BRAF V600E
Gene loci
- Chromosome 7q34.
Normal function
- BRAF encodes serine/threonine kinase in MAPK/ERK pathway, activated by RAS, phosphorylates MEK1/2 for ERK activation regulating growth, survival, differentiation.
Mutation effects
- V600E substitutes valine with glutamic acid at codon 600, mimicking phosphorylation, causing RAS-independent constitutive activation, leading to sustained MAPK signaling, promoting proliferation, survival, angiogenesis.
- Valine (V) is substituted by glutamic acid (E) at amino acid 600 → negative charge of the acidic glutamic acid residue causes it to mimics the phosphorylation of the nearby T599 threonine and S602 serine residues in the activation segment of BRAF, which are used to activate the wild type form of the protein. → The glutamate residue of the mutant therefore functions to activate BRAF by inhibiting the interaction of the BRAF's glycine rich loop and activation segment, which would ordinarily be inhibitory. → The loss of inhibition of BRAF leads to an increase in its basal activity and hence is oncogenic.
Detailed description: A point mutation
Clinical association
- Melanoma (~50%),
- Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC, 40-60%),
- Colorectal cancer (8-12%)
- NSCLC (1-2%)
- Hairy cell leukemia
- CNS tumours
- Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytomas
- Pilocytic astrocytomas/Pilomyxoid astrocytoma
- Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial tumours (DNET)
- Ganglioglioma
- Polymorphous low-grade neuroepithelial tumour of the young (PLNTY)
- Diffuse low-grade glioma, MAPK pathway-altered
- Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma / desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma
- Erdheim Chester disease
- Langerhan cell Histiocytosis
- Papillary type of craniopharyngioma
- Diffuse low-grade glioma, MAPK pathway-altered
Targetable treatment
- Targetable by BRAF inhibitors (vemurafenib, dabrafenib);
- Dabrafenib
- Inhibitor of the associated enzyme B-Raf
- Side effects include papilloma (warts), headache, nausea, vomiting, hyperkeratosis (thickening and toughening of the skin), hair loss, rash, joint pain, fever and tiredness
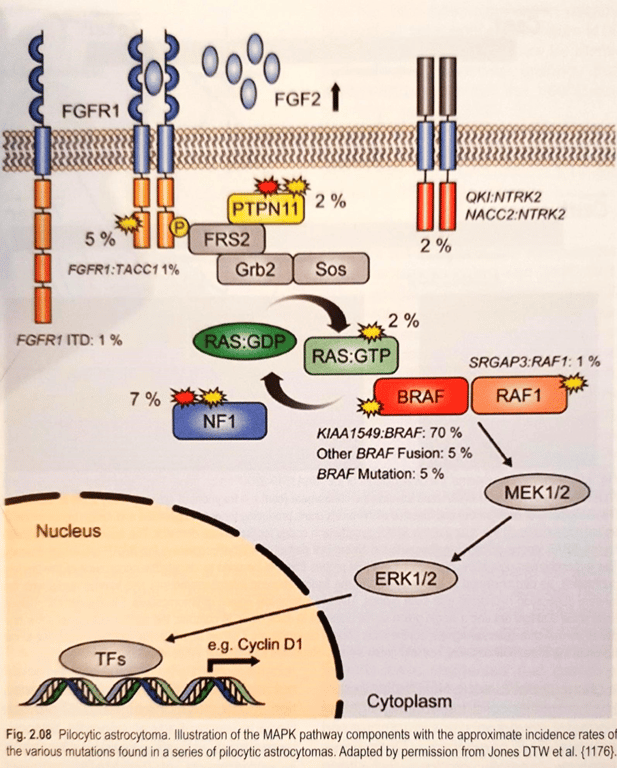
BRAF:KIAA1549 fusions
- Gene loci
- Tandem duplication on chromosome 7q34 involving KIAA1549 (exons 1-16/15) and BRAF (exons 9/11 onward).
- Normal function
- BRAF: Serine/threonine kinase in MAPK pathway, transduces signals from RAS to MEK/ERK for proliferation, differentiation.
- KIAA1549: Unknown/poorly characterized.
- Mutation effects
- KIAA1549 attached to BRAF (KIAA1549 while attaching removes the regulatory domain of BRAF) allowing it to be always activated. → MAPK/ERK activation independent of RAS → Drives neural stem cell proliferation, glioma formation.
- Tumours
- Pilocytic astrocytomas/Pilomyxoid astrocytoma
- Fusion occurs in approximately 60–70%
- Better prognosis.
- Rare