Gene loci
- Chromosome 7q36.
Normal function
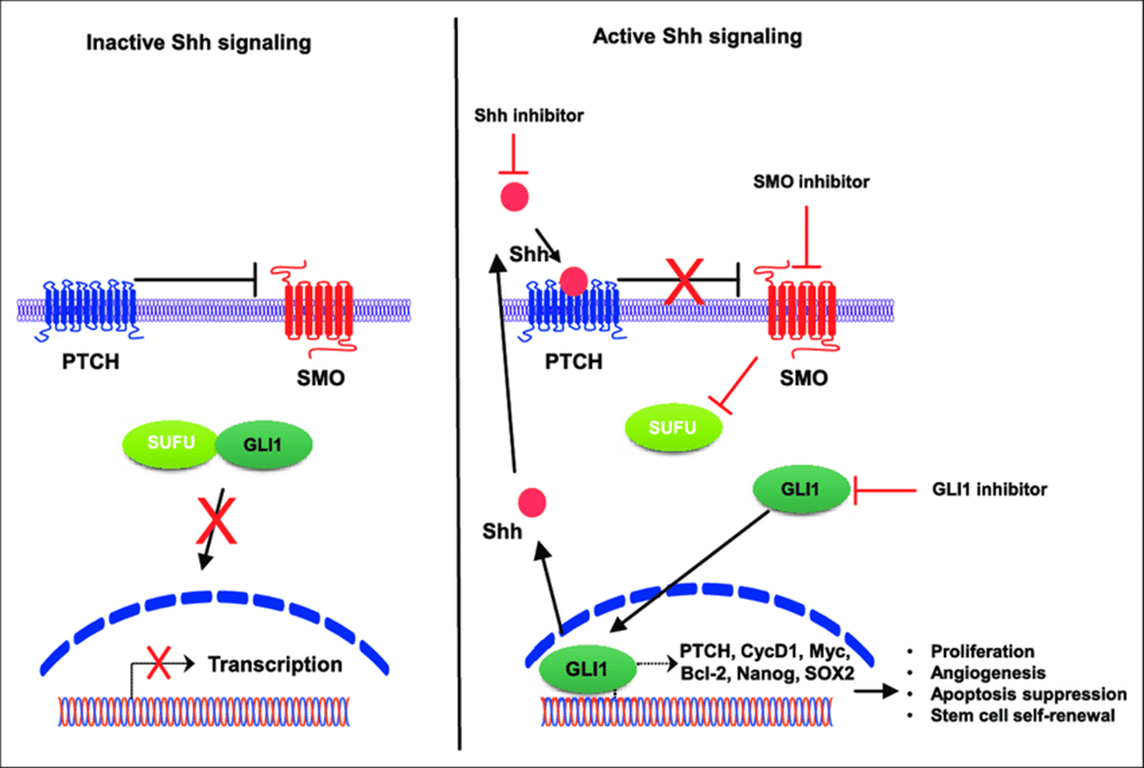
- Encodes a secreted morphogen that binds the PTCH1 receptor to activate SMO and downstream GLI transcription factors, controlling gene expression in hedgehog signalling.
- Critical for patterning and growth of ventral neural tube, forebrain, limb buds, craniofacial structures, and other organs by regulating cell proliferation, fate specification, and axis formation during embryogenesis.
Mutation effects
- Loss‑of‑function germline mutations (missense, nonsense, frameshift, splice, regulatory) reduce or abolish SHH signalling, leading to a spectrum of midline defects including holoprosencephaly and related craniofacial anomalies.
- Regulatory mutations affecting distant enhancers of the SHH locus (e.g. limb ZRS enhancer in LMBR1 intron) cause ectopic or reduced limb expression and result in preaxial polydactyly and other limb malformations without brain involvement.
Associated conditions
- Medulloblastoma SHH subtype
- Aberrant activation of SHH pathway (via SHH or upstream/downstream components) defines SHH‑activated medulloblastoma, where pathway mutations (PTCH1, SMO, SUFU, GLI2, etc.) and high SHH signalling drive tumorigenesis.
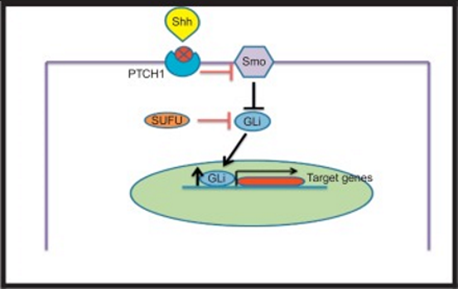
- SHH pathway for SHH activated medulloblastomas
- PTCH1 is an inhibitor of SHH signalling, when mutated can cause gorlin syndrome
- SHH signalling important in cerebellar development
- SHH secreted by purkinje cells → act as major mitogen for cerebellar granule cell progenitors in the external germinal layer
- SHH bind to PTC1 causing PTCH1 to inhibit SMO
- When SMO is inhibited GLI inhibition is released
- GLI act as transcription factor
- Hence SHH pathway activation can come from a range of mutation
- Loss of PTCH1 function
- Increased SHH, SMO or GLI activity
- SUFU is an inhibitor of GLI that can be a cause for gorlin syndrome
- Dysregulated SHH signalling is also implicated in other cancers, including basal cell carcinoma, glioblastoma and several digestive tract tumors, through autocrine or paracrine pathway activation.
- Holoprosencephaly type 3 and related phenotypes (single median maxillary incisor, midline facial defects) are classic consequences of germline SHH mutations.