General
- Aka: vermian aplasia/molar tooth midbrain-hindbrain malformation
Definition
- Molar tooth sign
- Deep interpeduncular fossa
- Vermian hypoplasia
Pathology
- Mainly autosomal recessive (except OFD1 gene mutation that is inherited with an X linked pattern)
- 25% recurrence risk in the affected family
- Genetic disease (26 genes) that encodes protein of the nonmotile primary cilia --> required for development and functioning of various cells
- Retinal photoreceptors
- Epithelial cells lining the renal tubules
- Bile ducts
- Neurons
- Required for neuronal cell proliferation and axonal migration in the cerebellum and brainstem
Presentation
- Hypotonia
- Ataxia
- Ocular motor apraxia
- Neonatal breathing dysregulation
- Intellectual disability of variable severity
- Systemic involvement
- Renal (nephronophthisis)
- Causes high mortality and morbidity for pt
- Ocular (colobomas, retinal dystrophy)
- Hepatic (congenital hepatic fibrosis)
- Causes high mortality and morbidity for pt
- Skeletal (various forms of polydactyly) involvement
Imaging
- MRI
- Cerebellar features
- “molar tooth sign”
- diagnostic criterion for Joubert syndrome
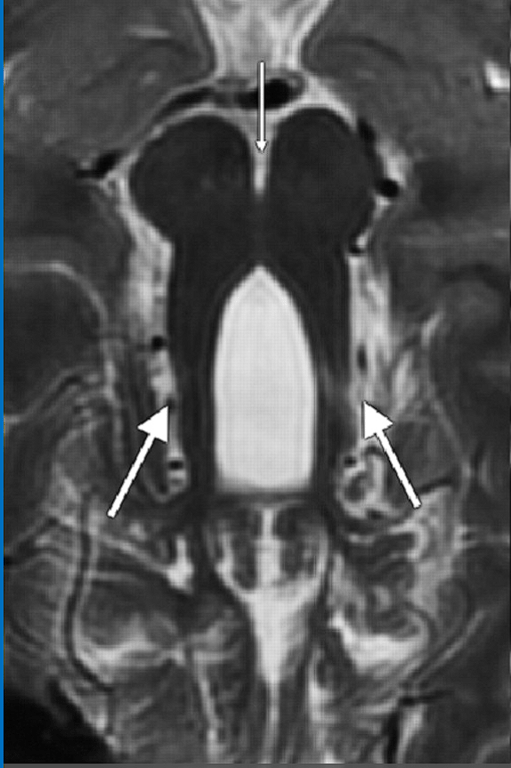
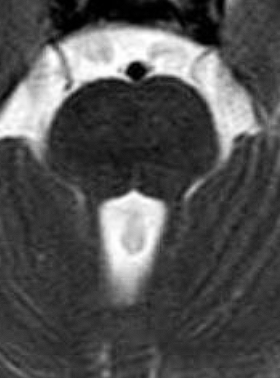
- elongated, thickened, and horizontally oriented superior cerebellar peduncles;
- a deep interpeduncular fossa;
- vermian hypoplasia
- Brainstem features (30% of patients)
- dysmorphic tectum and midbrain
- thickening and elongation of the midbrain
- small pons
- Supra tentorial features (30% of patients)
- Callosal dysgenesis
- Cephaloceles
- Hippocampal malrotation
