General
- Aka:
- Olfactory neuroblastoma
- Olfactory esthesioneuroblastoma
- Esthesioneurocytoma
- Olfactory placode tumour
- Growth
- Slow growing
- Begin as masses in superior olfactory recess → involve the anterior and middle ethmoid air-cells unilaterally → destroy surrounding bone → enter
- Anterior cranial fossa
- Orbits
- Ostia of paranasal sinus → sinus opacification
Numbers
- Incidence: 0.4/1million
- Age: 3-90 yrs
- Bimodal peak
- 20-30 yrs
- 60-70 yrs
Origin
- Olfactory neural crest cells in the upper nares
Clinical presentation
- Nasal stuffiness
- Rhinorrhea
- Epistaxis
- Often present late as there is large amount of space for tumour to grow
Grading system
- Histological- Hyams 1988
- High (1/2) vs low (3/4)
Microscopic Features | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
Pleomorphism | − | + | ++ | +++ |
Lobular architecture | + | + | +/− | +/− |
Neurofibrillary matrix | +++ | + | +/− | − |
Rosettes | + | + | +/− | +/− |
Mitoses | − | − | + | +++ |
Necrosis | − | − | + | +++ |
- Clinical- Kadish 1976
- There are a few different ones (Biller, Dulguerov and calcattera) but Kadish is the most fq used. Survival-Konuthula et al 2017
- Paradoxically B is better than A, (Kadish stage did not correlate with survival for early-stage disease) reason
- Selection bias
- B receive more aggressive treatment than A
- A is operated by non oncological surgeons
- Database data collection error
Modified Kadish | Features | 10-yr survival | Treatment |
A | Confined to Nasal Cavity | 80% | Endoscopic resection |
B | Extends to Paranasal Sinus | 88% | Endoscopic resection |
C | Local Extension (orbit or cribriform plate) | 77% | Bifrontal craniotomy with associated lateral rhinotomy |
D | Distant Metastasis | 50% | Bifrontal craniotomy with associated lateral rhinotomy |
Imaging
- General characteristic
- Dumpbell shaped mass: as it grows through the cribriform plate into the brain
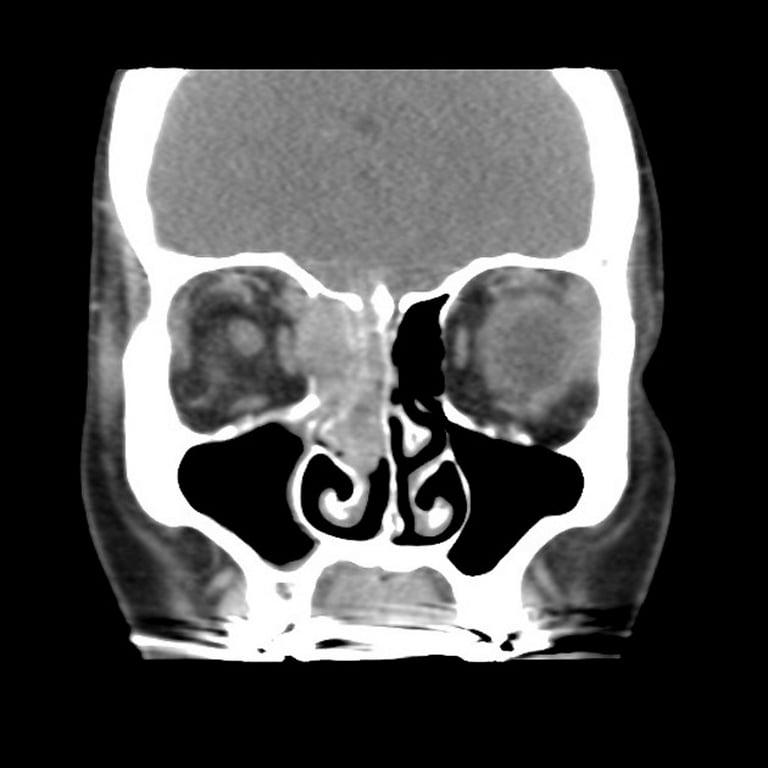
- CT
- Bony destruction
- Slow growing → bone is not aggressively destroyed but is remodelled and reabsorbed
- Soft tissue attenuation
- Focal calcification
- CT+C: homogeneous enhancement

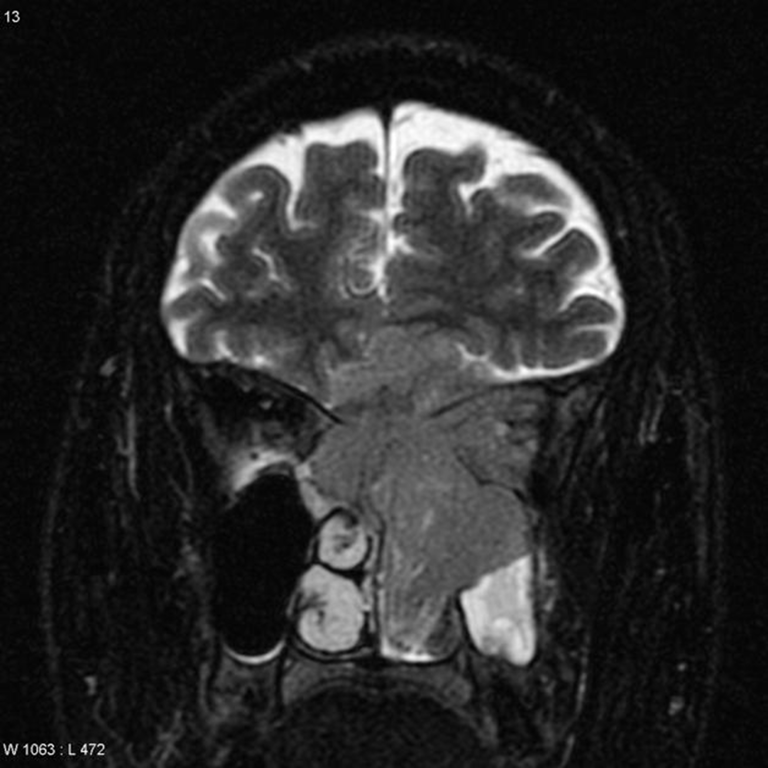
- MRI
- T1: heterogeneous intermediate signal
- T2: heterogeneous intermediate signal
- T1 C+ (Gd): variable enhancement (usually moderate to intense)
- If invades intracranially → forms peritumoral cyst between esthesioneuroblastoma and brain. Used for differential diagnosis


- Angiography/DSA
- Prominent tumour blush with arteriovenous shunting and persistent opacification.
- Nuclear medicine
- Same with other neuroblastoma
- MIBG-avid
Histopathology
- Macroscopic
- Multilobulated pink-grey tumour
- Microscopically
- Variable differentiation,
- Well-formed neural tissue to undifferentiated neuroblasts with pseudorosette formation
Treatment
- Surgery → chemo/radio
- See above
Prognosis
- Median overall survival (Van Gompell) is typically 7.2 yrs
- Mean progression free survival (Van Gompell) is 4.8 yrs
- 5 year survival (Konuthula): 77%
- 10 year survival (Konuthula): 67%
- Recurrent disease occurs in 2 pattern
- Intracranial recurrence → repeat transcranial resection or stereotactic radiosurgery
- Distant metastasis (even with lymph node disease) → modified radical neck dissection to understand extent of the disease → chemotherapy (platinum)