General
Pre-op
- Nurse baby prone
- prevent desiccation—keep the exposed neural tissue moist.
- Wrap open leaking defect in sarin wrap
- Examination
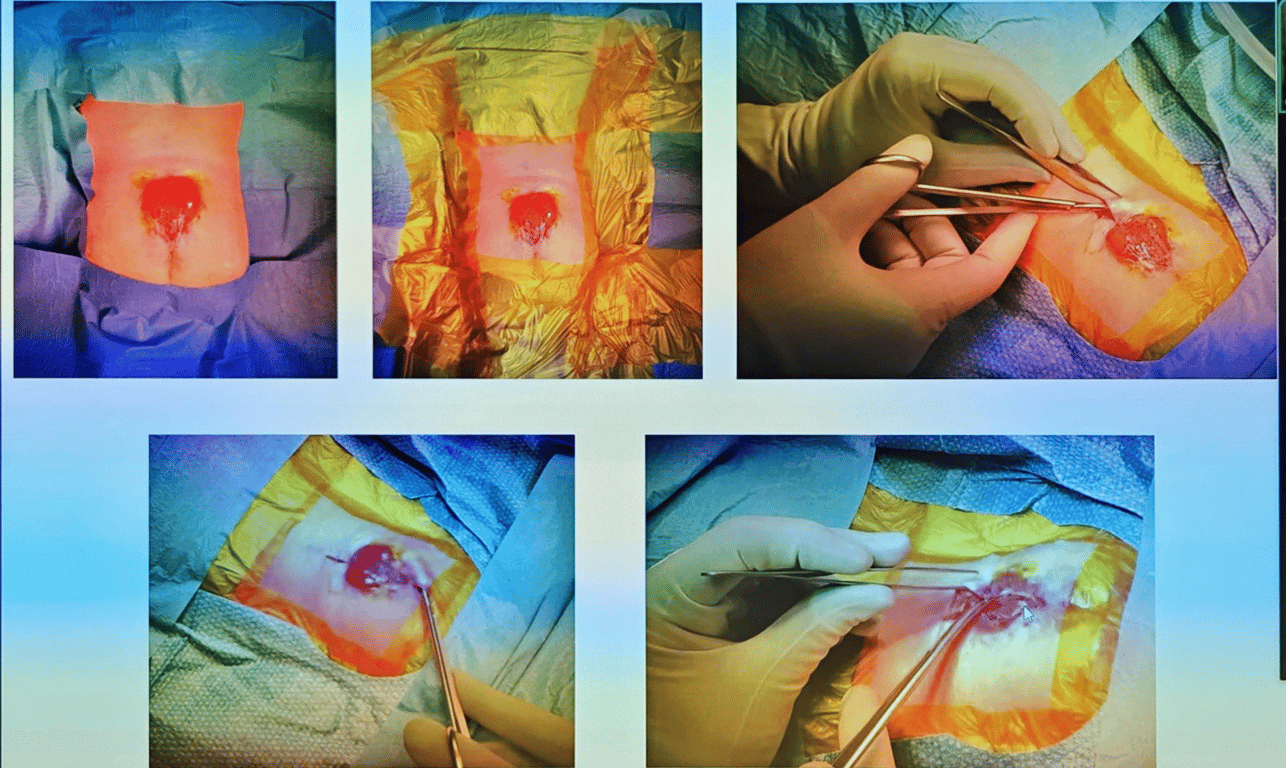
- Measure the skin defect
- if the skin defect with is larger than the height plastic will be needed
- Examine to see any contraction when dorsiflexing the ankle
- Check anal tone and wrinkling of the anal verge
- Consent and book patient into theatre lists and inform plastics if required
- Vancomycin infusion
- Use latex-free environment
- Reduces development of latex allergy, as well as attack by maternal antibodies that may have crossed through the placenta.
- Do not allow scrub solutions or chemical antimicrobials to contact neural placode.
- Betadine is neurotoxic
- Do not use monopolar cautery.
