General
- Complete absence of blood flow → neuronal death within 2–3 minutes from exhaustion of energy stores.
- Salvageable penumbra (tissue at risk) that retains viability for a period of time through suboptimal perfusion from collaterals.
- Local cerebral edema from the stroke results in compromise of these collaterals and progression of ischemic penumbra to infarction if flow is not restored and maintained.
- Prevention of this secondary neuronal injury drives the treatment of stroke and has led to the creation of designated Primary Stroke Centers that offer appropriate and timely triage and treatment of all potential stroke patients.
Bedside
- ECG
- 12 lead
- Prolonged
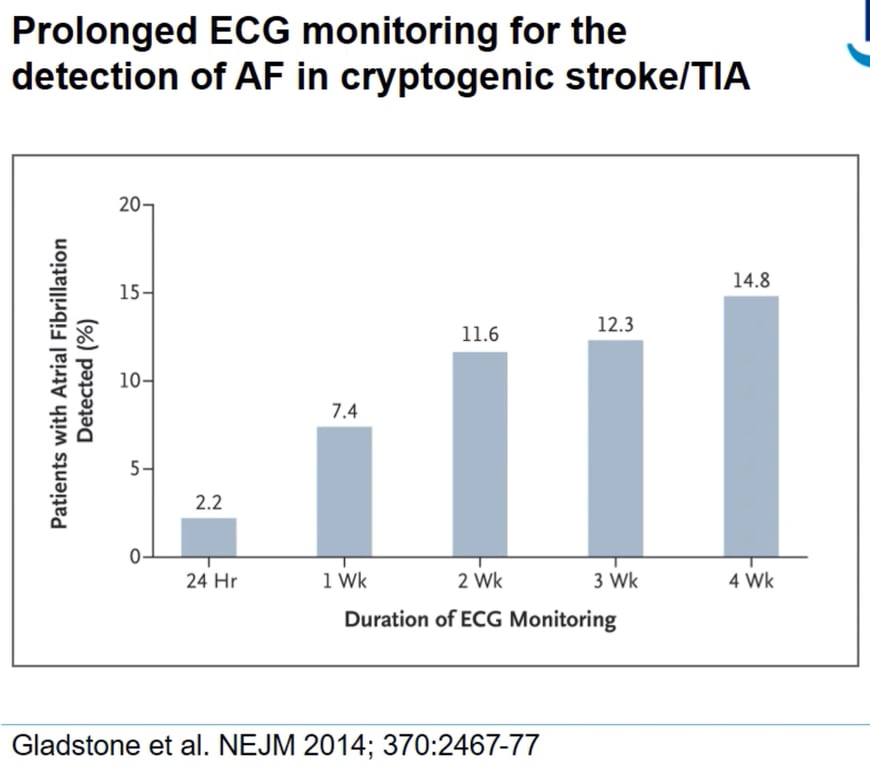
- Bloods:
- TFTs
- U&Es
- FBC
- ESR
- Thrombophilia screen
- Non-fasting glucose, HbA1c
- Fasting lipids
- Swallow test must be done within 4 hours of admission. Check swallow before prescribing and administering oral medication, oral fluids or diet.
Non cranial Imaging:
- Cardiac telemetry: for proxysmal AF
- Carotid ultrasound/CTA
- within 24 hours of new TIA / non-disabling stroke / amaurosis
- Carotid duplex and/or CTA of carotids: to identify carotid artery stenosis (suitability for Carotid endarterectomy)
- TTE: for cardiac thrombus
- No need for all patients
- TOE
- Thrombophilia screen
- Echocardiogram
- Bubble contrast
- Further investigation
- To identify aetiology of stroke
- MRI + DWI: to identify presence of acute stroke