General
- Aka:
- Osler Weber Rendu syndrome
- Hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT)
Diagnosis
- Curacao criteria:
- Spontaneous recurrent epistaxis
- Mucocutaneous telangiectasia
- AVMs of visceral organs
- First degree relatives with similar condition.
- Outcome
- Definite HHT if ≥3 criteria
- Possible HHT if only 2 criteria
Genetic
- An autosomal dominant disorder
Gene | Proportion of HHT Attributed to Pathogenic Variants in Gene |
ACVRLI | 52% |
ENG | 44% |
SM4D4 | 1% |
Unknown | 3% |
Pathophysiology
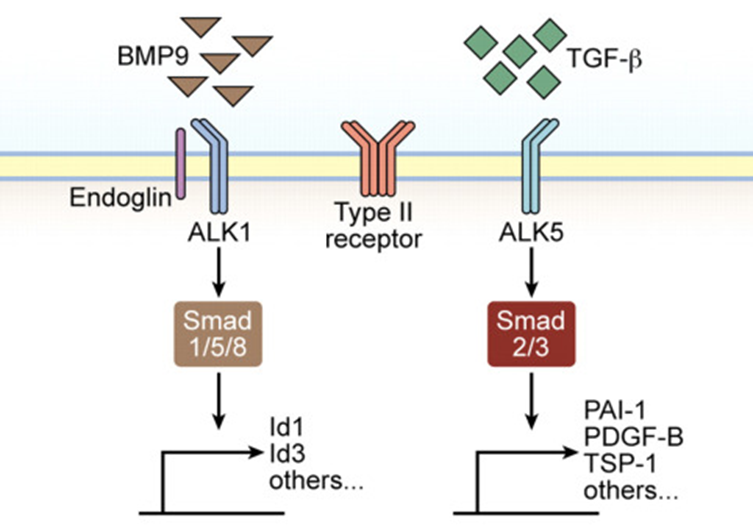
- Defects in a TGF-β superfamily receptor
- Defects in the endothelial cell junctions, endothelial cell degeneration, and weakness of the perivascular connective tissue are thought to cause dilation of capillaries and postcapillary venules, which manifest as telangiectasias.
- Genes most commonly implicated in HHT are the; Both are exclusively expressed on vascular endothelial cells. Two Genotypes
- Type I
- Endoglin gene (ENG; HHT type 1) = Type III TGF-β receptors
- on chromosome 9
- its coreceptor
- Underlying HHT1 – the most common type
- The endothelial cells in this syndrome lack the molecule endoglin and form abnormal vessels, especially after injury.
- is associated with
- Mucocutaneous telangiectasia,
- Pulmonary AVF
- Arteriovenous shunts of the CNS.
- Most often seen in the pediatric population and are always pial AVF (subtype C, ventral intradural AVF, or Type IV).
- Type 2
- ALK-1 gene (ALK1; HHT type 2) = Type I TGF-β receptors
- Activin receptor- like kinase- 1 (Alk- 1)
- On chromosome 12 (responsible for HHT2)
- Found on the surface of cells, particularly on the lining of developing arteries
- Other genes are less frequently involved
- The binding of TGF-β to the type II TGF-β receptor on endothelial cells, which is accelerated in the presence of endoglin, results in the phosphorylation of the type I TGF-β receptors ALK-5 and ALK-1.
- Phosphorylated ALK-5 activate Smad2/3
- Phosphorylated ALK-1 activate Smad1/5
- Activated Smad proteins dissociate from the type I TGF-β receptor, bind to Smad4, and enter the nucleus to transmit TGF-β signals by regulating transcription from specific gene promoters involved in angiogenesis.
- Endoglin and ALK-1 bind directly to bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-9 and BMP-10 and mediate their defects in conjunction with the type II BMP receptor (BMPR II).
- Therefore, a balance between the two signalling pathways involving ALK-5 and ALK-1 is important in determining the properties of endothelial cells during angiogenesis.
Location
- Skin telangiectasias (small AVMs) and AVMs in the
- Lungs
- 70% of patients with pulmonary AVMs will have HHT.
- Liver
- CNS
- Pretty much anywhere else in the body
Clinical presentation
- Classical triad
- Epistaxis (95%)
- Multiple mucocutaneous telangiectasias (small superficial arteriovenous malformations)
- Positive family history of HHT
- Intracranial haemorrhage
- Inc risk of pulmonary arterial venous fistula → paradoxical cerebral embolism → embolic stroke / cerebral abscess formation
Feature | % of Persons with Feature | Notes |
Epistaxis | 95% | ㅤ |
Telangiectases | 95% | Primarily on the lips/tongue/ buccal/nasal/GI mucosa, face & fingers |
Anaemia | 50% | ㅤ |
Pulmonary AVMs | 30-50% | ㅤ |
Hepatic AVMs | 40-70% | <10% symptomatic |
Cerebral AVMs | 10% | ㅤ |
Pulmonary hypertension | 1-5% | ㅤ |
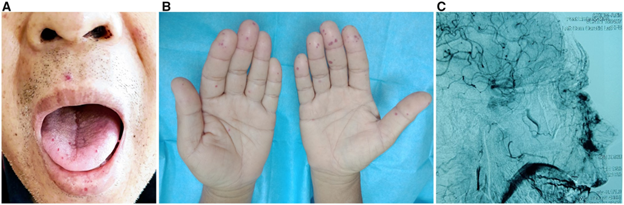
(B) palmer aspects of the hands
(C) post-embolization image showing contrast blush in the nasal, upper lip and hard palate areas.
Screening
- Molecular genetic testing is offered to at-risk family members if the germline pathogenic variant has been identified in the family.
- If the pathogenic variant in the family is not known, at-risk family members should be evaluated for signs and symptoms of HHT, and screening should be offered to at-risk family members if the diagnosis cannot be ruled out.