Definition
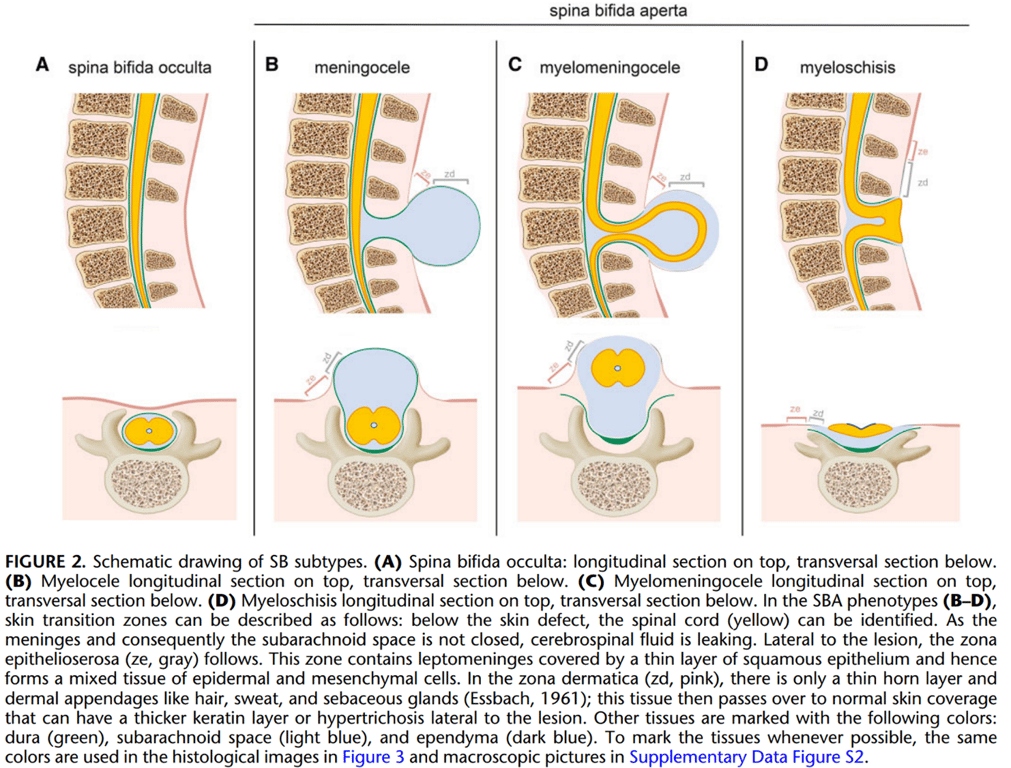
Open spinal dysraphism (Aka formerly spina bifida aperta or cystica):
- Definition:
- occurs when the cord and its covering communicate with the outside;
- no skin or tissues cover the sac
- Myelocele
- Hemimyelomeningocele
- hemimyelocele
Closed spinal dysraphism (formerly spina bifida occulta): occurs when the cord is covered by other normal mesenchymal elements
with subcutaneous mass
- lipoma with dural defect
- lipomyelomeningocele
- lipomyelocele/lipomyeloschisis
- terminal myelocystocele
- Are rare
- Characterised by syringocele (expansion of terminal central canal) herniating through a wide spina bifida and surrounded by a rostral meningocele.
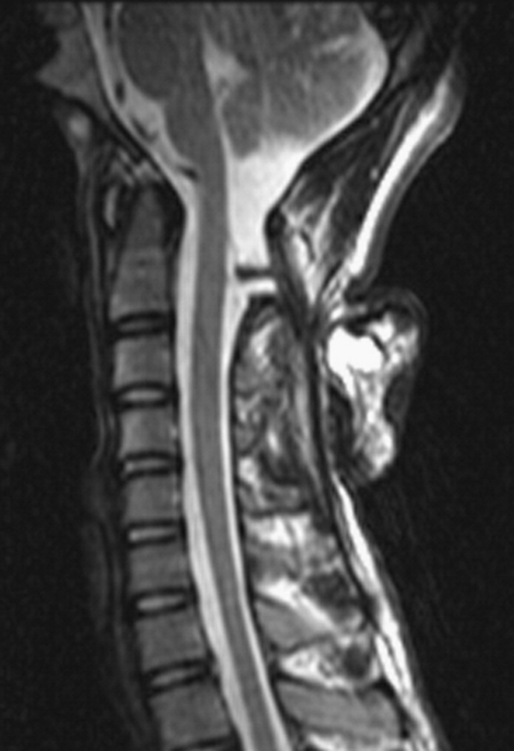
- Meningocele
- Posterior meningocele
- comprises 2.5% of CSD
- consists of herniation of CSF-filled meningeal sac (may also contain nerve roots/filum but not spinal cord) through posterior spina bifida.
without subcutaneous mass
- posterior spina bifida (isolated defect of the posterior neural arch of vertebra)
- intradural lipoma
- filar lipoma
- tight filum terminale
- persistent terminal ventricle
- disorders of midline notochordal integration
- dorsal dermal sinus
- dorsal enteric fistula
- neurenteric cyst
- Split cord malformations
- diastematomyelia
- diplomyelia
- disorders of notochordal formation
- Caudal regression syndrome
- type 1
- type 2
- Segmental spinal dysgenesis