Definition
- Separation or slippage of dens from C2 body at the growth plate.
Investigation
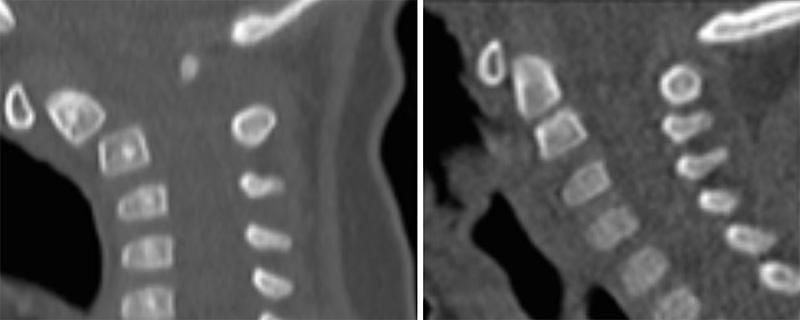
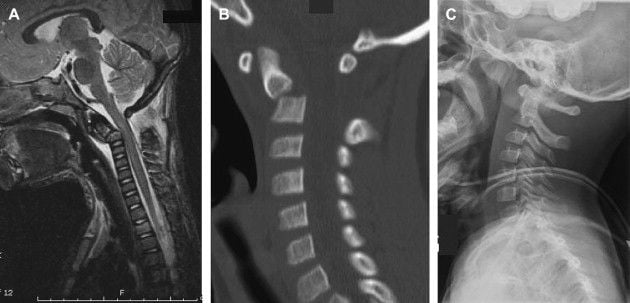
- Lateral C spine xray is diagnostic
- odontoid process to be angulated anteriorly, and rarely posteriorly.
Mechanism
- The neurocentral synchondrosis of C2 that may not fuse completely until age 7 years represents a vulnerable site of injury in young children.
- Injuries to the neurocentral or subdental synchondrosis may be seen in children up to 7 years of age, it most commonly occurs in pre-school-aged children.
- Mimics an odontoid type II fracture.
- Because the injury occurs through the epiphysis, it has a high likelihood of healing if closed reduction and immobilization are employed.
- 23% will develop neurologic deficit,
- 53% of these the SCI level occurs lower at the cervicothoracic junction.
Treatment
- Conservative
- Closed reduction
- Application of the halo device under ketamine anesthesia → realignment of the dens utilising C-arm fluoroscopy.
- Traction can be used but risk of over-distraction.
- External immobilisation (halo)
- for approximately 10 weeks.
- Outcome
- 80% fusion success rate.
- Surgical stabilisation
- Indicated
- External immobilisation is unable to maintain alignment of the odontoid atop the C2 body.
- Persistent instability after 3–6 months