- The fundamental unit of chromatin is the nucleosome particle, consisting of core histone proteins (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4) around which the DNA is wrapped.
- With the exception of H4, all core histone proteins have variant counterparts, which often differ in surprisingly few amino acids
- Mammalian cells have seven known sequence variants of histone H3.
- These are denoted as Histone H3.1, Histone H3.2, Histone H3.3, Histone H3.4 (H3T), Histone H3.5, Histone H3.X and Histone H3.Y but have highly conserved sequences differing only by a few amino acids.
- Can be
- Suppressed via methylation (H3K27me3) → increase transcription → more cancer
- Activated via acetylation (H3K27ac) → decrease transcription → less cancer
- Methods of acetylation (reduce methylation of H3 histones)
- H3K27M:
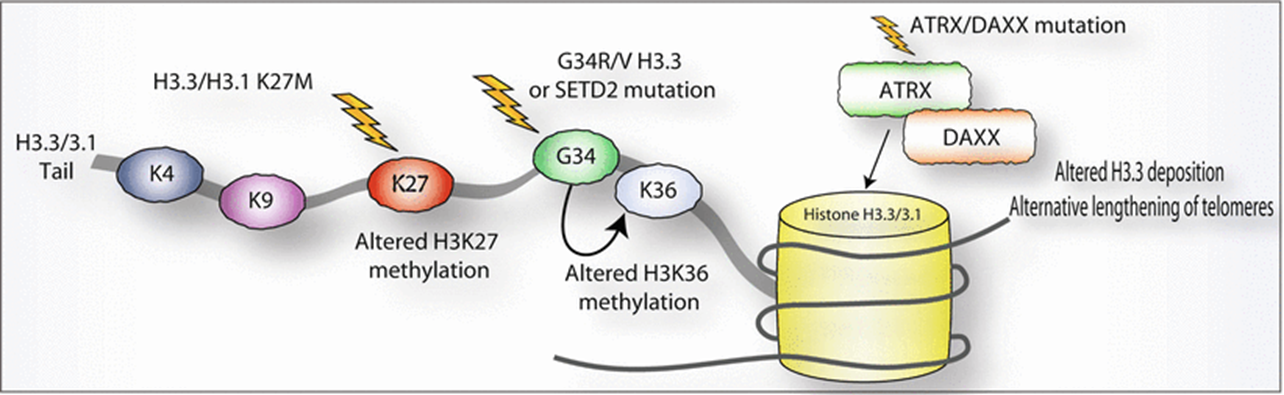
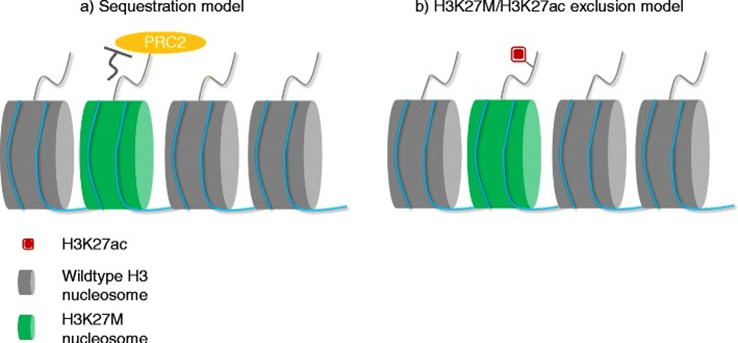
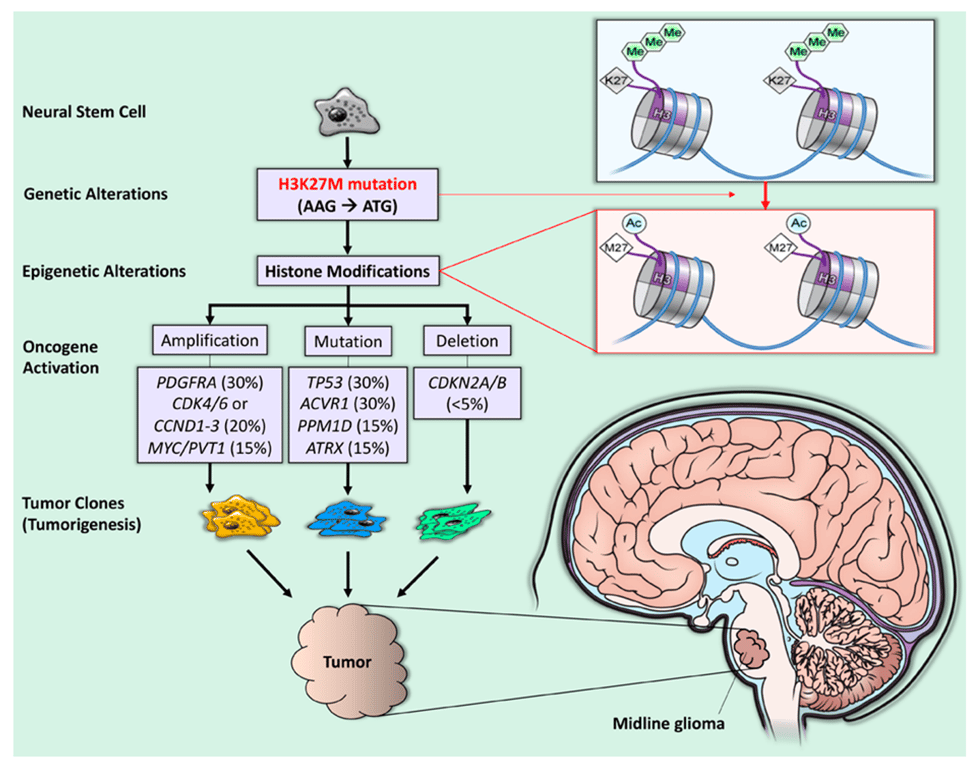
- Gain-of-function missense mutation (AAG → ATG), resulting in a lysine 27 to methionine (p. Lys27Met: K27M) substitution in histone 3 (H3) variants → Forming H3K27M nucleosome → H3K27M (but not H3 wt) interferes with the function of EZH2 → PRC2 cannot methylate H3K27M → so always in H3K27ac form
- The H3K27M mutation leads to the global loss of H3K27 trimethylation (green hexagons) and subsequent gain of H3K27 acetylation (blue circles), which is linked to oncogenesis (gene amplification, mutation, and deletion) and, subsequently, tumorigenesis
- H3 G34-mutant:
