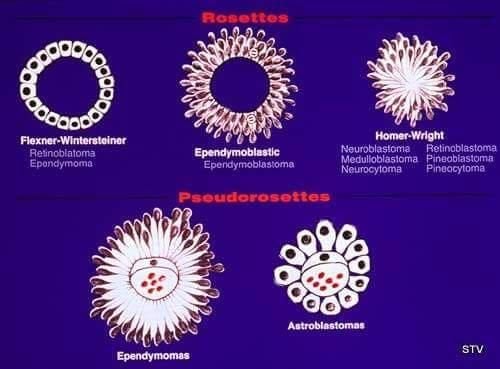
Summary of rosette patterns and associated tumors
Rosette Type | Associated Tumors |
Homer Wright rosette | Neuroblastoma, medulloblastoma, primitive neuroectodermal tumor, pineoblastoma |
Flexner-Wintersteiner rosette | Retinoblastoma, pineoblastoma, medulloepithelioma |
True ependymal rosette | Ependymoma |
Perivascular pseudorosette | Ependymoma, medulloblastoma, primitive neuroectodermal tumor, central neurocytoma, glioblastoma, monomorphous pilomyxoid astrocytomas |
Pineocytomatous rosette | Pineocytoma |
Neurocytic rosette | Central neurocytoma |
General
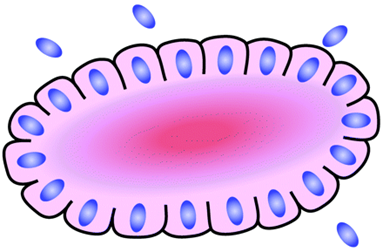
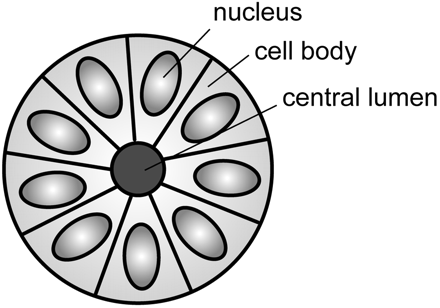
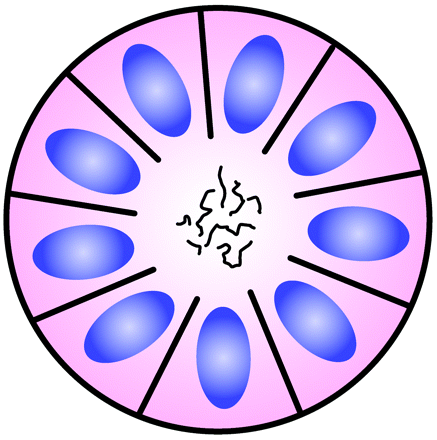
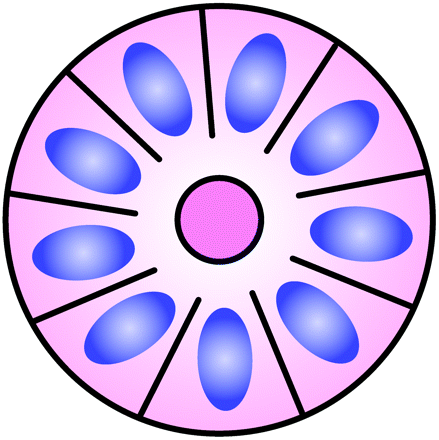
- Halo or spoke-wheel arrangement of cells surrounding a central core or hub (central hub may consist of an empty-appearing lumen or a space filled with cytoplasmic processes
- Primary vs secondary
- Primary rosettes form as a characteristic growth pattern of a given tumor type.
- Secondary rosettes result from the influence of external factors on tumor growth.
