General
- The most severe neurological complications occurs at young
Normal
- The cranial base and the neural arches grow and enlarge by endochondral ossification.
Normal foramen magnum growth
- Usually small at birth, the foramen magnum remains small, particularly in the transverse diameter. Growth of the skull is particularly robust and important in the first 18 months of life with achondroplastic patients growing significantly less rapidly
- There is very little difference in the actual size of the foramen between symptomatic and asymptomatic patients; the average adult foramen in patients is the size of the average normal newborn in the transverse diameter and the size of the average 2-year-old in the sagittal diameter
Mechanism
flowchart TD A["Defective endochondral<br>ossification"] --> B["Small or deformed foramina"] & D["Relative lack of rigidity of the bones"] & I["Premature fusion +<br>abnormal development of<br>the posterior skull<br>base synchondroses"] B --> C["Venous sinus obs(s)"] & n3["Stenosis of foramen magnum/retroflexed dens"] D --> E["Occipital condyle may<br>distort over time"] & n4["Base of the skull is<br>constantly under<br>pressure (from the<br>weight of the head and<br>the tension of the cervical<br>muscles)"] E --> F["Reducing size<br>of foramen magnum"] G["Increase likelihood of<br>medullary and upper<br>spinal cord compression"] --> H["Early death/neuro deficits/<br>Sleep Apnea/Respiratory<br>failure/Myelopathy/<br>Syringobulbia/<br>Syringomyelia"] I --> J["Hypertrophied margin<br>of the posterior aspect<br>of the foramen magnum"] J --> K["Appears as a bony<br>shelf radiologically<br>and surgically"] n4 --> n5["As a result of these forces<br>+ the “softness” of the bone"] C --> n6["Hydrocephalus (RARE-Most<br>patient do not have HCP)"] n3 --> n7["Blockage of CSF flow"] & G n7 --> n6 K --> n3 F --> n3 n5 --> n8["Foramen magnum<br>invaginates upward into the<br>skull"] n8 --> n3 n1@{ shape: rect} n3@{ shape: rect} n4@{ shape: rect}
Clinical features
- Present as
- Sudden infant death
- 4x Inc of infant sudden death below 4 years old
- Sleep apnea syndrome
- Respiratory failure, myelopathy
- Syringobulbia/syringomyelia
- Hydrocephalus
- Check for
- Ophistotonus
- Snoring
- Use sleep study to look for
- Mixed
- Airway obstruction which could also be due to enlarged adenoids
- Central sleep apnea (60% have it)
- PT do not move their abdomen when breathing at sleep
- Choking
Imaging


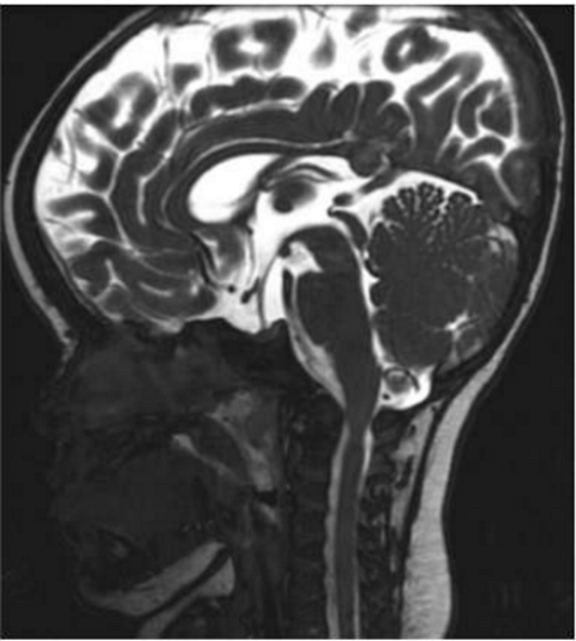
Treatment
- Foramen magnum stenosis
- Operative
- Surgical decompression of foramen magnum
- Indications for surgery
- myelopathy with upper motor neuron signs such as clonus and hyperreflexia,
- Central apnea as documented on sleep study
- Presence of a syrinx, with evidence of a narrow foramen magnum
- T2 signal change in the spinal cord on MR imaging.
- Technique
- Only do bony decompression as opening the Dura and damaging circular sinus can lead to death via exangunsion
- If open dural venous circular sinus will bleed profusely due to raised sinus venous pressure secondary to small skull base foramen