General
- AKA sincipital
- 15% of encephaloceles;
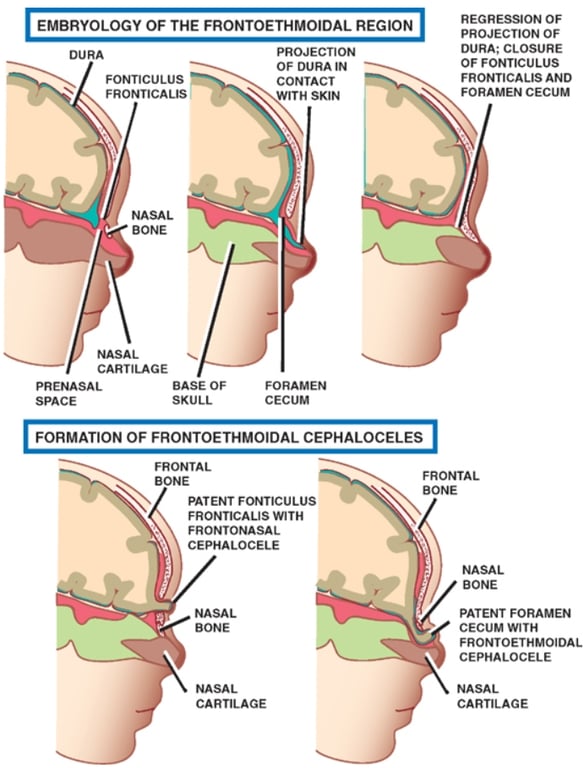
Due to
- Failure in the normal regression of a projection of dura that extends from the cranial cavity to the skin through a persistent foramen cecum or fonticulus frontalis.
- Persistence of this projection of dura may give rise to a dermal sinus tract, which in turn may give origin to a dermoid or epidermoid tumour
Examination
- Superficial skin-covered mass
- Nasal dimple and frequently hypertelorism.
Subtypes of frontoethmoidal cephaloceles are identified by the location of the bony defect
- Frontonasal cephalocele
- Location of the bony defect
- Frontal and nasal bones
- External defect in the nasion
- Frontoethmoidal cephalocele
- Location of the bony defect
- Frontal, nasal, and ethmoidal bones
- Defect between nasal bone and nasal cartilage
- Naso-orbital cephalocele
- Location of the bony defect:
- Frontal, lacrimal, and ethmoidal bones extending into the anteromedial portion of the orbit.
- Defect in the antero-inferior portion of medial orbital wall