General
- Meaning 'smooth brain’
- The most severe neuronal migration abnormality
Pathology
- Macroscopically
- Cerebral hemispheres are smooth
- Cortical sulci are absent
- Cerebral fissures are shallow
- Microscopically
- Cortical cell layers are aberrant
Types
Classic lissencephaly (Type 1)
- Strongly associated with subcortical band heterotopia
- Mechanism
- Neuronal migration does not fail completely but is disrupted --> failure of cortical gyri to develop
- Genetic (Microtubule function)
- hemizygous mutation in the DCX/XLIS gene on chromosome Xq22.3q23
- heterozygous (dominantly inherited) mutation in the LIS1 gene on chromosome 17p13.3
- Complete loss = fatal
- Features:
- Lissencephaly -pachygyria spectrum: to describe the spectrum of diseases that cause relative smoothness of the brain surface
- lissencephaly:
- Smooth brain surface
- Pachygyria:
- Broad & flat gyri with shallow sulci
- Thick cortex with abnormal cryoarchitecture;
- Metabolic CNS disorders.
- Agyria:
- no gyri
- completely smooth surface
- Partial = seizures + retardation.
- 4 layers of cortex
- Molecular layer
- External neuronal layer—thin
- Sparsely cellular layer
- Internal neuronal layer—thick
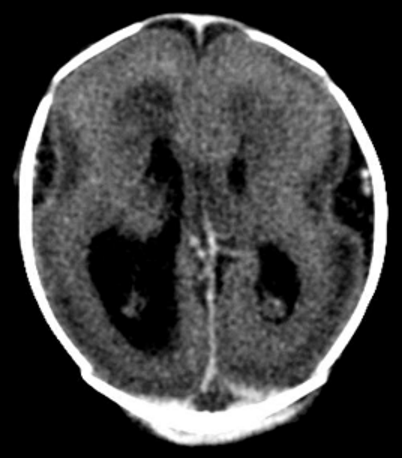
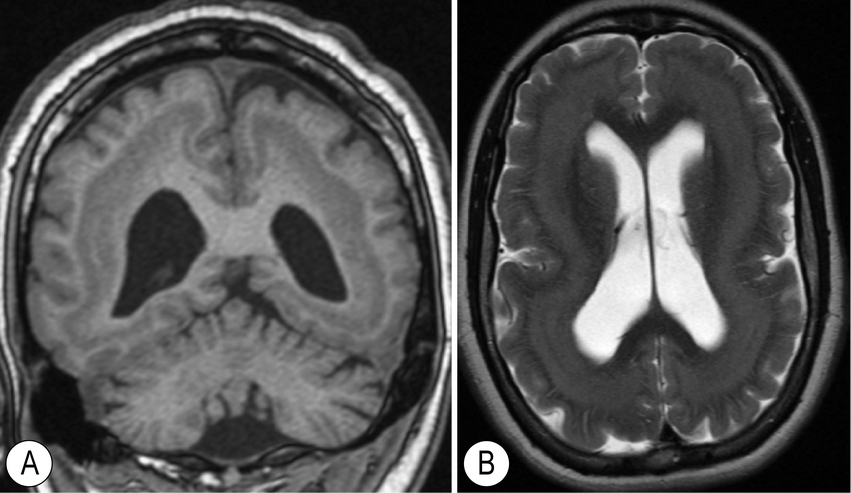
Cobblestone lissencephaly (Type 2)
- Cerebral cortex is disorganized, and appears pebbled or nodular due to complete displacement of the cerebral cortex with clusters of cortical neurons separated by glio-mesenchymal tissue
- Due to neurones fail to overmigration of glioneural elements.
- neuroglial tissue interrupts pia as it enters subarachnoid space resulting in fine stippling;
- marked disorganization of neurons, glia and blood vessels
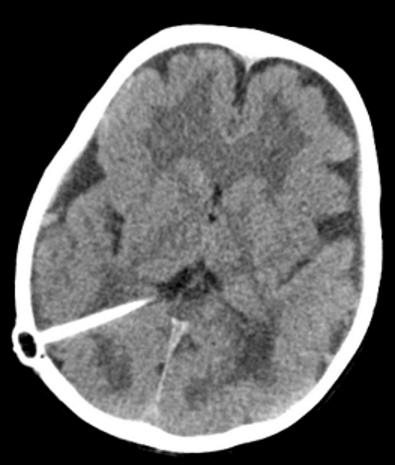
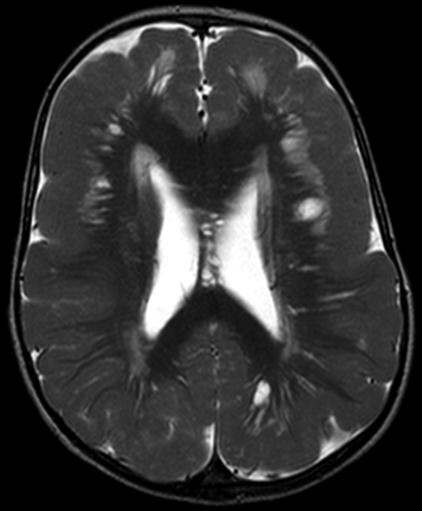
Feature | Marginal glioneuronal heterotopia | Type 2 cobblestone lissencephaly |
Location | Affects a focal part of the brain | Affects the entire cerebral cortex |
Appearance | Nodules of neurons and glial cells | Cobblestone" appearance |
Severity | Can range from mild to severe | Typically associated with severe symptoms |
Symptoms | Developmental delays Seizures Intellectual disability Asymptomatic | Severe developmental delays, Intellectual disability Seizures Movement disorders |
Clinical features
- Severely mentally retarded
- Don’t survive > 2 yrs