General
- Most cases are found in children younger than 3 years.
- If they protrude into the cranial cavity, they may be the source of cerebral symptoms.
- Are ectodermal rests or inclusions that may be located in the
- Scalp,
- Diploic spaces,
- Between the internal surface of the inner table and the dura.
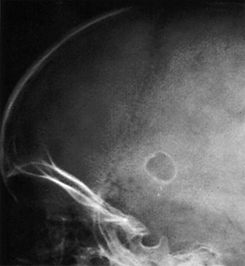
Xray
- A small oval defect in the parietal bone with a sharply defined sclerotic border.
- The margin is due to flaring of the edge of the bone into a marginal ridge.
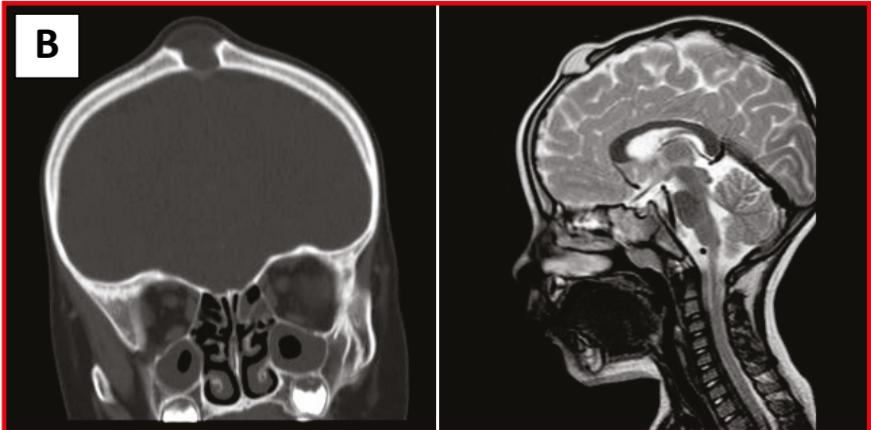
CT
- When epidermoid grow within the bone or impinge on it, they produce local destruction of bone that appears radiographically as a sharply demarcated lucency surrounded by a smooth sclerotic margin, which sometimes may be scalloped.
Natural history
- Epidermoids are usually benign and grow slowly
- The lesions usually disappear within a few years of discovery.
Surgery
- Indication
- Infected or at risk lesions
- Dermoid cysts that have a tract to the skin represent an infection risk.
- Cosmesis,
- To confirm histological diagnosis
- Lesion is painful when a patient lies down or combs their hair etc.