- Migrational disorders
- Ventriculomegaly
Case
Joubert syndrome in a 5-year-old child who presented with ataxia, ocular motor apraxia, and cog- nitive impairment
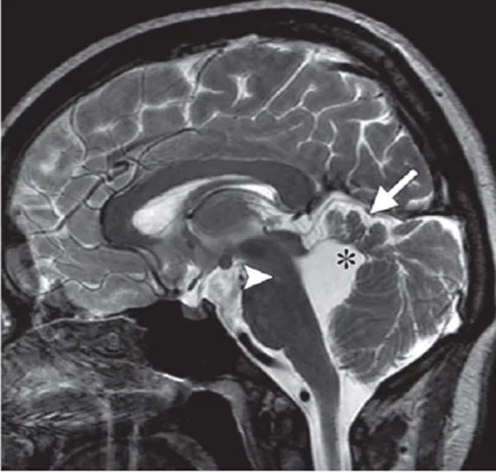
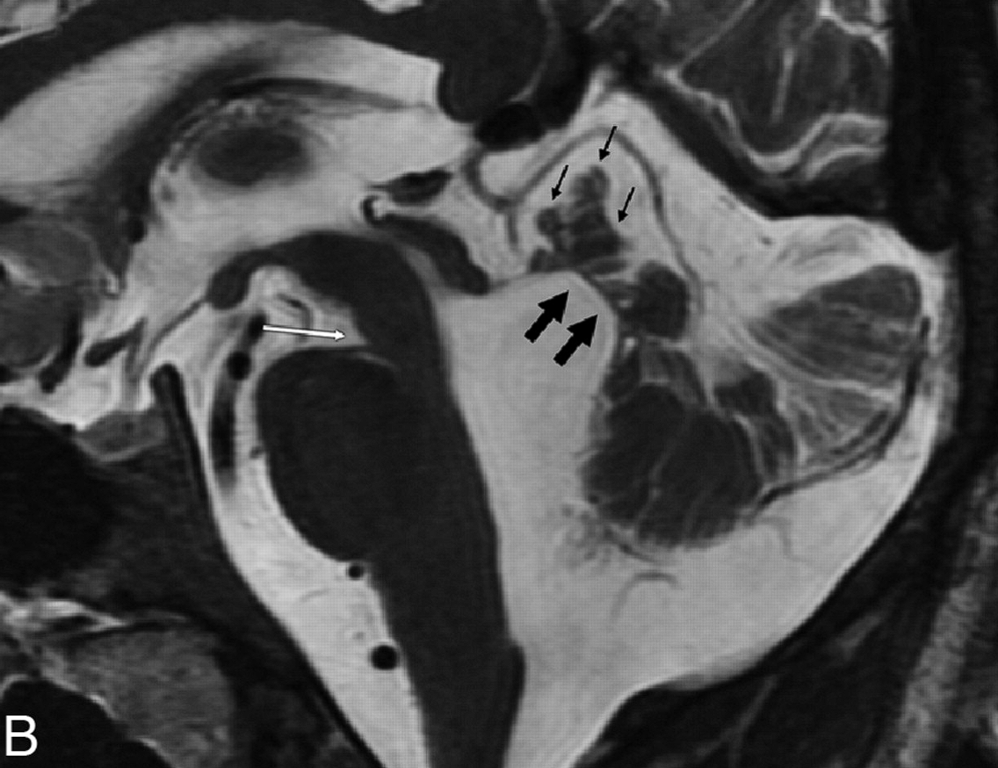
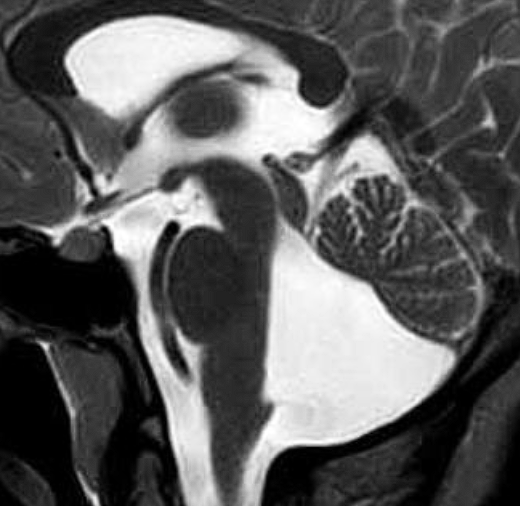
Sagittal T2-weighted MR image shows hypoplasia and dysplasia of the vermis (arrow), enlargement of the fourth ventricle with upward and posterior displacement of the fastigium O, and a nar- row pontomesencephalic isthmus (arrowhead).
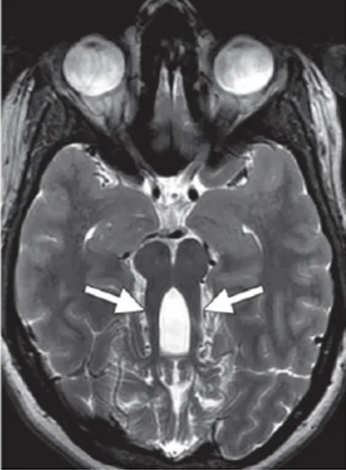
Axial T2-weighted MR image shows elongated, thickened, and horizontally oriented superior cerebellar peduncles (arrows) and a deepened interpeduncular fossa, resulting in the characteristic molar tooth sign.
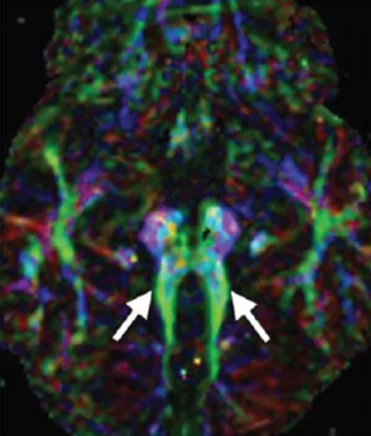
Axial color-coded fractional anisotropic map obtained at the level of the pontomesencephalic junction shows the horizontal orientation of the superior cerebellar peduncles (green [arrows]) and the absence of decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncles.
Outcome
- High morbidity and mortality
- Due to renal and hepatic involvement
Ddx
Features | Joubert's syndrome | Isolated cerebellar vermis hypoplasia/atrophy |
Inferior Vermis | Hypoplasia/agenesis | Hypoplasia/agenesis |
4th ventricle communication with Cisterna Magna | Communicates | Communication |
Cerebellar hemispheres | Reduced | Normal |
4th ventricle size | Enlarged | Normal |
Position of 4th ventricle choroid plexus | Normal | Normal |
Post fossa size | Normal | Normal |
Hydrocephalus | No | No |
Images