- An acquired missense mutation in the H3-3A (H3F3A) gene, resulting in substitution at position p.G35 (G34) on the tail of the histone variant H3.3 → replacement of the amino acid glycine (G) with arginine (R) or valine (V) leads to steric hindrance and blocks the capacity of НЗ p.K37 (K36) methylation-modulating enzymes (SETD2 and KDM2A) to bind to the mutant histone H3.3 tail. → diminished levels of H3 p.K37me2 (K36me2) and H3 p.K37me3 (р.КЗ6meЗ) on the mutant histone H3.3 tail → transcriptional reprogramming → recapitulating that of the developing forebrain, and causes prominent upregulation of the protooncogene MYCN
- Normally (at the differentiated cells):
- EZH2 part of PRC2 will allow PRC2 to methylate Histone (H3) → supressing transcription of oncogenes
- In PFA (Ependymoma) and DMG H3K27 altered
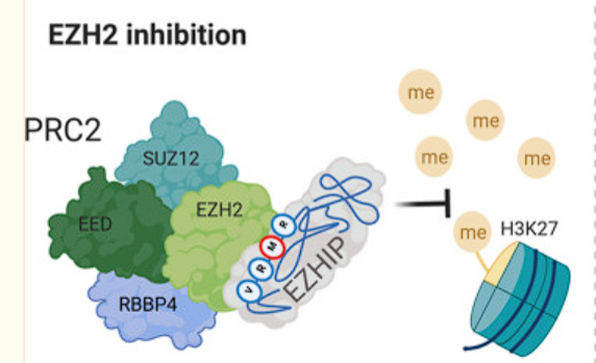
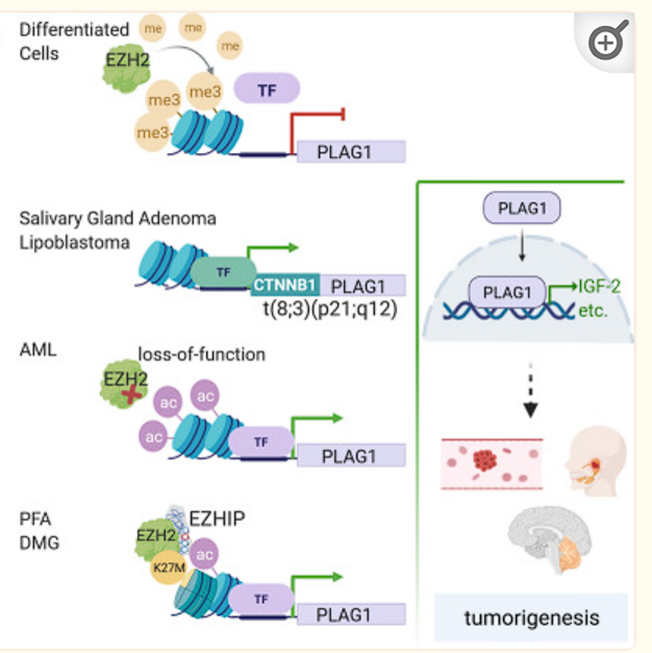
- EZHIP is expressed → EZHIP binds to EZH2 on PRC2 → PRC2 cannot methylate Histones → acetylation of histones occur → increased transcription of oncogenes (PLAG1) → cancer causing
Abbr. | Meaning |
H3 | H3 family of histones |
K | Standard abbreviation for lysine |
27 | Position of amino acid residue (counting from N-terminus) |
me | Methyl group |
3 | Number of methyl groups added |
Histone mutation
Enhancer of zeste homolog inhibitory protein (EZHIP) expression → EZHIP binds to EZH2 on PRC2 → PRC2 cannot methylate Histones → acetylation of histones occur → increased transcription of oncogenes (PLAG1) → cancer causing