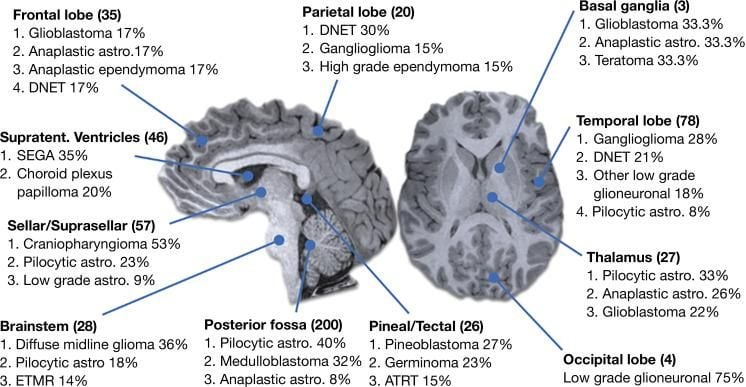
For all tumour
- Paediatric brain tumours, 2nd only to haematological malignancies
- Overall incidence approximately 5/100,000 persons/year (compared to 20-30/100,000 in adults)
- 60-70% are gliomas;
- Age variation for all tumours
Commonest cancers in <1 year: | Commonest cancers 1-10 years: | Commonest cancers >10 years: |
Neuroblastoma Leukaemia Germ cell tumours CNS tumours Wilms tumour | Leukaemia's CNS tumours Neuroblastoma Wilms tumor Germ cell tumors/Soft tissue sarcoma | Leukemias CNS tumors Lymphoma Bone tumors/Soft tissue sarcomas Germ cell tumors |
- Childhood mortality UK
- Brain tumours 35%
- Leukaemia 21%
- Tumours of other sites 44%
For CNS tumours
- Most common malignant paediatric tumour: Medulloblastoma
- Most common paediatric tumour is pilocytic astrocytoma
- Specific frequency for all ages
- Astrocytomas 30%, 0.84/100,000/year
- Medulloblastoma (15-20%), 0.65/100,000/year
- Craniopharyngioma (10-15%), 0.73/100,000/year
- Ependymomas (5-10%), 0.28/100,000/year
- germ cell tumours (5-10%)
- Primary childhood CNS tumors incidence by WHO group:
- Neuroepithelial tissue: 3.7/100,000
- Astrocytic: 1.3/100,000/year
- Ependymoma: 0.28/100,000/year
- Sellar region: 0.73/100,000/year
- Embryonal CNS tumors: 0.65/100,000/year
- Neuronal and mixed neuronal-glial: 0.37/100,000/year
- Unclassified: 0.3/100,000/year
- Cranial and paraspinal nerves: 0.27/100,000/year
- Meninges: 0.22/100,000/year
- Germ cell tumors and cysts: 0.21/100,000/year
- Lymphoma and hemopoetic: 0.03/100,000/year
- Age variation for CNS tumours
- Extremely rare, 0.5-1.5%
- Improved fetal USG and fetal/neonatal MRI
- Distinct histological and clinical behaviour compared to tumours of infancy (1-2 years old)
- The most common type is teratoma (26.6% to 48%)
- Frequently occur before 32 weeks of gestation
- Resemble normal embryonic development
- Possibly due to aberrant and residual cells during the formation of CNS
- Others:
- Astrocytoma (7.4% to 28.8%)
- Choroid plexus papilloma (3.7% to 13.2%)
- Embryonal tumor (3% to 13%)
- Supratentorial tumors:
- Ratio: 1.5:1 (more common than infratentorial)
- Common types:
- High-grade astrocytomas
- Ependymomas
- Medulloblastomas
- Other rare embryonal tumors:
- Supratentorial PNET (Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor)
- ATRT (Atypical Teratoid Rhabdoid Tumor)
- Supratentorial tumours are more common in <3 years
- Posterior fossa tumours are more common between 3-11 years
- Paediatric PF tumours are less common than superior tentorial tumour
- Posterior fossa tumours
- Commoner in children over 1 year old
- Constitute just under 2/3 of intracranial tumours >1
- Supratentorial commoner in < 1
- Only 15% in adults.
