Definition
- Focal collections of normal neurons in abnormal locations due to neuronal migration interruption
Mechanism
- Radial neuronal migration fails completely--> Collections of normal “cortical” neurons that fail to reach the cortex --> forming islands of Gray matter in white matter
- FLNA mutation (Chr Xq28), which encodes an actin-binding protein called filamin
- Fatal in males, heterogeneous in females
Clinical presentation
- Almost always has seizures in 20-30s
Radiology
- Non enhancing
Subtypes (location)
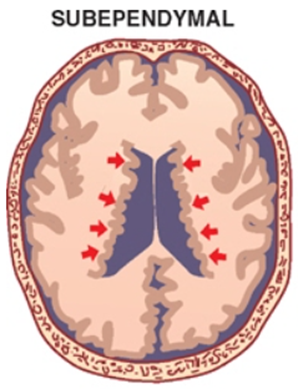
Subependymal (periventricular) heterotopia
- Most common
- Can be
- Unilateral periventricular nodular heterotopia
- Bilateral periventricular nodular heterotopia
- X-linked dominant disorder
- only seen in females
- lethal in males
- Presentation
- Normal motor function
- Normal development
- Onset of seizures in the second decade of life
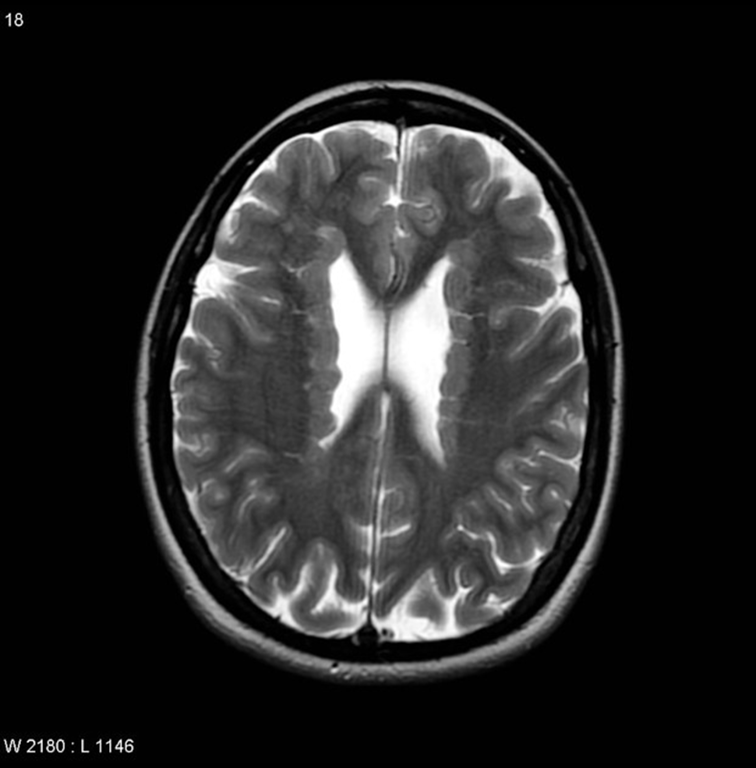
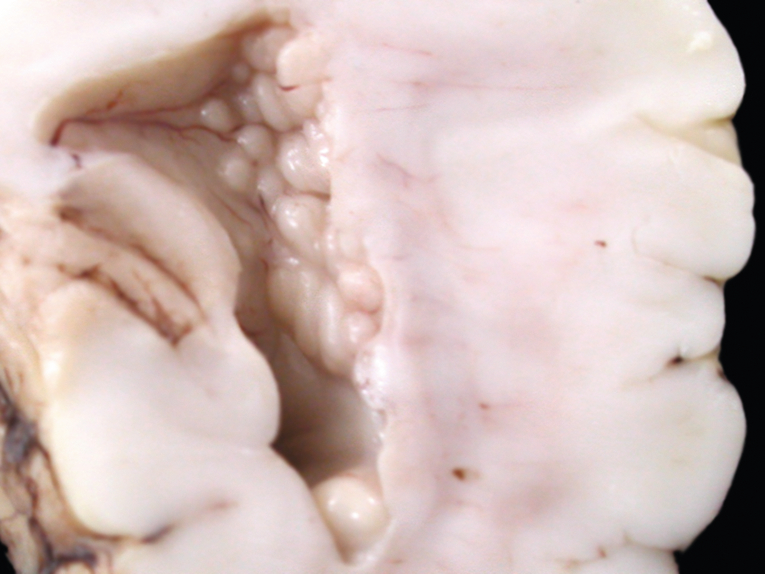
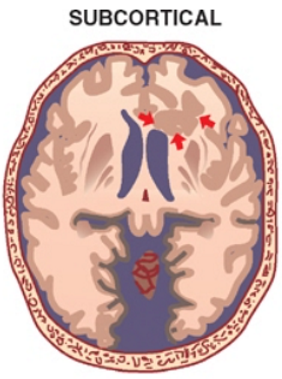
Focal subcortical heterotopia
- Presentation
- Depends on size
- Normal to severely abnormal developmental delay
- Normal to severe motor disturbances
- Seizure disorder.