- Local swelling
Types
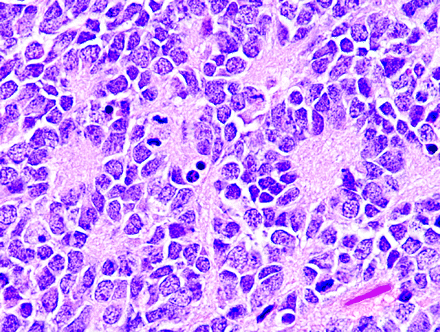
- Homer Wright Rosette
- Core:
- Neuropil: primitive neuronal processes or neurites
- Found in
- PNETs (Primitive neuroectodermal tumours of the central nervous system (CNS PNET)-no longer used term but use to be an umbrella term for
- Medulloblastomas
- Pineoblastomas
- Embryonal tumour with multi-layered rosettes (Ependymoblastoma)
- Medulloepithelioma
- High-grade glioma
- Mech of formation: unknown
- Sign of neuronal differentiation
- Neuron mature and differentiate → neuron cell bodies secrete adhesion molecules → cell bodies attach to each other → forcing the neuropil (primitive neuronal processes or neurites) to clump up in the center → forming Homer Wright Rosette
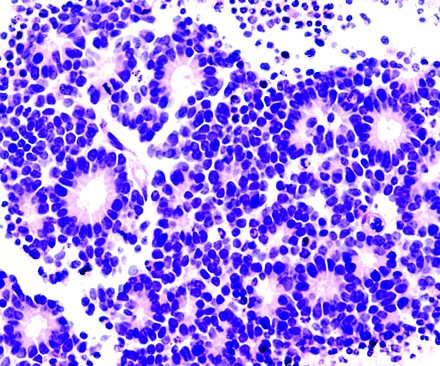
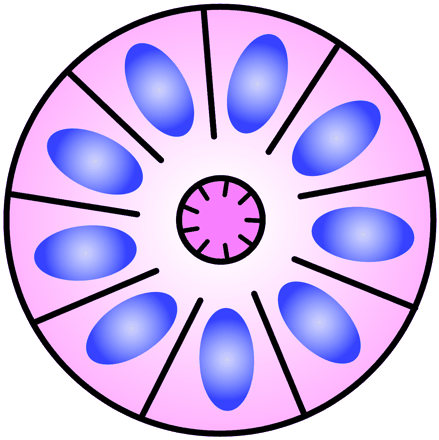
- Flexner-Wintersteiner Rosette
- A halo of cells surrounds a largely empty central hub. Small cytoplasmic extensions from the cells project into the lumen.
- Core:
- Small cytoplasmic extensions of the encircling cells
- Found in
- Retinoblastomas
- Mechanism
- A sign of neuronal differentiation
- Form mech might be like homer wright rosette
- True Ependymal Rosette
- Core: empty
- Can be elongated rather than a ball like: called ependymal canals
- Mech
- May represent an attempt by the tumor cells to recapitulate the formation of ventricles with ependymal linings
- Found in ependymoma
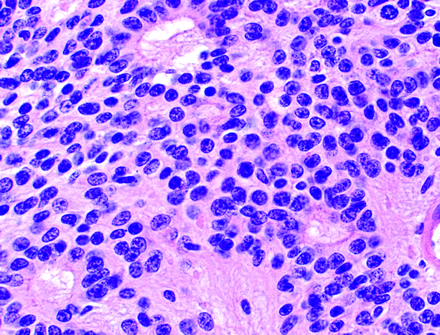
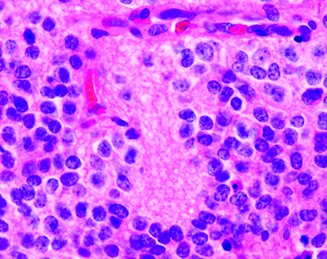
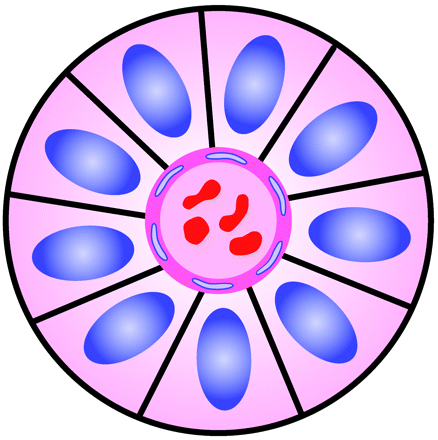
- Perivascular Pseudo-rosette
- Core: blood vessels
- Pseudo because it is not a true lumen in the centre
- Found in (MEN GAP Pants)
- Glioblastoma
- Astroblastoma, MN1-altered
- Angiocentric glioma
- Pilomyxoid astrocytoma
- Ependymomas
- Better than true ependymoma rosette in dx ependymoma
- Neurocytomas (central)
- PNETs
- Medulloblastomas
- Mech
- No idea
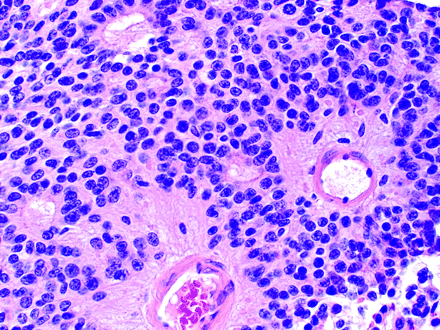
- Pineocytomatous and Neurocytic Rosettes
- Located in
- Internal granular layer of the cerebellum
- Dentate fascia of the hippocampus
- Core:
- Neuropil-rich rosettes
- Similar to the Homer Wright rosette, but they are generally larger and more irregular in contour
- These cells are more differentiated than homer-wright rosettes cells
- Found in
- Pineocytomatous rosettes in pineocytomas
- Neurocytic rosettes in central neurocytoma