Basic
Epigenetic Mechanism | Description | Additional Information |
DNA methylation | Changes the expression of a DNA segment without changing the sequence. Involved with aging, carcinogenesis, genomic imprinting, transposable element repression, and X chromosome inactivation (lyonization). | DNA is methylated in imprinting. Methylation within gene promoter (CpG islands) typically represses (silences) gene transcription. CpG methylation makes DNA mute. Dysregulated DNA methylation is implicated in Fragile X syndrome. DNA methylation is like for MGMT methylation |
Histone methylation | Usually causes reversible transcriptional suppression, but can also cause activation depending on location of methyl groups. | Histone methylation mostly makes DNA mute. Lysine and arginine residues of histones can be methylated. Histone methylation is like for H3 methylation |
Histone acetylation | Removal of histone’s ⊕ charge → relaxed DNA coiling → ↑ transcription. | Thyroid hormone synthesis is altered by acetylation of the thyroid hormone receptor. Histone acetylation makes DNA active. |
Histone deacetylation | Removal of acetyl groups → tightened DNA coiling → ↓ transcription. | Histone deacetylation may be responsible for altered gene expression in Huntington disease. Histone deacetylation deactivates DNA. |
Tumours involved
- Histone proteins responsible for DNA packaging in paediatric GBM (H3K27M and H3G34R/ V
mutations) - Mutations of histone H3 family 3A (H3F3A) have been identified in paediatric brain stem and midline glioblastomas
- Diffuse midline glioma, H3 K27-altered
- Altered because H3K27 can be
- H3K27M nucleosome mutation OR
- EZHIP overexpressed
- H3K27Mutations that cause low H3K27me3 levels in diffuse midline gliomas (DMG), are rare in PFA ependymomas and have been identified in only 4.2% of cases
- Diffuse hemispheric glioma, H3 G34-mutant
- Point mutations between glycine- to- arginine/ valine alteration at codon 34 (G34R/ V) within H3F3A.
- In adults they occur in 3.4% of all glioblastomas
- These tend to be midline tumours in younger adults
- Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumour
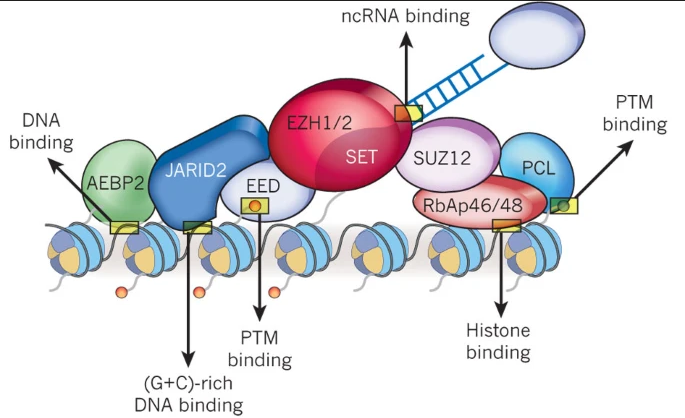
- Mutation of SUZ12 and EED → inactivation of PRC2 → Loss of H3 p.K28me3 (K27me3) methylation
- Posterior fossa Ependymoma A (PFA)
- EZHIP over expression rather than H3K27Mutations
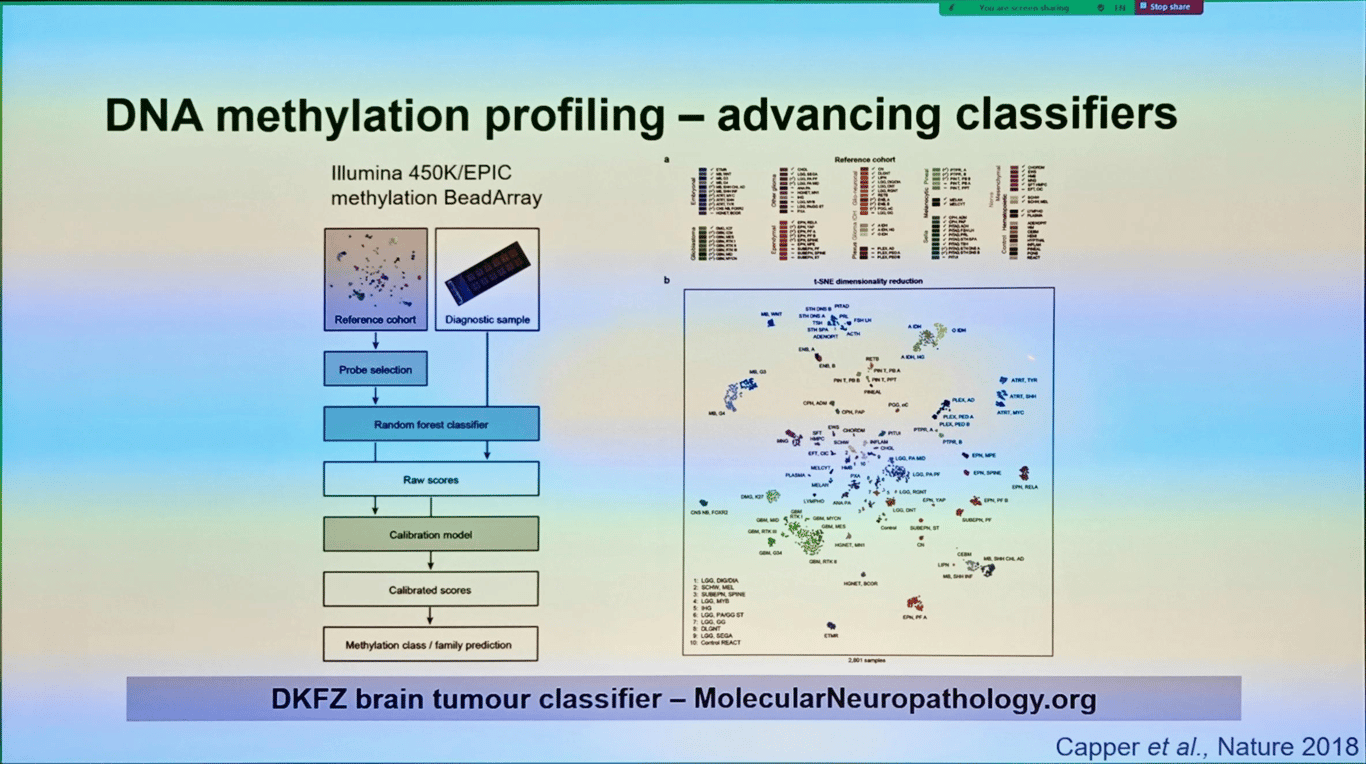
DNA methylation profiling