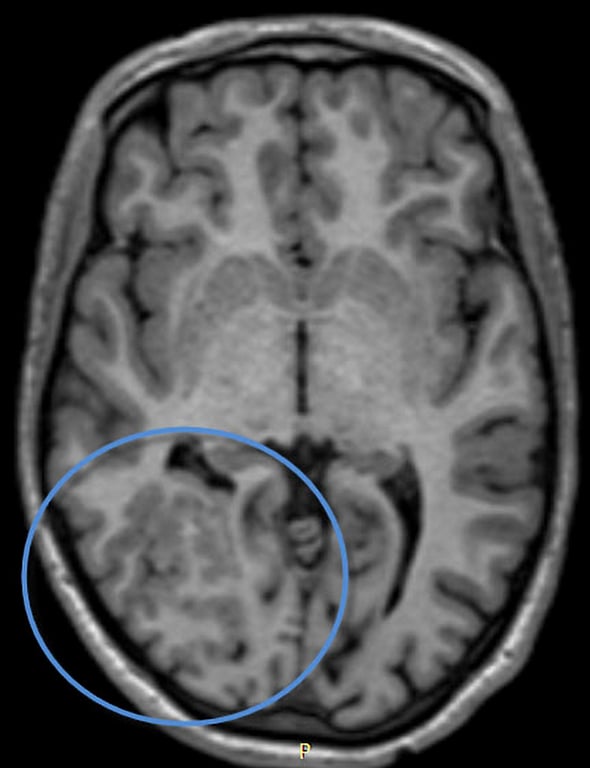
Band heterotopia
- Aka diffuse gray matter heterotopia
- Presentation
- moderate to severe developmental delay
- medically intractable seizures.
- Strongly associated with Classic T1 Lissencephaly

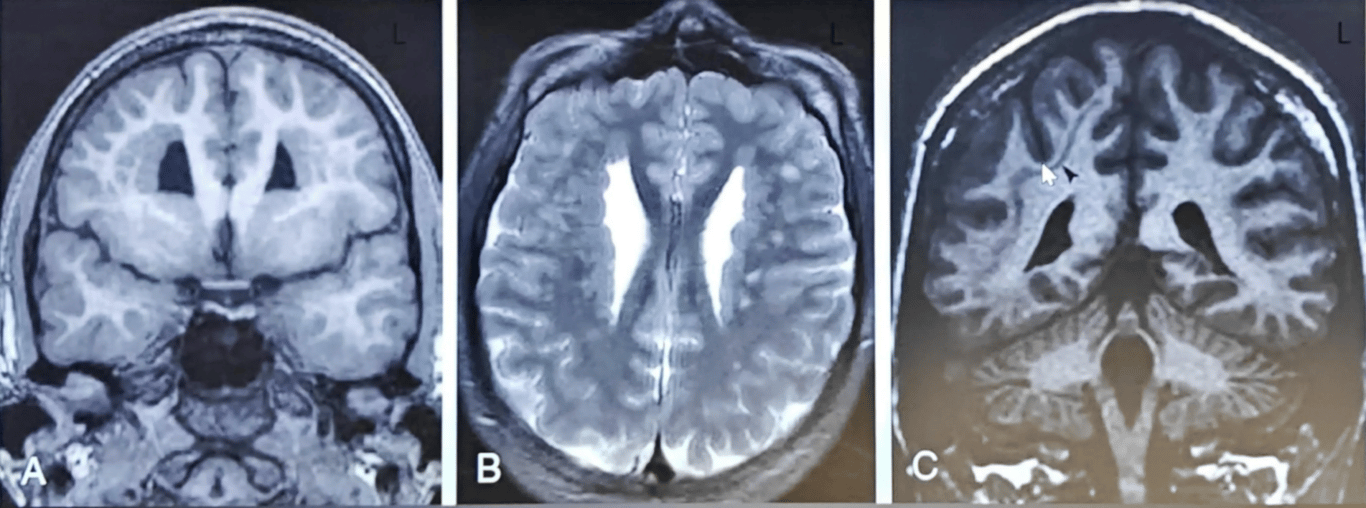
A, B: Coronal T1 and axial T2 showing extensive bilateral subependymal nodular gray matter heterotopia
C: Coronal T1 showing band heteretopia in right cerebral hemisphere
Marginal glioneuronal heterotopia
- Overmigration of neurons and glial cells into the leptomeninges Microscopically and not visible on imaging.
Feature | Marginal glioneuronal heterotopia | Type 2 cobblestone lissencephaly |
Location | Affects a focal part of the brain | Affects the entire cerebral cortex |
Appearance | Nodules of neurons and glial cells | Cobblestone" appearance |
Severity | Can range from mild to severe | Typically associated with severe symptoms |
Symptoms | Developmental delays Seizures Intellectual disability Asymptomatic | Severe developmental delays, Intellectual disability Seizures Movement disorders |