- Needle fenestration
- Open procedures:
- Surgical resection
- Fenestration
- Cyst shunting: e.g. cyst peritoneal shunt