General
- PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog
Gene loci
- Chromosome 10q23.31.
Normal function
- Encodes a dual‑specificity phosphatase whose main role is lipid phosphatase activity: it dephosphorylates PIP3 to PIP2, antagonizing PI3K and thereby inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.
- Acts as a tumor suppressor by regulating cell‑cycle progression, apoptosis, metabolism, migration, and stem cell self‑renewal through negative control of PI3K/AKT and additional protein targets.
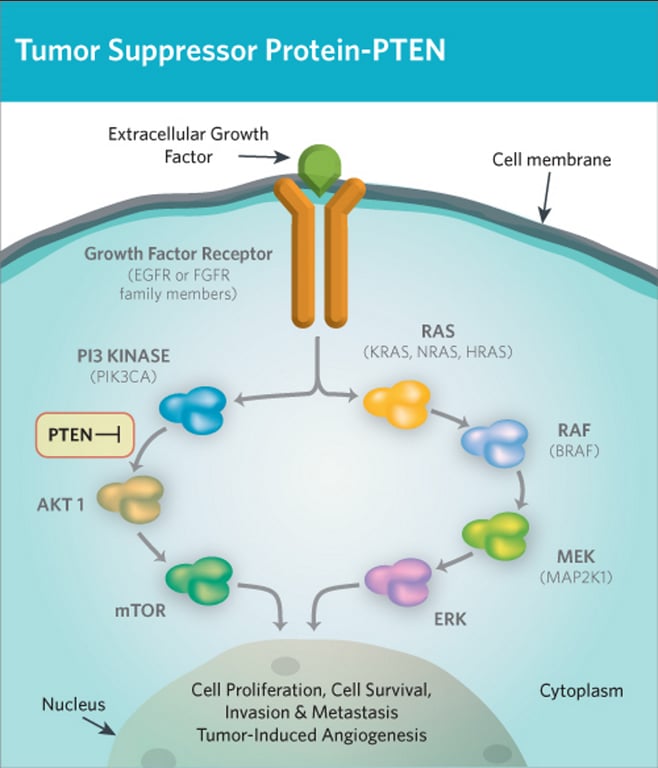
Mutation effects
- Somatic alterations (missense, nonsense, frameshift, splice, deletions, promoter methylation) cause loss or reduction of PTEN function, leading to unchecked PI3K/AKT/mTOR activation, enhanced proliferation, survival, and genomic instability.
- Germline loss‑of‑function mutations reduce PTEN dosage and confer a systemic cancer‑predisposition state with multiple hamartomas and increased malignant transformation risk in many tissues.
Clinical association
- Germline PTEN mutations cause PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome (PHTS)
- Encompassing
- Cowden syndrome
- Bannayan‑Riley‑Ruvalcaba syndrome
- High lifetime risks of breast, thyroid, endometrial, colorectal, kidney cancers and melanoma, plus macrocephaly and mucocutaneous lesions.
- Somatic PTEN loss or mutation is frequent in
- GBM
- Contributes to tumor progression and therapy resistance.