Definition:
- Rare Idiopathic nonhereditary congenital phakomatoses which presents with multiple AVM that tend to be large and predominantly affect the
- Brain
- AVM localize to the midbrain region
- Arteriovenous malformation in the right suprasellar region, near the optic chiasm
- Can bleed
- Causes
- Seizures,
- Headaches,
- Hemiparesis,
- Cranial neuropathies
- Hydrocephalus.
- Eye
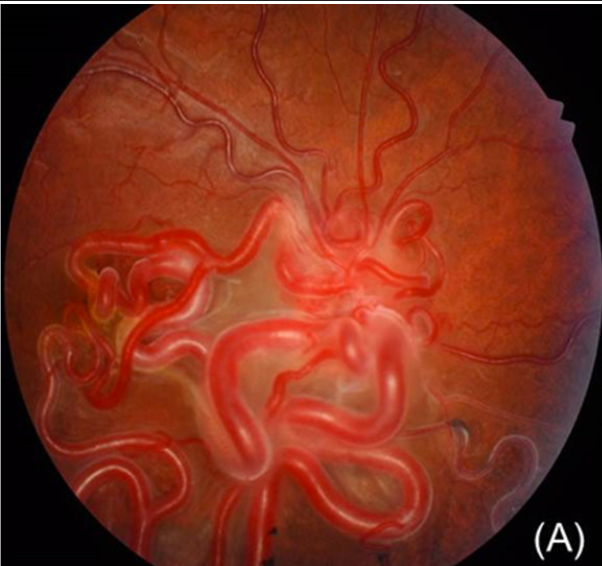
- AVM over optic disc and extending variably to the retinal periphery
- Right eye showed a retinal arteriovenous malformation with large-calibre convoluted, tortuous retinal vessels extending from the disc
- 30% of the patients with the retinal findings have brain findings and 8% of the patients with brain findings have retinal findings
- Vision: normal to no light perception due to
- Obscuration of the visual centres
- Choroidal infarctions,
- Retina ischemia,
- Compression of the optic nerve or retinal vascular occlusions
- Normal do not bleed
- Facial structures (AVM)

Might be part of cerebrofacial arteriovenous metameric syndrome (CAMS)
- Think of it like metameric AVM of the spine but in the head
- The concept of cerebrofacial arteriovenous metameric syndrome (CAMS) is a classification system that describes the spectrum of phenotypical expression of AVM in the cerebral, orbital, and facial region.
- There are 3 types of CAMS.
- CAMS1 involves corpus callosum, hypothalamus, olfactory tract, forehead, and nose.
- CAMS2 involves cortex and diencephalon, optic chiasma, optic nerve, retina, sphenoid, maxilla, and cheek. Wyburn-Mason syndrome has been named as CAMS2 according to this system of classification.
- CAMS3 involves the cerebellum, temporal bone, and mandible