Definitions
- 2 primary features:
- Hypoplasia of the optic nerves
- Hypoplasia or absence of the septum pellucidum
- Hypothalamic-pituitary dysplasia or dysfunction
Clinical features
- Visual disturbances
- Nystagmus
- Red. visual acuity
- Endocrine deficiency
- Growth hormone
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone.
Numbers
- Mostly sporadic
No Aetiology factors
- Some association with
- maternal diabetes
- Intrauterine CMV infection
Mechanism
- Unknown
- ? occurs when the development of the prosencephalon is affected
Clinical presentation
- Seizures (50%)
- Pituitary dysfunction
- Visual symptoms
- Nystagmus
- Decreased visual acuity.
Ophthalmoscopic examination
- optic nerve hypoplasia
- a pale optic nerve head
- isolated tortuosity of the retinal vein.
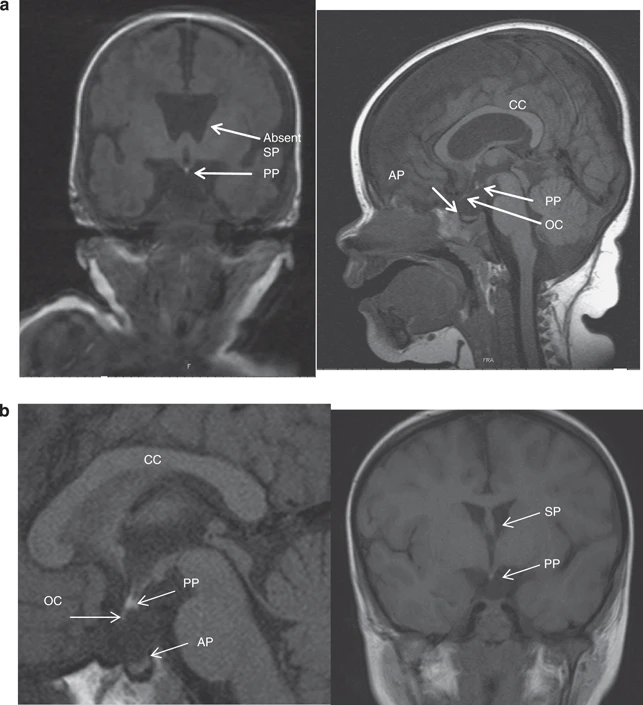
MRI
- corpus callosum agenesis lead to a box-like shape of the frontal horns in coronal planes,
- low-lying fornix (due to absent septum),
- pituitary hypoplasia/empty sella/ectopic posterior pituitary gland,
- hypothalamic hypoplasia,
- optic nerve and/or optic chiasm hypoplasia (visualization difficult as mild form ophthalmological findings more reliable)
- Brain parenchyma congenital anomalies
- malformations of cortical development (schizencephaly and gray matter heterotopia)
- olfactory hypoplasia (arrhinencephaly)
- hypoplasia of white matter
- ventriculomegaly
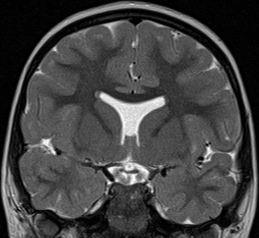
- Absent septum pellucidum,
- Right optic nerve hypoplasia,
- “Point-down” appearance of the frontal horns of the lateral ventricles.