General
- TERT: Telomerase reverse transcriptase
Gene loci
- Chromosome 5p15.33.
Normal function
- Encodes the catalytic telomerase reverse transcriptase subunit that adds telomeric repeats to chromosome ends using the RNA template TERC, maintaining telomere length and genomic stability in stem, germ, and activated immune cells.
- TERT expression is tightly repressed in most somatic cells and is rate‑limiting for telomerase activity, thereby restricting replicative potential and acting as an anti‑tumor barrier
Mutation effects
- Recurrent promoter hotspot mutations (C228T, C250T) create de novo ETS transcription factor binding sites, leading to increased TERT transcription and telomerase reactivation, which enables cellular immortalization and supports oncogenic signaling.
- ETS transcription factor binding sites are short DNA sequences that members of the ETS (E‑twenty six) transcription factor family recognize and bind.
- Other genetic and epigenetic changes (copy gain, rearrangements, SNPs at the promoter, altered chromatin looping) also upregulate TERT and confer telomere‑independent functions, including modulation of WNT/β‑catenin and other pathways, further promoting tumor progression.
- TERT promoter mutations can cooperate with oncogenic drivers such as BRAF V600E.
Clinical association
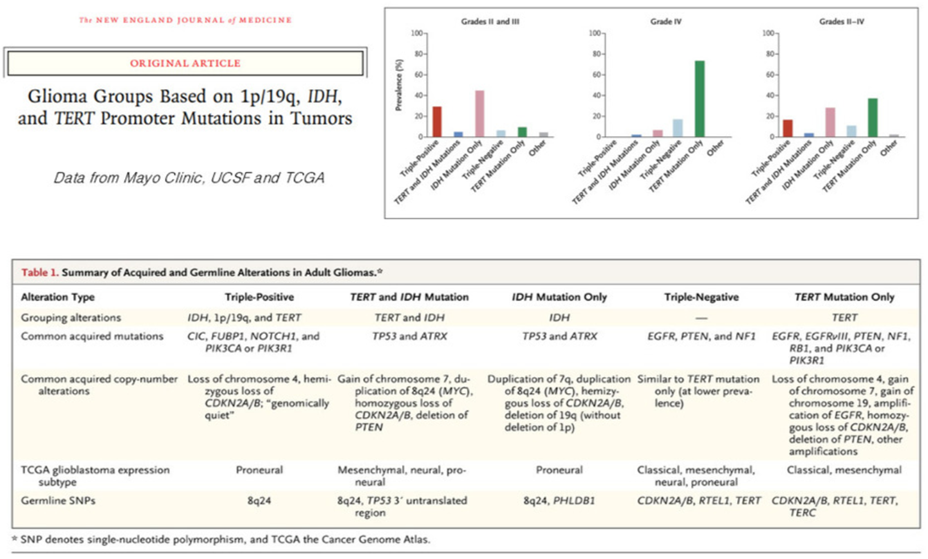
- TERT promoter gene mutations commonly occur with 1p/19q codeletion
- TERT promoter gene mutations are mutually exclusive in gliomas TP53 mutations
- pTERT mutations are commonly found in
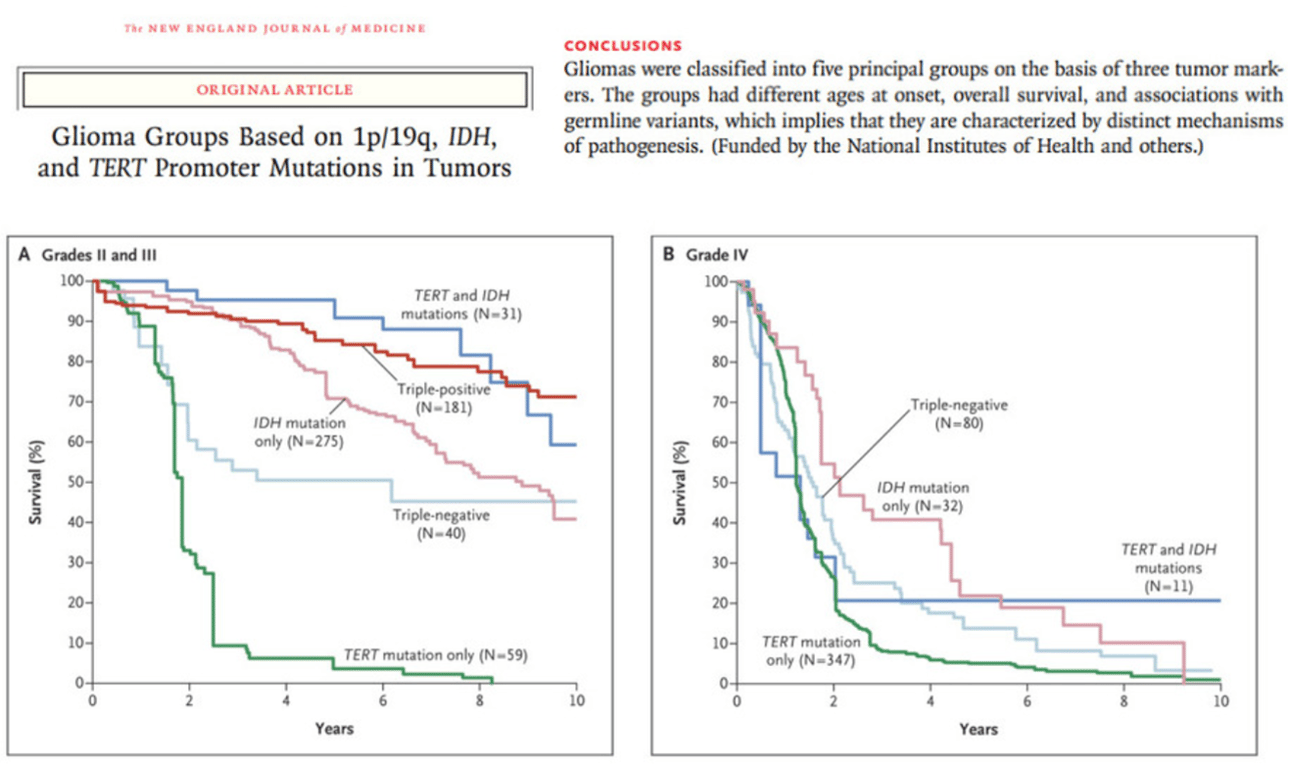
- LGGs that were positive for all three markers, so called ‘triple positive’, had the best overall survival
- pTERT mutation with other genetic aberrations, such as IDH mutation and 1p/19q co-deletion
- pTERT mutations alone confer to poorer prognosis
- pTERT mutations with IDH mutations together confer to better prognosis
- TERT mutations have poorest prognosis for low grade
- pTERT mutation was present in only 10% of astrocytomas and GBM IDH-mutant (also called secondary GBM)
- By contrast, in higher-grade gliomas (HGGs) such as GBM the combination of pTERT mutation with IDH mutation and 1p/19q status did not result into a significant discrimination of the overall prognosis
- Prognostic value of this marker
- Hotspot C228T and C250T mutations
- Median progression free survival:
- Mutant: 10.1 months
- Wildtype: 179 months
Oligodendroglioma (78%)
Grade II and III
Primary glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) (81%)
Type of mutation | Overall survival |
TERT promoter mutations | Median 11.3 months |
Without TERT or IDH1/2 mutations | Median 16.6 months |
IDH-only mutant GBM | Median 42.3 months |
Meningiomas
WHO Grade | Percentage of tumour with mutation |
1 | 1.7% |
2 | 5.7% |
3 | 20.0% |