General
- Definition: A rare genetic disorder caused by mutations in filamin B and carbohydrate sulfotransferase 3 deficiency, that presents with characteristic findings of ligamentous hyperlaxity, abnormal facial features, cervical kyphosis, and multiple joint dislocations.
- Diagnosis is made based on family history associated with typical radiographic and clinical features.
- No commercially available diagnostic test exists due to the variety of genetic mutations.
- Treatment is usually open reduction for joint dislocations and early posterior spinal fusion for cervical kyphosis to prevent neurological deterioration.
Epidemiology
- Incidence: 1/100,000
Aetiology
- Genetics
- Both AD and AR inheritance patterns
- AD linked to a mutation of the gene encoding filamin B
- AR linked to carbohydrate sulfotransferase 3 deficiency
Associated conditions
Orthopaedic manisfestations
- Hand deformities
- Dislocations
- Hips
- Knees (usually bilateral)
- Shoulders
- Elbows (radial head)
- Clubfeet
Spinal
- Scoliosis
- Cervical kyphosis
- May present with extremity weakness secondary to myelopathy
- Caused by hypoplasia of the cervical vertebrae
Clinical presentation
Symptoms
- Patients have normal intelligence
Signs
- Hypotonia
- Uncommon but may be due to cervical compression
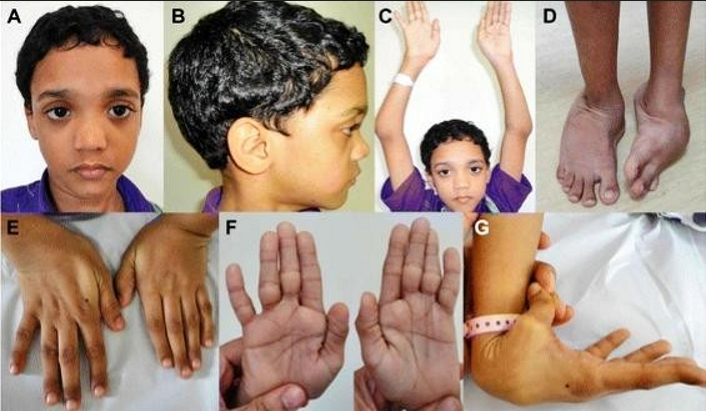
- Abnormal facial features
- Flattened nasal bridge
- Hypertelorism
- Prominent forehead
- Hands
- Long cylindrical fingers that do not taper
- Wide distal phalanx at the thumb
- Elbows
- Bilateral radial head dislocations may be present
- Knees
- Look for bilateral knee dislocations
- Foot deformities
- Equinovarus
- Eqinovalgus
- Clubfeet
Imaging
Radiographs
- AP and lateral of cervical spine
- During first year of life
- Prior to any intubation to avoid iatrogenic spinal cord injury
- AP pelvis and lateral of hips
- Ultrasound if less than 3 months
- Findings
- Hypoplasia of vertebrae
- Cervical kyphosis with subluxation
- Hip dislocation
MRI
- Cervical kyphosis
- Myelopathy
Treatment
- Cervical kyphosis
- Operative
- Posterior cervical fusion
- Indications
- Patients with significant kyphosis but no neurologic deficits
- Recommended to be performed during the first 18 months of life to prevent neurological deterioration
- Anterior/posterior cervical decompression and fusion
- Indications
- Cervical kyphosis with neurologic deficits