Definition
- Is an umbrella term for lesions in the brain attributed to pathology of small arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, or small veins.
Aka
- Cerebral microangiopathy
- Leukoaraiosis
- A radiological descriptor applied to white matter hypodensities on CT and high signal changes on T2-weighted MRI of presumed vascular origin
Numbers
- More common with increasing age
- The prevalence of white matter lesions in the general population is reported to be between 39 to 96%
Differential diagnosis
- Arteriolosclerosis (age-related and vascular risk factor-related small vessel disease):
- Binswanger disease
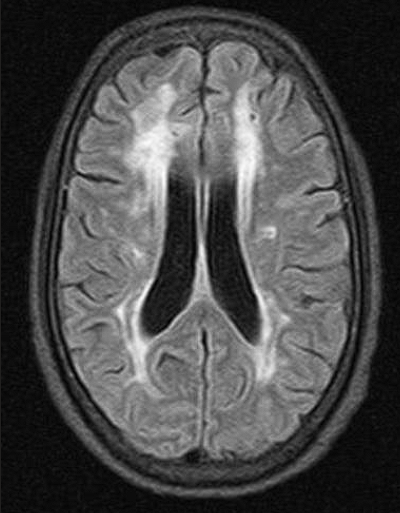
- Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (sporadic or hereditary)
- Inherited/genetic small vessel diseases other than cerebral amyloid angiopathy, such as
- CADASIL
- CARASIL
- MELAS
- Fabry disease
- Retinal vasculopathy with cerebral leukoencephalopathy
- COL4A1 brain small-vessel disease
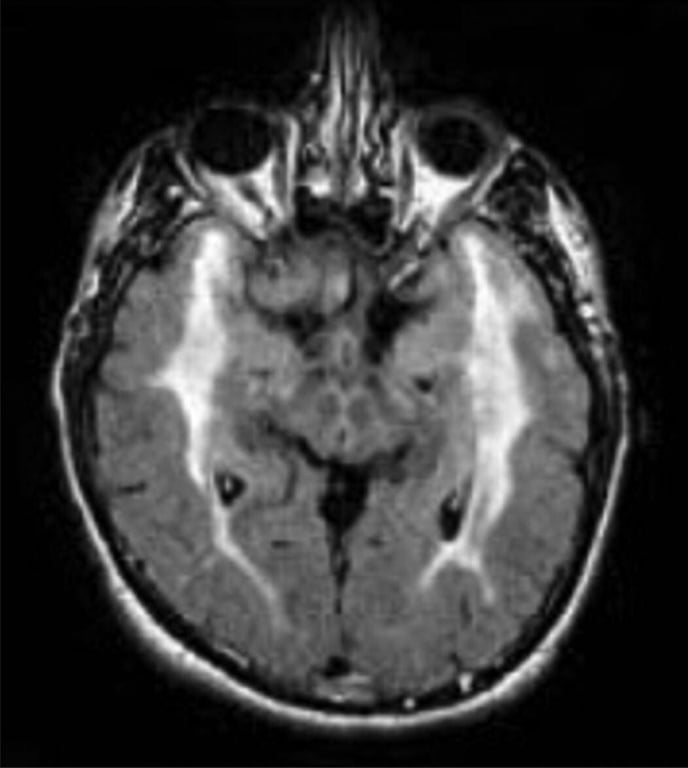
- Inflammatory and immunologically mediated small vessel diseases (CNS vasculitis)
- Venous collagenosis
- Other small vessel diseases, such as
- Post-radiation angiopathy
- Non-amyloid microvessel degeneration in Alzheimer disease
Pathology
- Juxtaventricular white matter changes
- (<3 mm from the ventricular surface),
- Eg ependymitis granularis, are not related to small vessel disease, but rather represent cerebrospinal fluid leak due to disruption of the ependyma
- Periventricular white matter lesions
- Periventricular defined as 3-13 mm from the ventricular surface
- This area is haemodynamically determined
- This region is a vascular border zone vascularised by non-collateralising ventriculofugal vessels arising from subependymal arteries --> prone to local and systemic decrease in cerebral blood flow --> watershed infarcts especially when located along the posterior horns and it is correlated with carotid artery stenosis 8.
- A predictor of watershed infarcts
- Deep and subcortical white matter lesions
- Deep white matter changes (>13 mm from the ventricular surface, >4 mm from the corticomedullary junction)
- Due to lipohyalinosis (small vessel disease), i.e. incomplete arteriosclerosis.
- A predictor of lacunar infarcts.