Intra-op
- Help with intubation of child when supine
- Get neonatal set ready
- Clean skin with saline
- Betadine contact with neural tissue is toxic
- Drape widely to allow for plastic skin mobilization
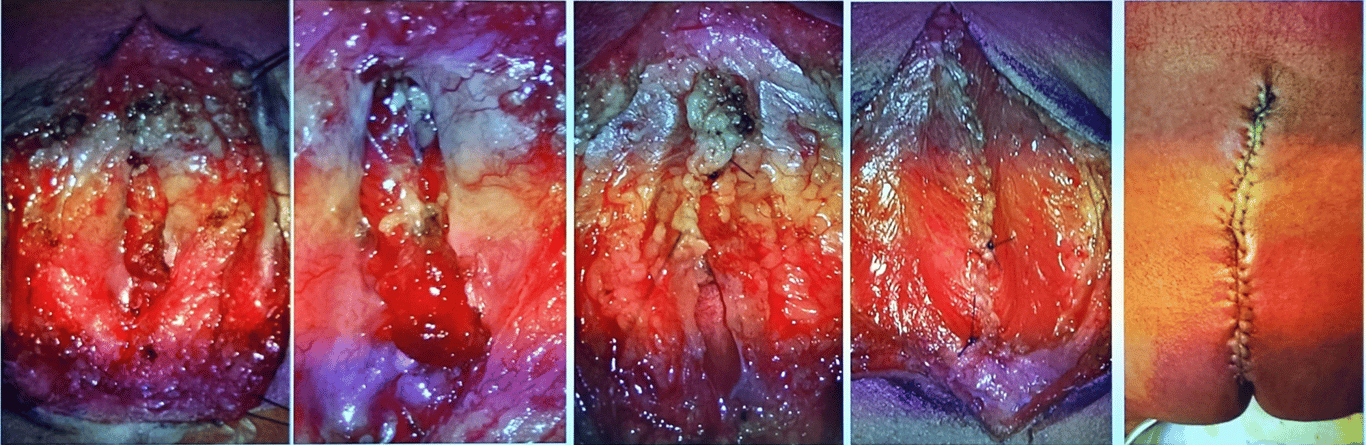
- Using microscope or loops identify the neural placode and it's layers
Dealing with pathology
- Begin by dividing the abnormal epithelial covering from the normal skin.
- The pia-arachnoid may be separated from the neural tissue.
- Define the pia layer (placode) and dissect it off the surrounding tissues suture the pia layer with 5.0 pds
- place 3 tagging sutures to close the open chord before running a continuous suture
- Avoid placing tension on the neural placode.
- The dura
- It often helps to start with normal dura above, and then work down.
- The dura can then be isolated around the periphery and followed deep to the spinal canal superiorly.
- The dura is then also formed into a tube and approximated in a water-tight closure.
- If the dura cannot be closed, the placode may be judiciously trimmed.
- Use 5.0 PDS to tag the Dura together to running suture to close the dual defect
- Place tisseal glue on the sutured pseudo-dura
- The filum terminale should be divided if it can be located.
- The skin is then mobilized and closed.
- Dermoid tumors may result from retained skin during the closure, but alternatively dermoids may also be present congenitally.
- Kyphotic deformity,
- Repaired at the same sitting as the MM defect closure.
- The kyphotic bone is rongeured, and 2–0 Vicryl is used to suture the adjacent bones.
- Post op bracing optional
- Skin closure plastics involvement with 4.0 monocyrl
- Multiple layer closure
- 5 layers should be attempted if not 2
- Benefit
- If tethering occurs in the future can be easier to release with multilayerd closure
- No evidence that multiple layer closure either improves neurologic function or prevents later tethering,
- Silastic does not prevent adherence in series with long follow-up (>6 yrs), and may even render untethering procedures more difficult.
Post op
- MRI Whole spine and brain
- Keep patient off all incisions
- Bladder catheterization regimen
- Daily OFC measurements
- Avoid narcotics
- Midbrain malformation (associated chiari 2) renders these patients more sensitive to respiratory depression from narcotics
- If not shunted
- Regular head U/S (twice weekly to weekly)
- Keep patient flat to ↓ CSF pressure on incision
- If a kyphectomy was done, use of a brace is optional (surgeon preference)
Images