General
- Aka: cortical dysplasia
Definition
- Multiple small gyri due to a defect in the normal six-layered lamination of the cortex leading to an abnormal distribution of neurons
Mechanism
- Neuronal organization deficit
- Disturbances (typically between 17 and 25-26 weeks of gestation).
- In the late stages of neuronal migration OR
- In the early stages of cortical organization
- This result in the abnormal development of the deep layer of cerebral cortex which manifests as multiple small gyri separated by small sulci → irregular bumpy cortical surface
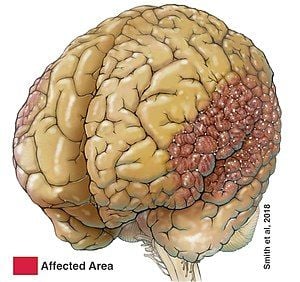
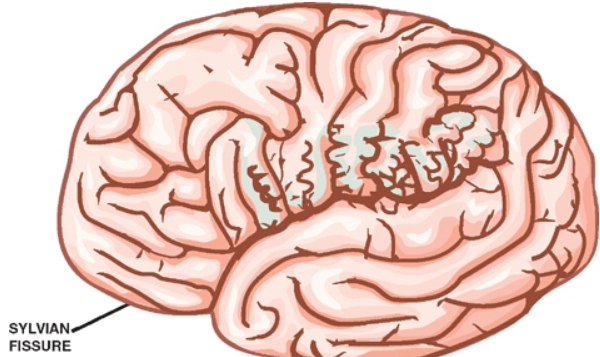
Imaging
- Small gyri with shallow sulci.
- May be difficult to diagnose by CT/MRI, and may be confused with pachygyria (T1 lissencephaly)
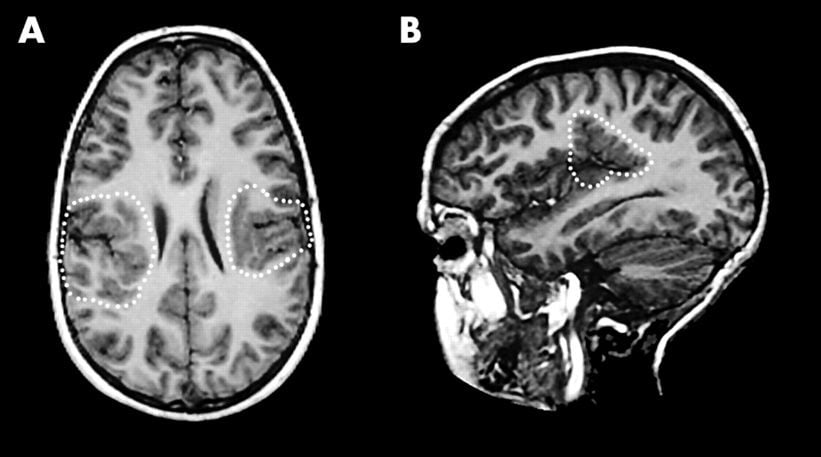
Subtypes
- Diffuse or focal
- Unilateral or bilateral
- Symmetric or asymmetric
Location
- Affect a variable portion of the cortex in one or both hemispheres.
- Most common: Posterior end of the sylvian fissure
- Because of telencephalic flexure
- Sylvian cortex (80%)
- frontal lobes (70%)
- Less common
- parietal, temporal and occipital lobes.
- Can be
- Bilateral (60%) or Unilateral (40%)
- Focal or diffuse
- Symmetric or asymmetric.
Pathology
- Hemispheric surfaces have multiple festoon-like convolutions with four cortical layers only;
- Polymicrogyria may demonstrate an irregular and bumpy surface or may be paradoxically smooth as a result of coalescence of microgyri in the molecular (surface) layer
Aetiology
- Intrauterine ischemia
- In utero vascular occlusion (in association with schizencephaly);
- Intrauterine infection (CMV or toxoplasmosis),
- Metabolic disorders (peroxisomal storage disorders, pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency),
- Genetic syndromes (Aicardi syndrome, DiGeorge syndrome, and Warburg Micro syndrome).
- Mutation of SRPX2 (bilateral sylvian polymicrogyria)
- PAX6
- TBR2
- GPR56
Presentation
- Seizures (80%)
- Infantile seizures with marked developmental delay (also possibly contralateral hemiplegia).
- Microcephaly
- Hypotonia
- Severe motor and intellectual dysfunction
- depending on the extent of cortical involvement