General
- AKA atretic cephaloceles,
Definition
- small subscalp lesions that consist of dura, fibrous tissue, and dysplastic brain tissue.
Epidemiology
- Common presentation in infants and young children.
Clinical presentation
- Palpable midline parietal soft tissue mass.
Pathology
- It is thought to represent involuted true cephalocele (meningocele or encephalocele) connected to dura mater via a fibrous stalk.
Associations
- Increased incidence of intracranial anomalies.
Radiographic features
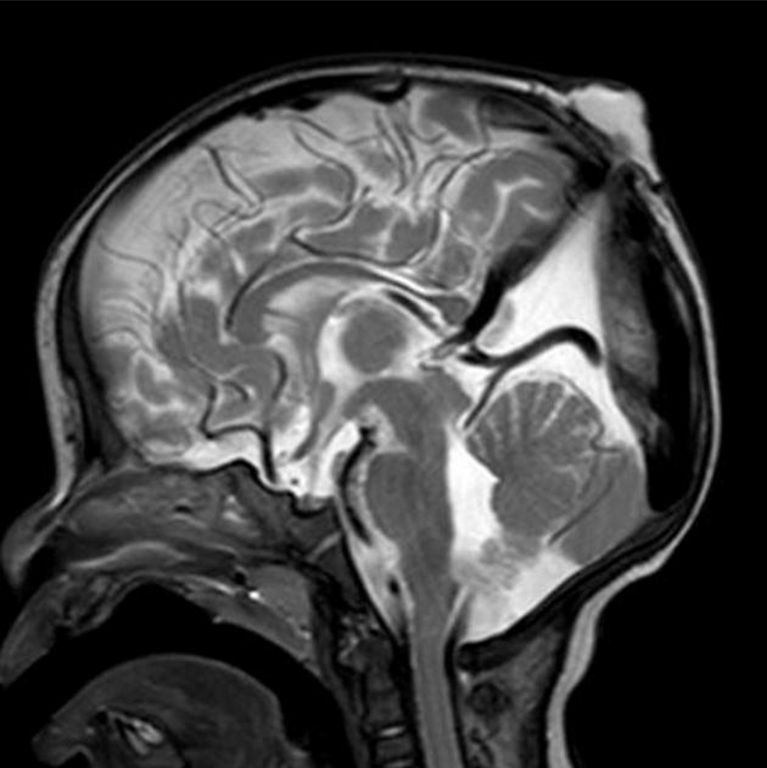
- subgaleal soft tissue mass with an intracranial extension via a sharply demarcated calvarial defect (cranium bifidum)
- CSF tract and vertical falcine vein point to the subcutaneous scalp mass
- vertically orientated primitive falcine vein
- fibrous stalk connecting the cephalocele
- focal fenestration of superior sagittal sinus at the atretic parietal cephalocele
- prominence of the superior cerebellar cistern and suprapineal recess
- superior peaking of the posterior tentorium
- spinning top configuration of the tentorial incisura
Differential diagnosis
- sinus pericranii
- dermoid or epidermoid cyst
- cephalohaematoma
- sebaceous cyst
- vascular lesions (haemangioma)
Treatment and prognosis
- Good