Consist of
- Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs)
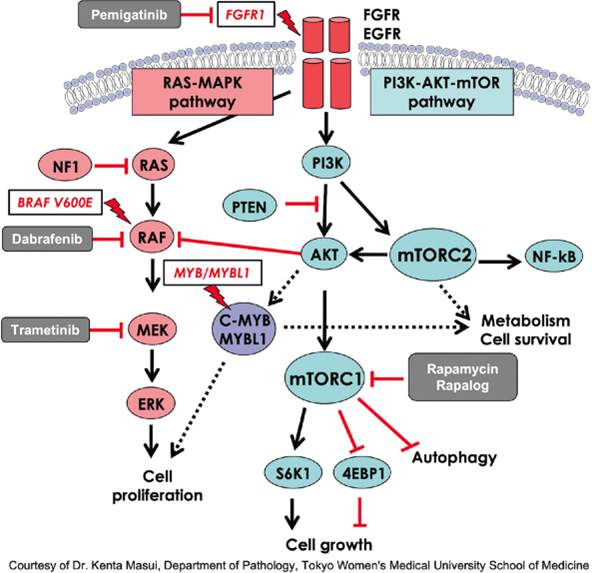
- Mutations or amplifications in EGFR, other RTKs activate upstream MAPK signaling.
- RAS GTPases
- Oncogenic mutations in HRAS, KRAS, NRAS (most frequent MAPK alterations) lock RAS in GTP-bound active state.
- RAF kinases
- BRAF mutations (e.g., V600E), fusions (e.g., KIAA1549-BRAF), CRAF alterations; class I (high activity), class II/III (impaired kinase).
- MEK kinases
- Mutations in MAP2K1 (MEK1), MAP2K2 (MEK2) cause constitutive activation.
- ERK1/2
- Rare mutations/amplifications leading to hyperactivation.
- Other modules
- JNK pathway (MAPK8/9/10, MAP2K4/7), p38 pathway (MAPK14/11/12/13, MAP2K3/6) mutations.
Associated tumours
- Pilocytic astrocytoma (pLGG, ~70% MAPK alterations: BRAF fusions, V600E, NF1).
- Polymorphous low-grade neuroepithelial tumor of the young (PLNTY, BRAF V600E, FGFR2/3).
- Diffuse astrocytoma, AYA-type (MAPK-altered: NF1, PTPN11, BRAF, CDKN2A/2B del).
- Ganglioglioma, high-grade glioma (BRAF alterations).
- Glioblastoma (GBM, p38 MAPK activation correlated with grade, invasion).
- H3K27M-mutant diffuse midline glioma (some MAPK alterations in long survivors).
- Diffuse low-grade glioma, MAPK pathway-altered