0-4 years | 5-9 years | 10-14 years | 15-19 years |
Gliomas (excluding PA) Pilocytic astrocytoma Medulloblastoma PNET Pituitary tumors | Gliomas (excluding PA) Pilocytic astrocytoma Medulloblastoma PNET Pituitary tumors | Gliomas (excluding PA) Pilocytic astrocytoma Medulloblastoma PNET Pituitary tumors | Gliomas (excluding PA) Pilocytic astrocytoma Medulloblastoma PNET Pituitary tumors |
Age dependent relative fq
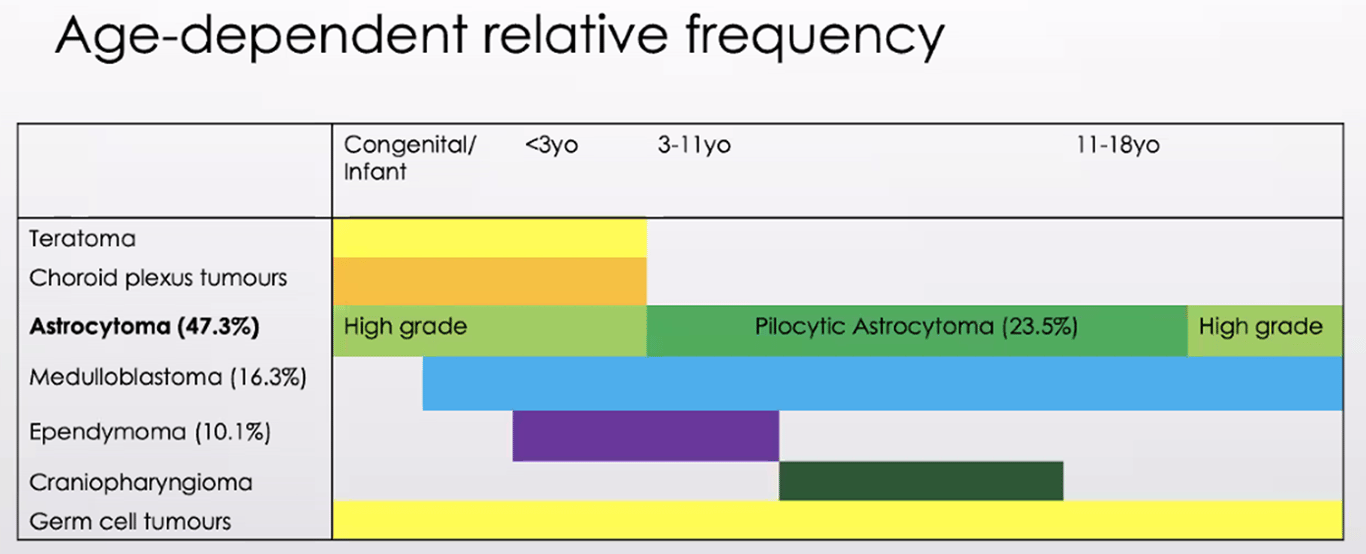
Congenital brain tumours < 60 days
Tumors in Young Children (<3 years old)
Location
Tumour | % of posterior fossa tumours in children |
Pilocytic astrocytomas | 35% |
Medulloblastoma | 30% |
Ependymomas | 20-30% |
Brainstem gliomas | 10-20% |
- Paediatric brain mets
- Overall rate approximates 4% in patient followed up > 10 years.
- Cerebral hematogenous metastases were reported in (Curless
2002)
4.4% | Neuroblastoma |
1.9% | Rhabdomyosarcoma |
6.5% | Osteosarcoma |
3.3% | Ewing sarcoma patients |
3.6% | melanoma patients |
13.5% | germ cell tumors |
1.3% | Wilms tumor |
Treatment decision making
- Importance of avoidance of morbidity , in particular endocrine and hypothalamic functions which may affect growth
- Long term sequelue with chemo/RT
Common syndromes
- Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (Gorlin's syndrome)
- Turcot's syndrome A
- Li-Fraumeni syndrome
- Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome